Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
MECHANICS - STATICS (LW-23-SJU) Course Content Week 7 - Module 07: Kinetics of a Particle Kinetics of a Particle Equation of Motion: Normal and Tangential
MECHANICS - STATICS (LW-23-SJU)\ Course Content Week 7 - Module 07: Kinetics of a Particle\ Kinetics of a Particle\ Equation of Motion: Normal and Tangential Coordinates\ Page 8 of 18\ When a particle moves over a known curved path, the equation of motion for the particle may be written in the tangential, normal, and binormal directions giving the following three scalar equations of motion:\ Vector Formulation\
\\\\sum vec(F)=mvec(a)\ \\\\sum F_(t)hat(u)_(t)+\\\\sum F_(n)hat(u)_(n)+\\\\sum F_(b)hat(u)_(b)=ma_(t)hat(u)_(t)+ma_(n)hat(u)_(n)\ Scalar Representation\
1_(t)\
\\\\sum F_(t)=ma_(t) where a_(t)=v^()\ \\\\sum F_(n)=ma_(n) where a_(n)=(v^(2))/(\\\ ho )\ \\\\sum F_(b)=0, 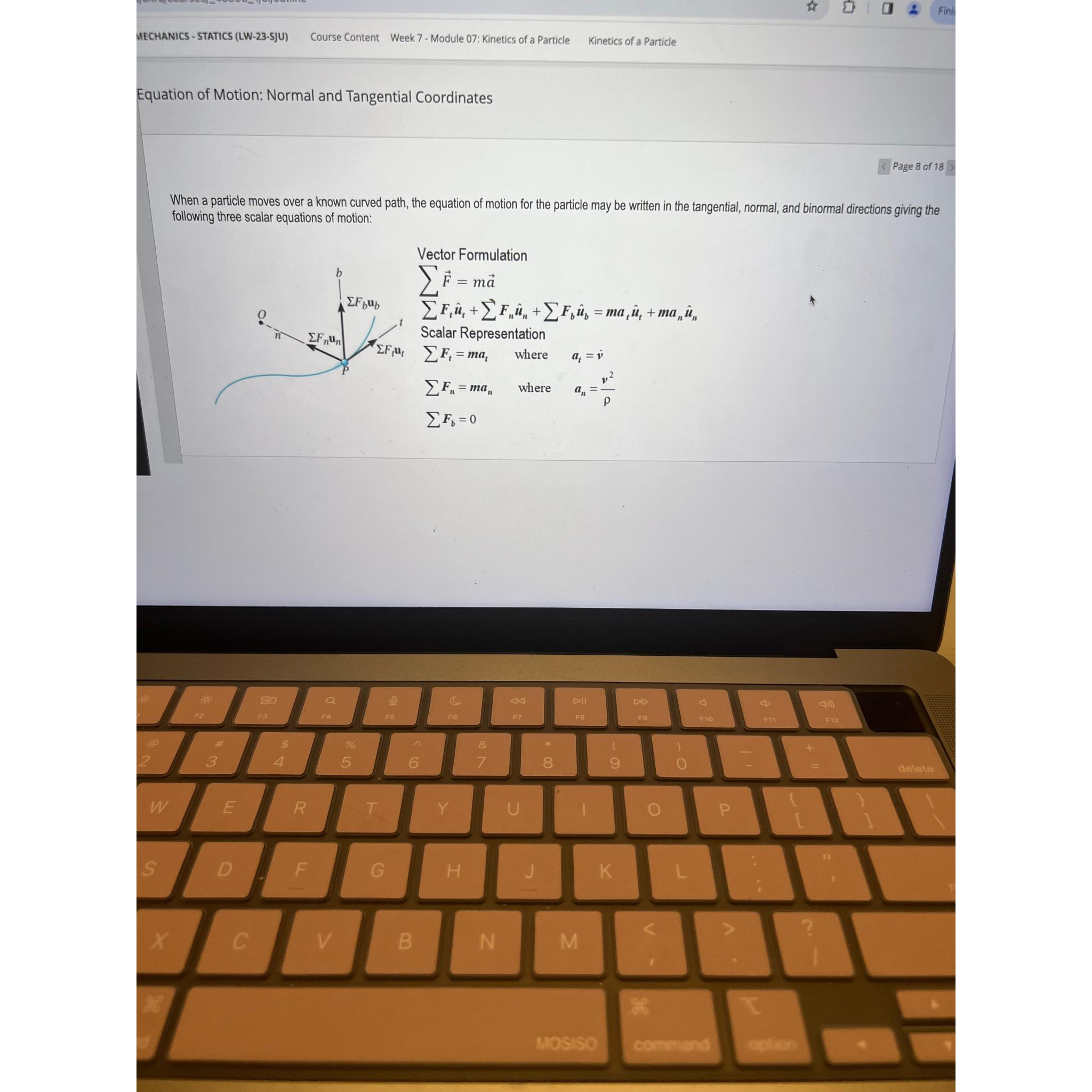
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


