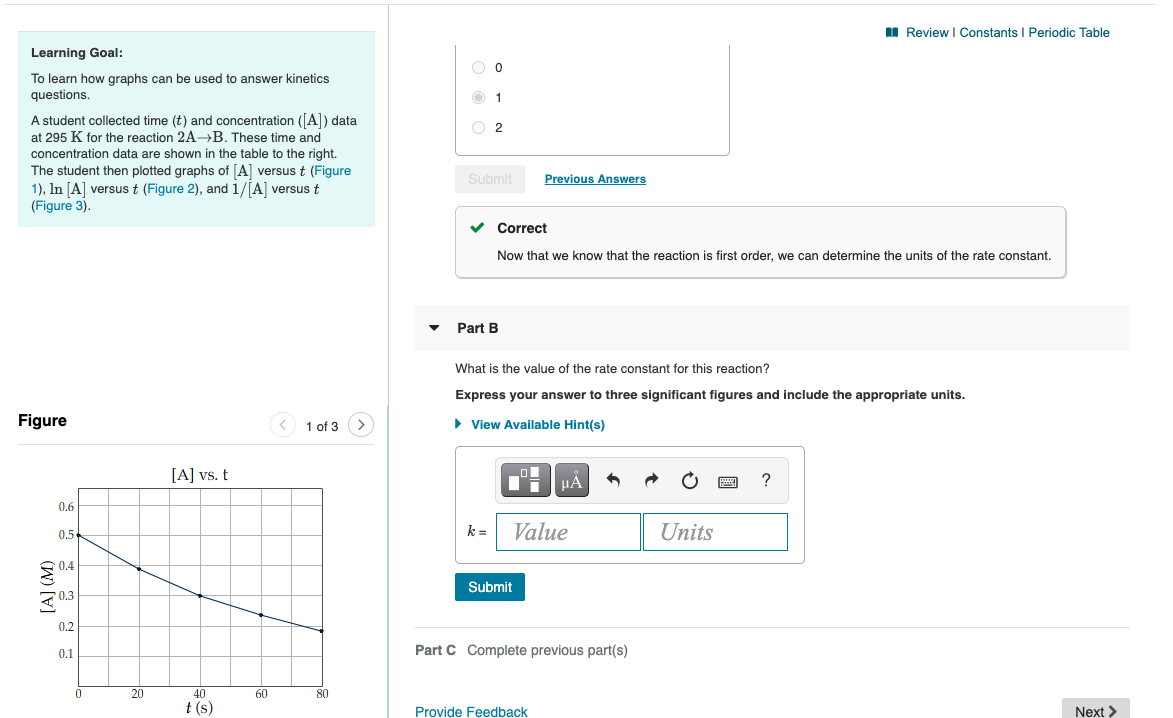
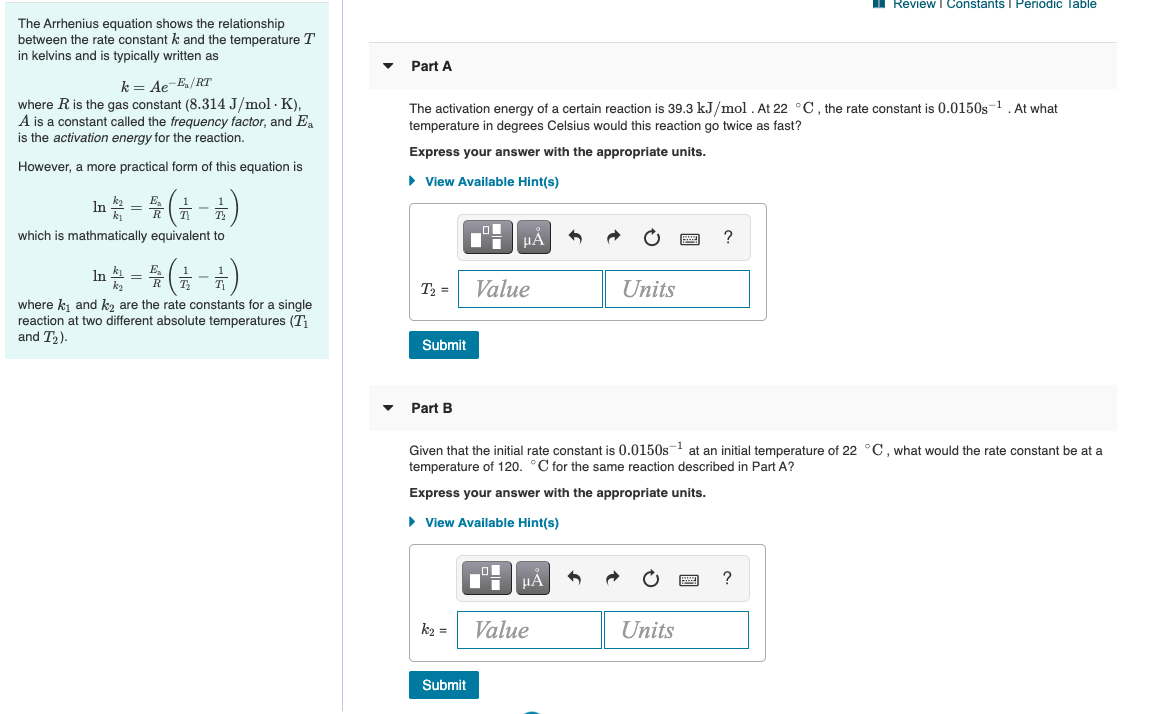
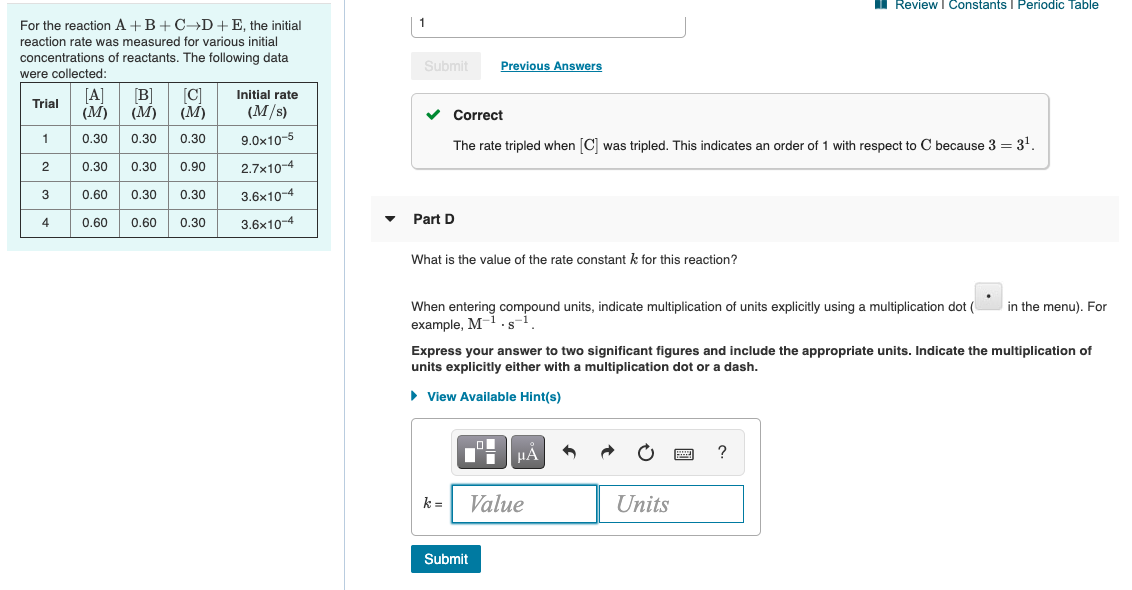
MI Review Constants Periodic Table 0 Learning Goal: To learn how graphs can be used to answer kinetics questions. O2 A student collected time (t) and concentration ([A]) data at 295 K for the reaction 2AB. These time and concentration data are shown in the table to the right. The student then plotted graphs of (A) versus t (Figure 1), In [A] versus t (Figure 2), and 1/[A] versust (Figure 3). Submit Previous Answers Correct Now that we know that the reaction is first order, we can determine the units of the rate constant. Part B What is the value of the rate constant for this reaction? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 3 View Available Hint(s) [A] vs. t ? 1.6 0.5 k= Value Units 0.4 [A] (M) Submit 0.2 0.1 Part C Complete previous part(s) 0 20 60 80 40 t(s) Provide Feedback Next > Review I Constants 1 Periodic lable The Arrhenius equation shows the relationship between the rate constant k and the temperature T in kelvins and is typically written as Part A k= Ae-E/RT where R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol K), A is a constant called the frequency factor, and Ea is the activation energy for the reaction. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 39.3 kJ/mol At 22C, the rate constant is 0.0150s-1 At what temperature in degrees Celsius would this reaction go twice as fast? Express your answer with the appropriate units. However, a more practical form of this equation is View Available Hint(s) In -#- (1-6) LO which is mathmatically equivalent to ? T2 = Value Units In ki = ky where ki and k2 are the rate constants for a single reaction at two different absolute temperatures (T and T2). Submit Part B Given that the initial rate constant is 0.0150s-1 at an initial temperature of 22 C, what would the rate constant be at a temperature of 120. C for the same reaction described in Part A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) H ? k2 = Value Units Submit Review | Constants 1 Periodic Table 1 Submit Previous Answers For the reaction A+B+CD+E, the initial reaction rate was measured for various initial concentrations of reactants. The following data were collected: B] Trial C Initial rate (M) (M) (M) (M/s) 1 0.30 0.30 0.30 9.0x10-5 Correct The rate tripled when [C] was tripled. This indicates an order of 1 with respect to C because 3 = 34. 2 0.30 0.30 0.90 2.7x10-4 3 0.60 0.30 0.30 3.6x10-4 3.6x10-4 4 0.60 0.60 0.30 Part D What is the value of the rate constant k for this reaction? in the menu). For When entering compound units, indicate multiplication of units explicitly using a multiplication dot example, M S Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Indicate the multiplication of units explicitly either with a multiplication dot or a dash. View Available Hint(s) ? ku Value Units Submit









