Question
Mastery Problem: Manufacturing Cost Variance (Actual Costs Compared to Standard Costs) Manufacturing cost variances may come from material costs that are higher or lower than
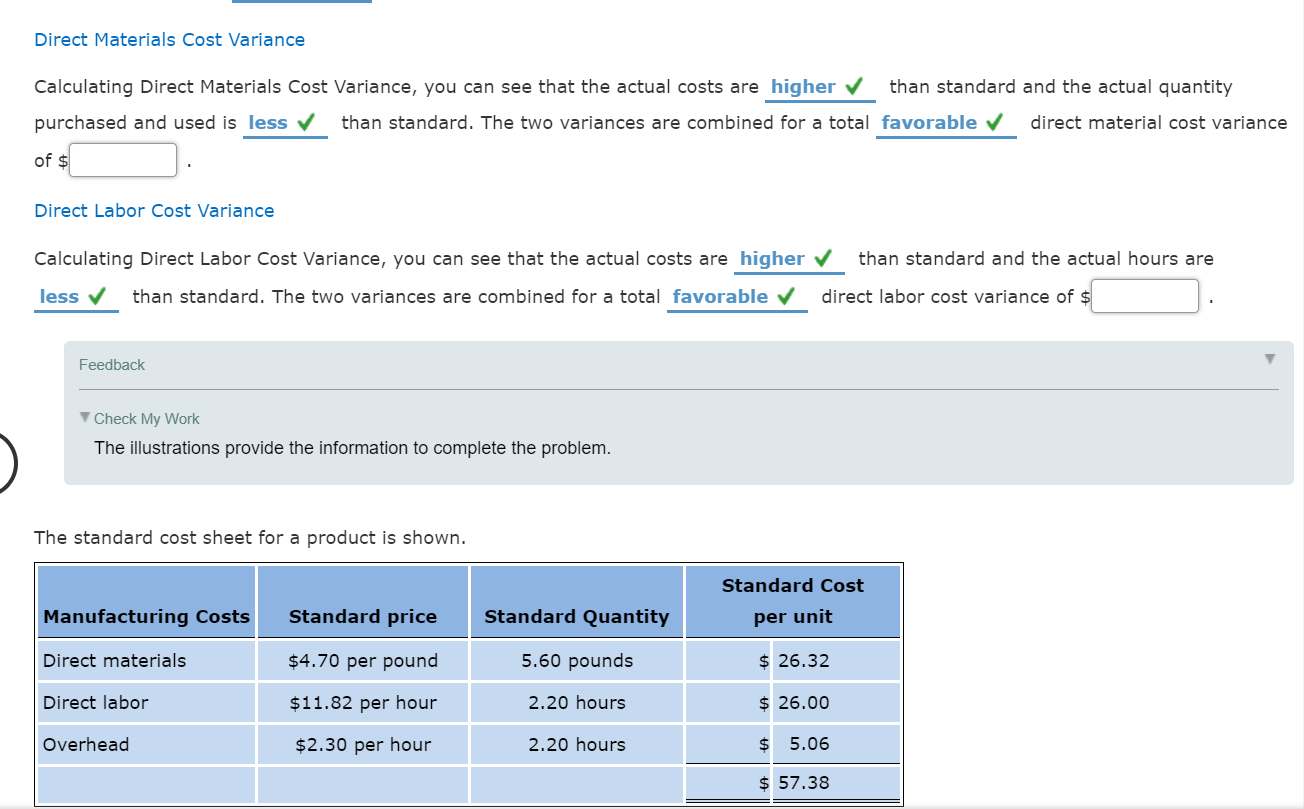
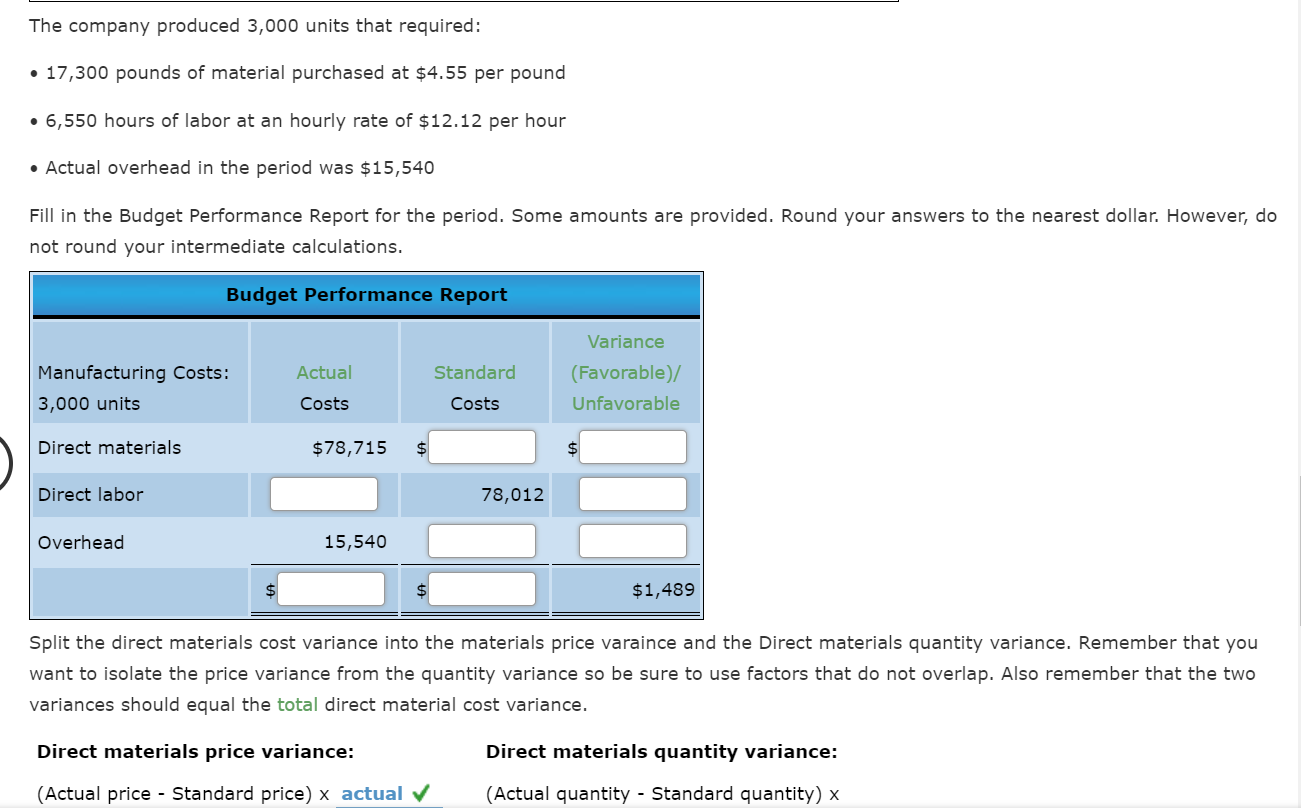
Mastery Problem: Manufacturing Cost Variance (Actual Costs Compared to Standard Costs) Manufacturing cost variances may come from material costs that are higher or lower than expected, material usage that is not what was expected, higher or lower labor costs than expected, or more or less time spent to produce an item than expected. Overhead cost and volume variances are another cause for costs to be higher or lower than what was expected. The total manufacturing variance can be broken down by cost type (materials, labor, overhead) and further by cost variances within cost types and usage or efficiency variances within cost types: Total Manufacturing Cost Variance Direct Materials Cost Variance Direct Labor Cost Variance 7 Direct Materials Price Variance Direct Materials Quantity Variance Direct Labor Rate Variance Direct Labor Time Variance Factory Overhead Cost Variance Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance Manufacturing cost variances are determined using a standard costing system. Standard costs are predetermined costs that should be incurred under efficient operating conditions. Standard costing is most suited to manufacturing organizations, where activities consist of common or repetitive operations and the direct costs required to produce each item are defined. In a standard costing system, it is important to understand that costs are compared to budget based on a flexible budget rather than a fixed budget. Flexible budgets use standard costs and actual production volume. This means that the actual costs in the period are compared to the number of units produced in the period at the standard cost. Feedback Check My Work Standards are set up as part of the budgeting process and are used when per unit costs can be estimated under efficient operating conditions. Remember that flexible budgets account for changes in volume. If actual costs are greater than standard costs, the variance is unfavorable alternatively, if actual costs are less than standard Direct Materials Cost Variance Calculating Direct Materials Cost Variance, you can see that the actual costs are higher purchased and used is less than standard and the actual quantity than standard. The two variances are combined for a total favorable direct material cost variance of $ Direct Labor Cost Variance Calculating Direct Labor Cost Variance, you can see that the actual costs are higher less than standard. The two variances are combined for a total favorable Feedback Check My Work The illustrations provide the information to complete the problem. The standard cost sheet for a product is shown. than standard and the actual hours are direct labor cost variance of $ Standard Cost Manufacturing Costs Direct materials Standard price $4.70 per pound Standard Quantity 5.60 pounds per unit $ 26.32 Direct labor $11.82 per hour 2.20 hours $ 26.00 Overhead $2.30 per hour 2.20 hours $ 5.06 $ 57.38 The company produced 3,000 units that required: 17,300 pounds of material purchased at $4.55 per pound 6,550 hours of labor at an hourly rate of $12.12 per hour Actual overhead in the period was $15,540 Fill in the Budget Performance Report for the period. Some amounts are provided. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. However, do not round your intermediate calculations. Budget Performance Report Manufacturing Costs: 3,000 units Actual Costs Standard Costs Variance (Favorable)/ Unfavorable Direct materials $78,715 $ Direct labor 78,012 Overhead 15,540 $1,489 Split the direct materials cost variance into the materials price varaince and the Direct materials quantity variance. Remember that you want to isolate the price variance from the quantity variance so be sure to use factors that do not overlap. Also remember that the two variances should equal the total direct material cost variance. Direct materials price variance: Direct materials quantity variance: (Actual price - Standard price) x actual (Actual quantity - Standard quantity) x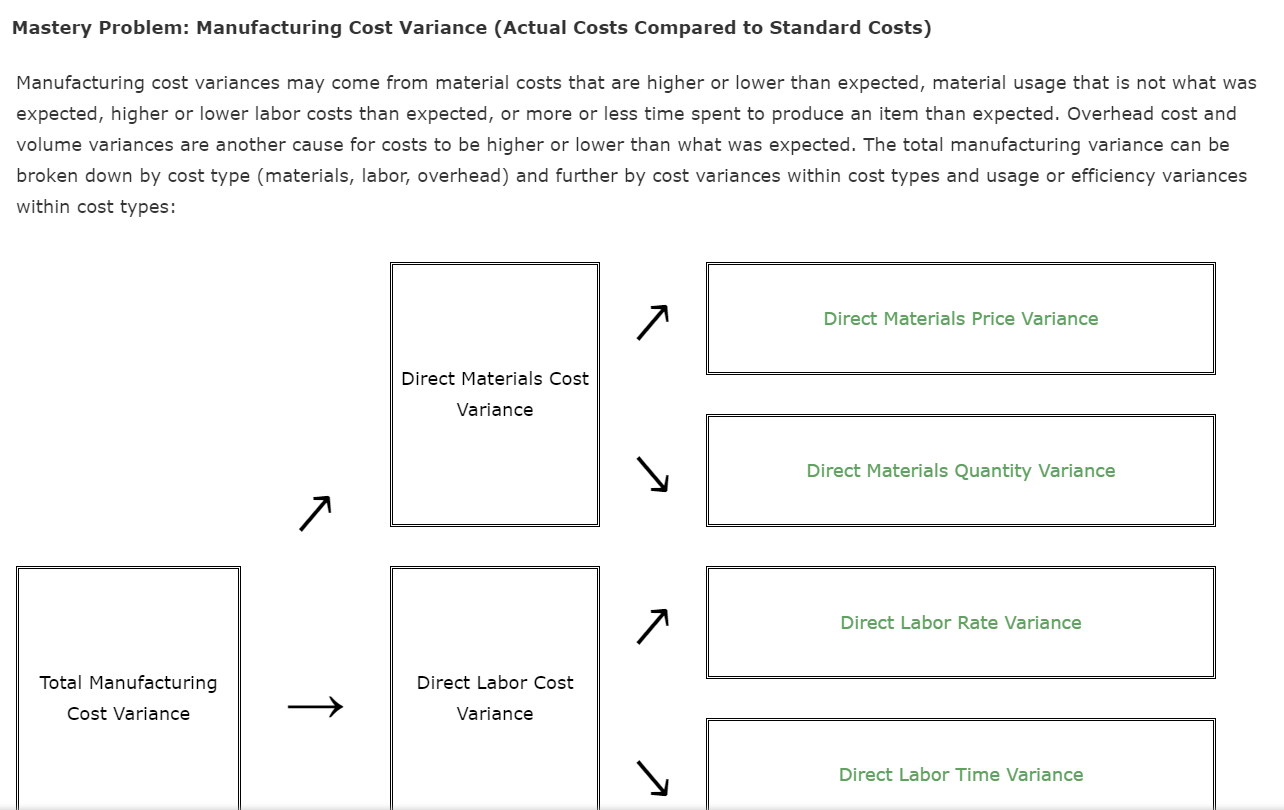

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


