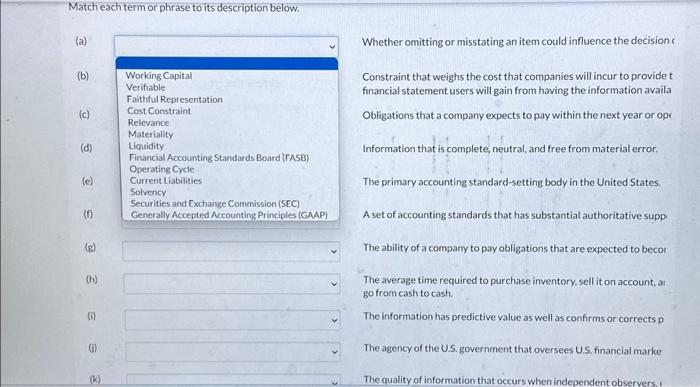
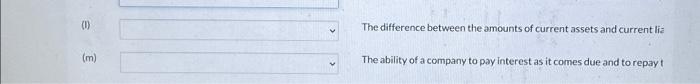
Match each term or phrase to its description below. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (i) (k) Whether omitting or misstating an item could influence the decision c Constraint that weighs the cost that companies will incur to provide t financial statement users will gain from having the information availa Obligations that a company expects to pay within the next year or ope Information that is complete, neutral, and free from material error. The primary accounting standard-setting body in the United States. A set of accounting standards that has substantial authoritative supp The ability of a company to pay obligations that are expected to becor The average time required to purchase inventory, sell it on account, al go from cash to cash. The information has predictive value as well as confirms or corrects p The agency of the U.S. government that oversees U.S. financial marke The quality of information that occurs when independent observers. (1) The difference between the amounts of current assets and current lia (m) The ability of a company to pay interest as it comes due and to repay Whether omitting or misstating an item could influence the decision of a financial statement user. Constraint that weighs the cost that companies will incur to provide the information against the benefit that financial statement users will gain from having the information available. Obligations that a company expects to pay within the next year or operating cycle, whichever is longer. Information that is complete, neutral, and free from material error. The primary accounting standard-setting body in the United States. A set of accounting standards that has substantial authoritative support and which guide accounting professionals. The ability of a company to pay obligations that are expected to become due within the next year or operating cycle. The average time required to purchase inventory, sell it on account, and then collect cash from customers - that is, go from cash to cash. The information has predictive value as well as confirms or corrects prior expectations. The agency of the U.S. government that oversees U.S. financial markets and accounting standard-setting bodies. The difference between the amounts of current assets and current liabilities. The ability of a company to pay interest as it comes due and to repay the balance of a debt due at its maturity