Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of yourchoice from Column "B" in the space provided under "A" & match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower caseletter of your choice under column "B".
Please note that I need only even-numbered questions (#2, #4, #6, #8, #10, #12, #14, #16 & #18). Thank you.
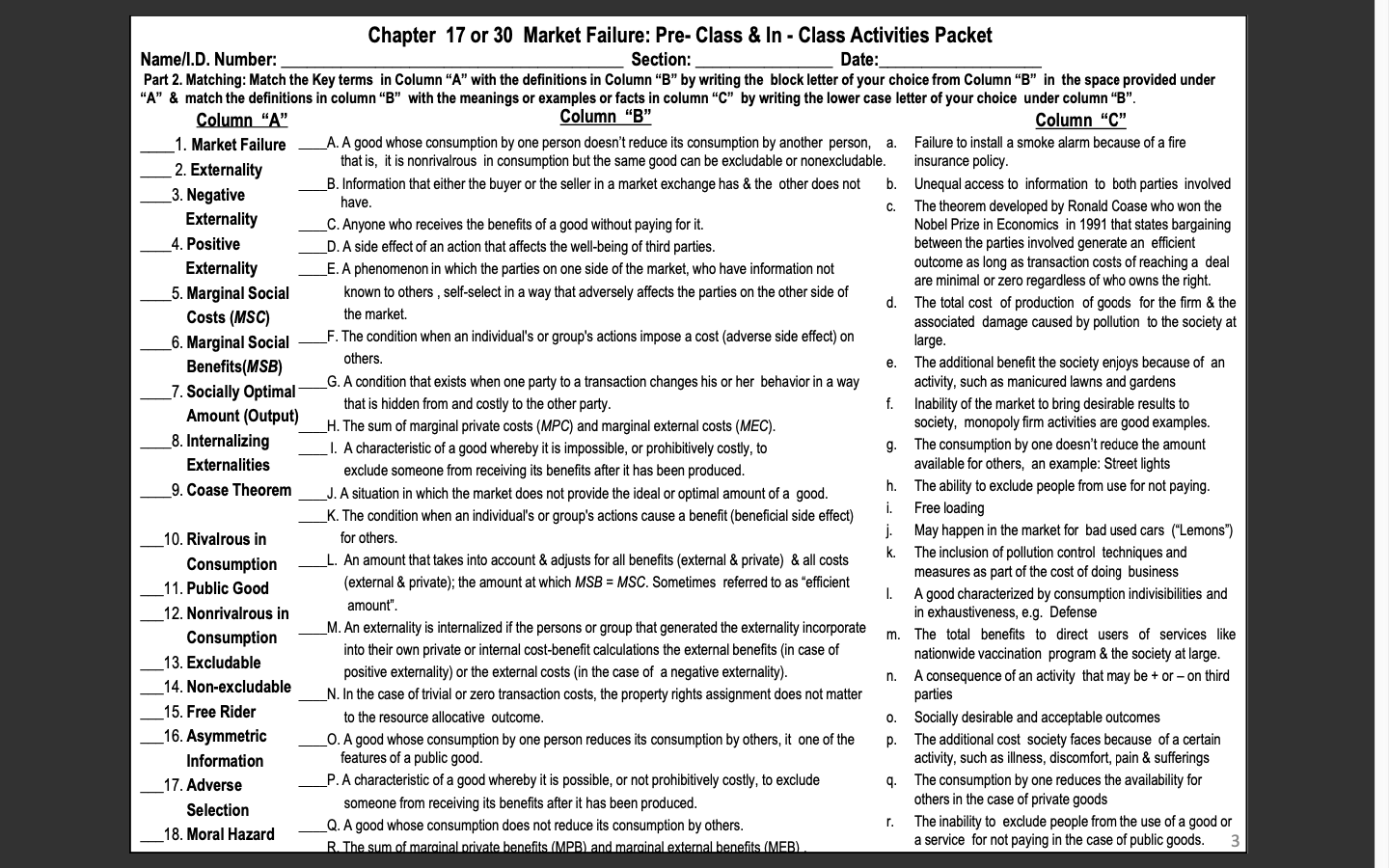
Chapter 17 or 30 Market Failure: Pre- Class & In - Class Activities Packet Name/I.D. Number: Section: Date: Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice from Column "B" in the space provided under "A" & match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or facts in column "C" by writing the lower case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" Column "B' Column "C" 1. Market Failure A. A good whose consumption by one person doesn't reduce its consumption by another person, a. Failure to install a smoke alarm because of a fire 2. Externality that is, it is nonrivalrous in consumption but the same good can be excludable or nonexcludable. insurance policy. b. Unequal access to information to both parties involved 3. Negative B. Information that either the buyer or the seller in a market exchange has & the other does not have. C. The theorem developed by Ronald Coase who won the Externality C. Anyone who receives the benefits of a good without paying for it. Nobel Prize in Economics in 1991 that states bargaining 4. Positive D. A side effect of an action that affects the well-being of third parties. between the parties involved generate an efficient Externality E. A phenomenon in which the parties on one side of the market, who have information not outcome as long as transaction costs of reaching a deal known to others , self-select in a way that adversely affects the parties on the other side of are minimal or zero regardless of who owns the right. 5. Marginal Social d. The total cost of production of goods for the firm & the Costs (MSC) the market associated damage caused by pollution to the society at 6. Marginal Social F. The condition when an individual's or group's actions impose a cost (adverse side effect) on large. Benefits(MSB) others. e. The additional benefit the society enjoys because of an 7. Socially Optimal G. A condition that exists when one party to a transaction changes his or her behavior in a way activity, such as manicured lawns and gardens Amount (Output) that is hidden from and costly to the other party. f. Inability of the market to bring desirable results to H. The sum of marginal private costs (MPC) and marginal external costs (MEC). society, monopoly firm activities are good examples. 8. Internalizing 1. A characteristic of a good whereby it is impossible, or prohibitively costly, to g. The consumption by one doesn't reduce the amount Externalities exclude someone from receiving its benefits after it has been produced. available for others, an example: Street lights 9. Coase Theorem J. A situation in which the market does not provide the ideal or optimal amount of a good. h. The ability to exclude people from use for not paying. K. The condition when an individual's or group's actions cause a benefit (beneficial side effect) Free loading 10. Rivalrous in for others. May happen in the market for bad used cars ("Lemons") K. The inclusion of pollution control techniques and Consumption L. An amount that takes into account & adjusts for all benefits (external & private) & all costs (external & private); the amount at which MSB = MSC. Sometimes referred to as "efficient measures as part of the cost of doing business 11. Public Good 1. A good characterized by consumption indivisibilityes and 12. Nonrivalrous in amount". in exhaustiveness, e.g. Defense Consumption M. An externality is internalized if the persons or group that generated the externality incorporate . The total benefits to direct users of services like into their own private or internal cost-benefit calculations the external benefits (in case of 13. Excludable nationwide vaccination program & the society at large. positive externality) or the external costs (in the case of a negative externality). 14. Non-excludable A consequence of an activity that may be + or - on third N. In the case of trivial or zero transaction costs, the property rights assignment does not matter parties 15. Free Rider to the resource allocationtcome 0. Socially desirable and acceptable outcomes 16. Asymmetric O. A good whose consumption by one person reduces its consumption by others, it one of the P. The additional cost society faces because of a certain Information features of a public good. activity, such as illness, discomfort, pain & sufferings 17. Adverse P. A characteristic of a good whereby it is possible, or not prohibitively costly, to exclude q. The consumption by one reduces the availability for others in the case of private goods Selection someone from receiving its benefits after it has been produced. r. 18. Moral Hazard _Q. A good whose consumption does not reduce its consumption by others. The inability to exclude people from the use of a good or R. The sum of marginal private benefits (MPB) and marginal external benefits (MEB) a service for not paying in the case of public goods. 3