Question
Math project Introduction and Goals Bulk materials are materials sold by weight or volume. For example, a landscaper may buy a 20 lb bag of
Math project
Introduction and Goals
Bulk materials are materials sold by weight or volume. For example, a landscaper may buy a 20 lb bag of grass seed or a cubic yard of gravel.
For this project, you will design a storage site where bulk materials are stored in conical piles.
First you'll research characteristics of several bulk materials. Then you'll design your storage site and perform calculations based on the characteristics of your materials. Finally, you'll reflect on various aspects of the project.
Project Instructions
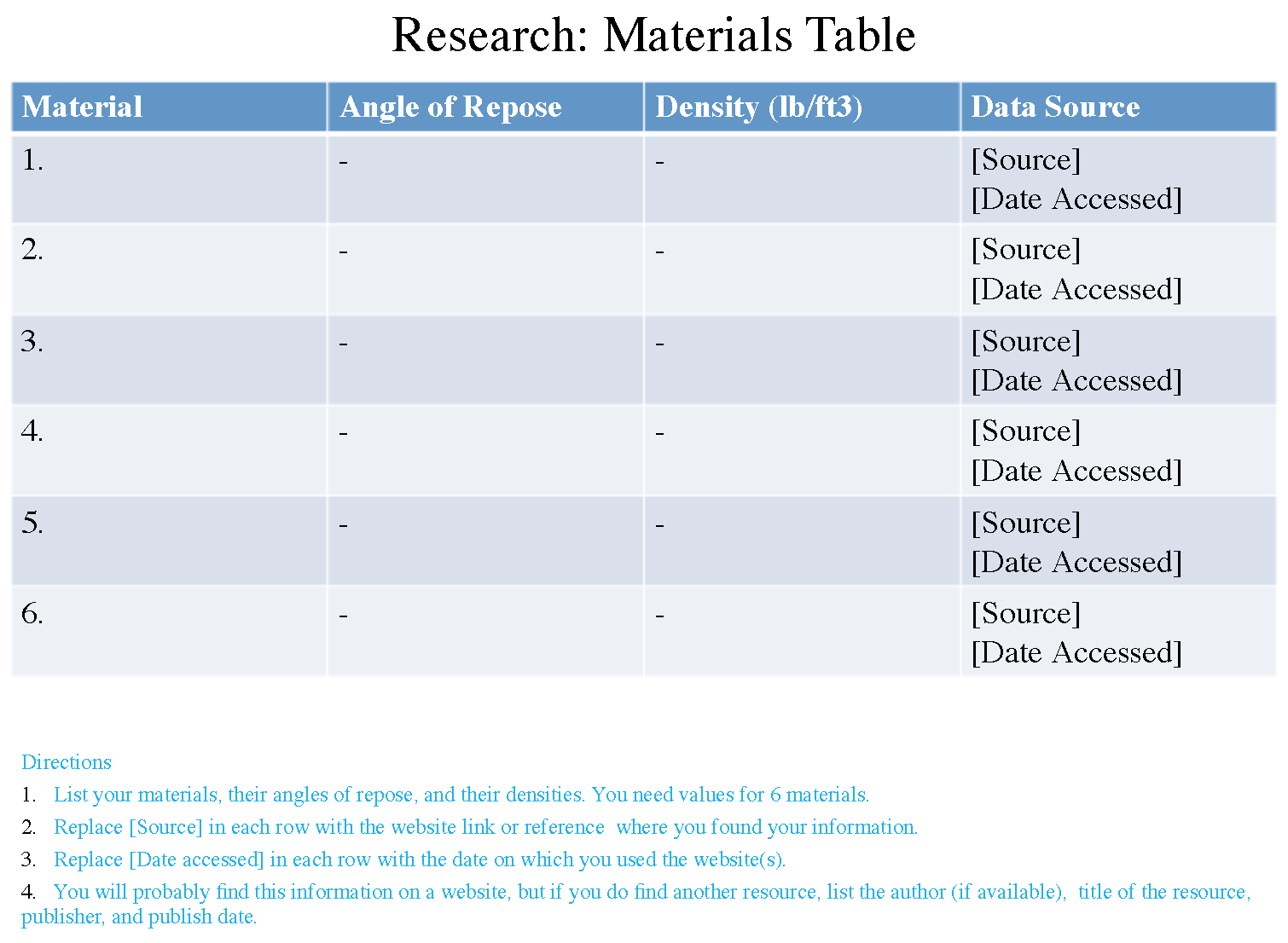
- Use the Internet to find the angles of repose for 6 bulk materials you can store in conical piles.
- Do not use the same materials that are in the sample project. Note that the sample project uses only 5 materials. Your project needs 6 materials.
- Do not choose materials whose angle of repose is 0.
- Do not choose materials that all have the same angle of repose. Try for a variety of angles.
- If you are given a range, use the middle of the range.
- Tip: In the search bar, enter the phrase angle of repose bulk materials chart.
- Find the densities of the materials you chose. You may find them on the same page as you found the angles of repose, or you may need to do another search.
- If you are given a range, use the middle of the range.
- Tip: In the search bar, enter the phrase densities of bulk materials.
- List densities in lb/ft3 (pounds per cubic foot.) You may need to convert some densities.
- Convert kilograms per cubic meter to pounds per cubic foot by multiplying by 0.062:
- (x kg/m3) ? (0.062) = y lb/ft3
- Convert pounds per cubic yard to pounds per cubic foot by multiplying by 0.037:
- (x lbs/yard3) ? (0.037) = y lb/ft3
- Tip: If you find an unknown density, do an Internet search for the conversion. For example, if you type "5 grams per cubic centimeter to pounds per cubic foot" into most search engines, you'll get this answer:
- (5 grams) per (cubic centimeter) = 312.139803 pounds per (cubic foot)
- Open your presentation, and follow the directions to complete the Research slides.
Project Writing
- Before you begin writing, complete the Practice Test, a computer-scored, ungraded assessment. You'll practice working with angles and cones?skills essential to completing your project. Reach out to your teacher with any questions you have after taking this Practice Test.
- Follow the directions in the presentation to complete each Writing slide.
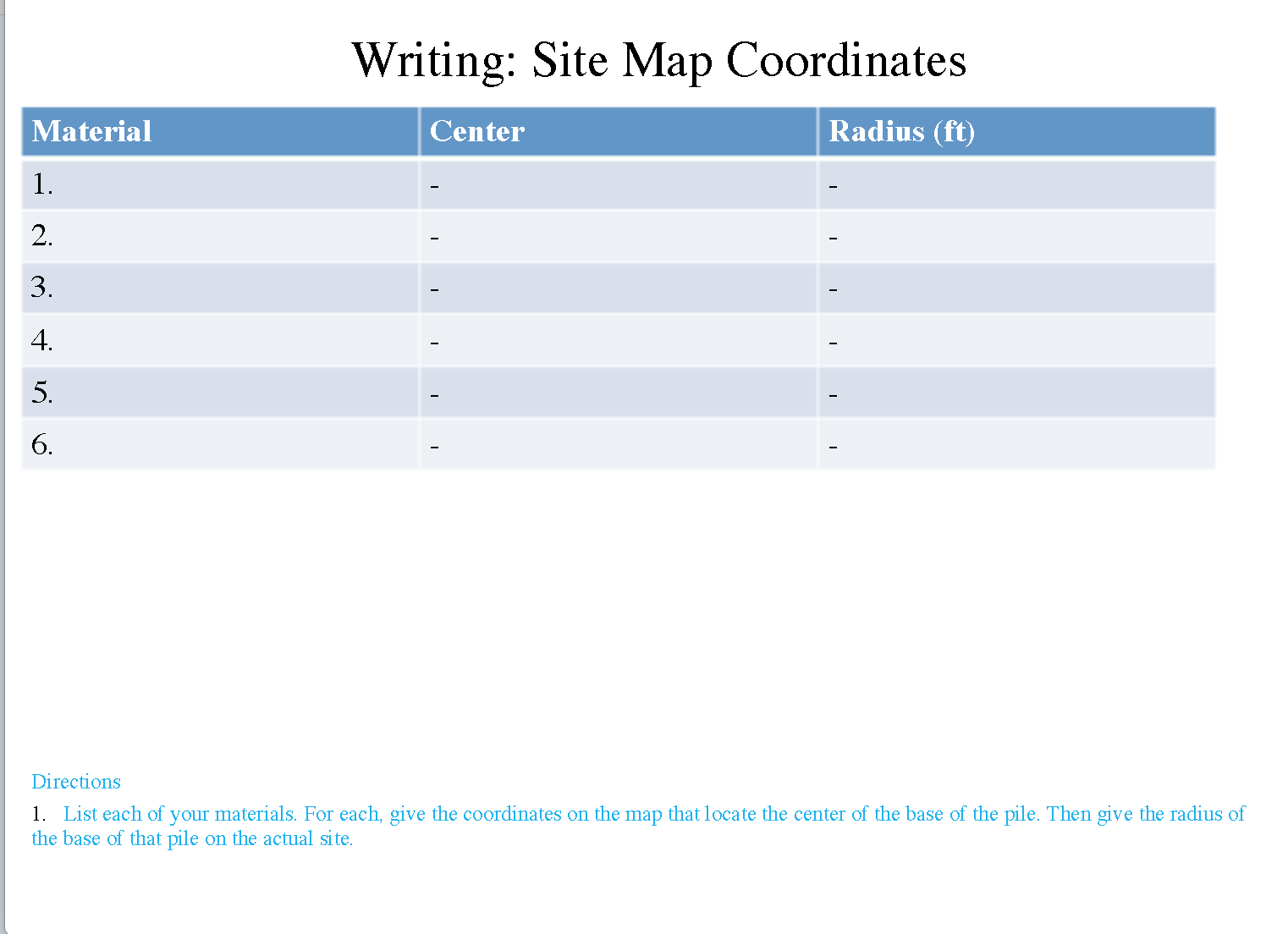
- On the Site Map slides, design and describe your storage site. Use the SiteMap.ggb file to draw your design.
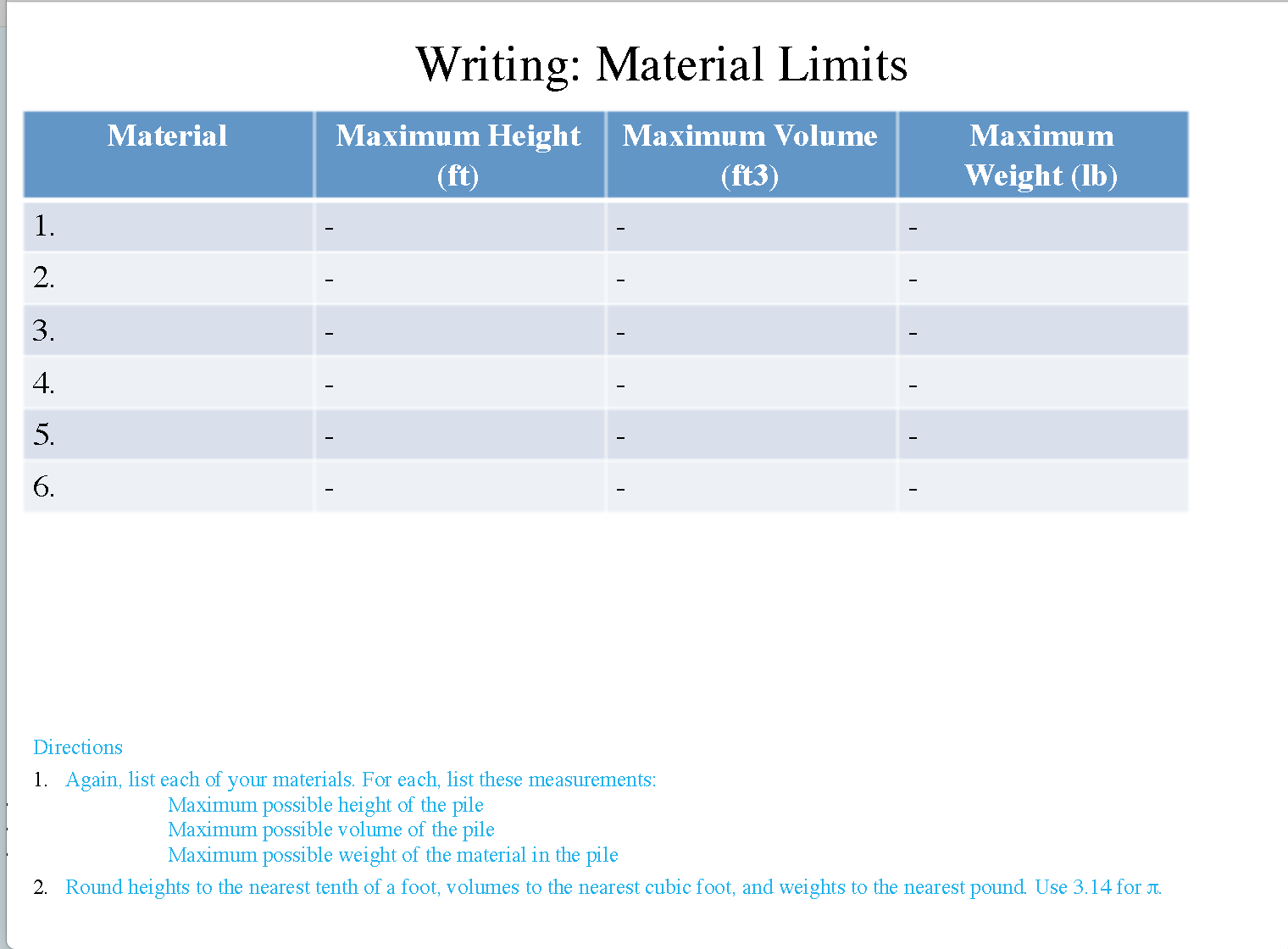
- On the Calculations slides, determine the maximum possible height, volume, and weight for each pile of materials in your design. Then discuss how a specific customer order can be delivered efficiently.
- Tip: When you want to find the maximum possible height of a pile, sketch a cross section of the cone labeled with its height, radius, and angle of repose.
- On the Model slide, choose a scale for a model of your storage site and describe how to use the scale to find areas and volumes. Assume maximum amounts of materials are stocked. Do not use the same scale as the sample project.
Project Reflection
Look back over the Writing slides in your presentation. Follow the directions in the presentation to complete the Reflection slide.
Submission
Confirm that your presentation contains all your work:
- Materials table and source information
- Site map and table with the center and radius of each pile
- Table with maximum heights, volumes, and weights, and description of order delivery
- Discussion involving the scale of a model and how the scale can be used to find measures on the model
- Your reflection
Here is the template





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


