Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Mia Wiz sells computers. During May, it sold 400 computers at a $1,000 per unit price. The fixed budget for May predicted sales of
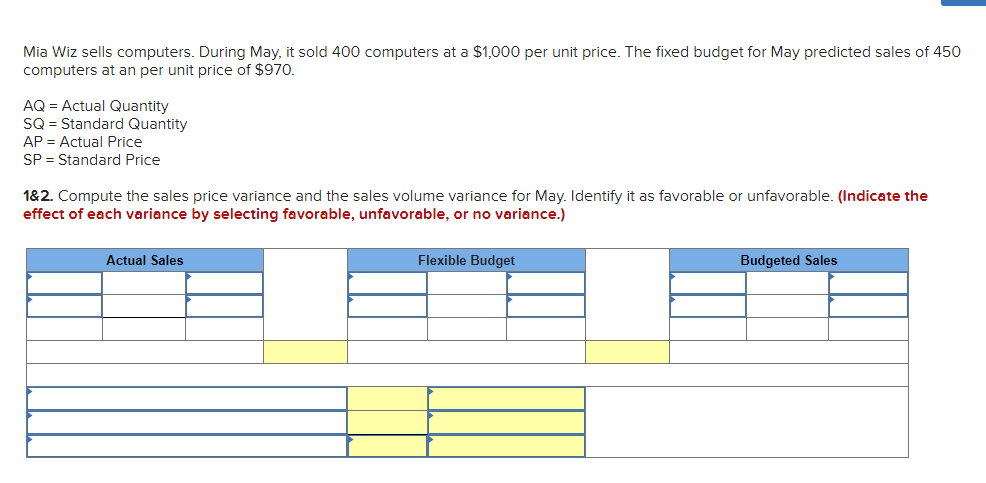
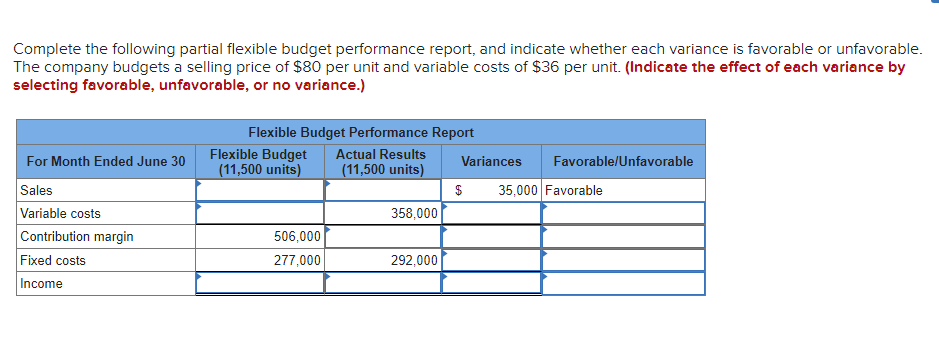

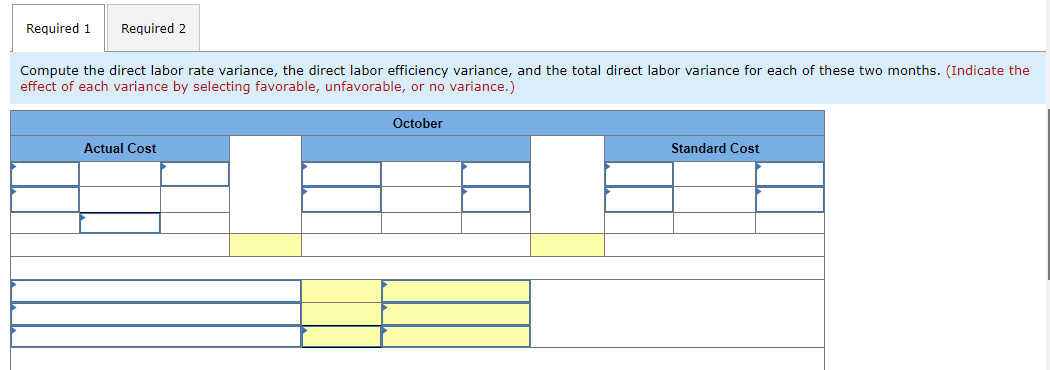
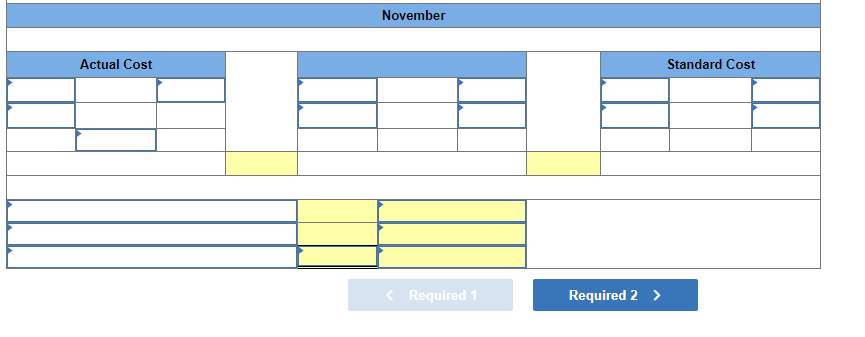
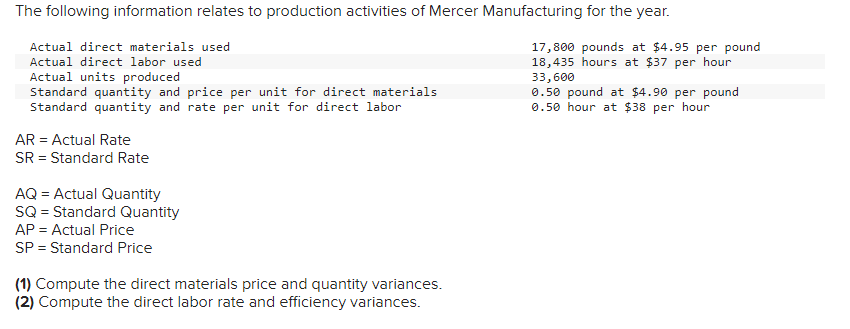
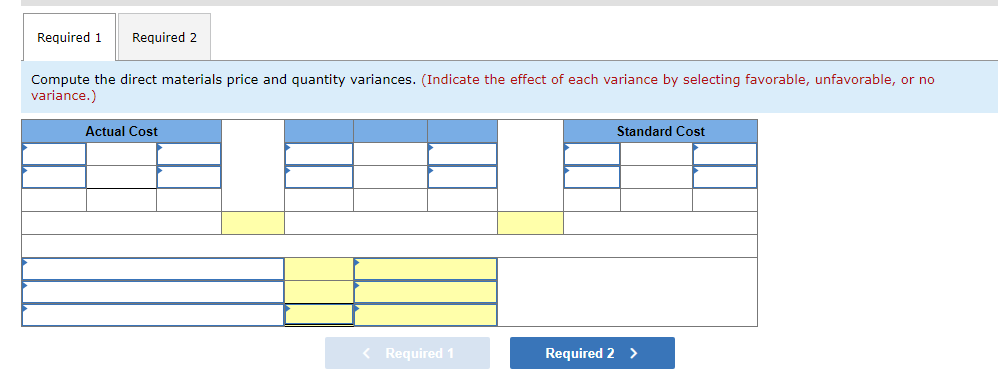
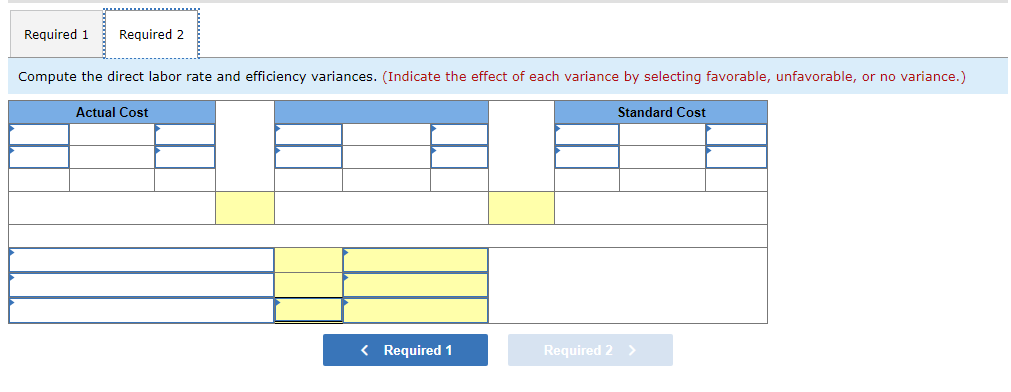
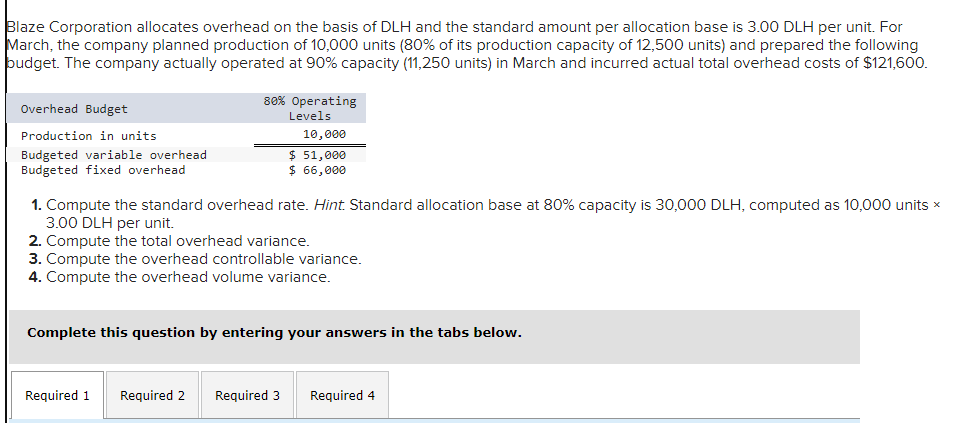
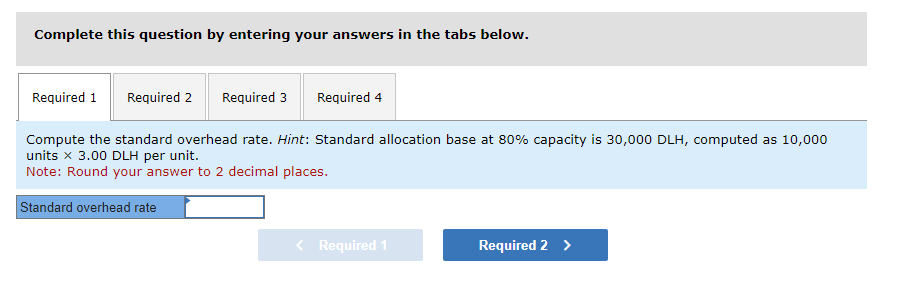
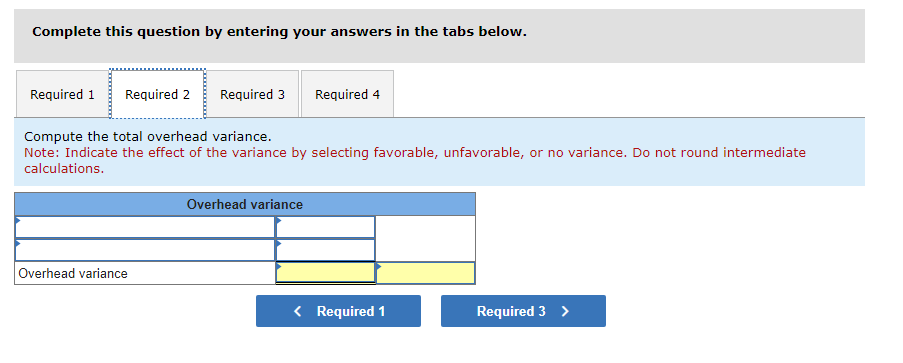
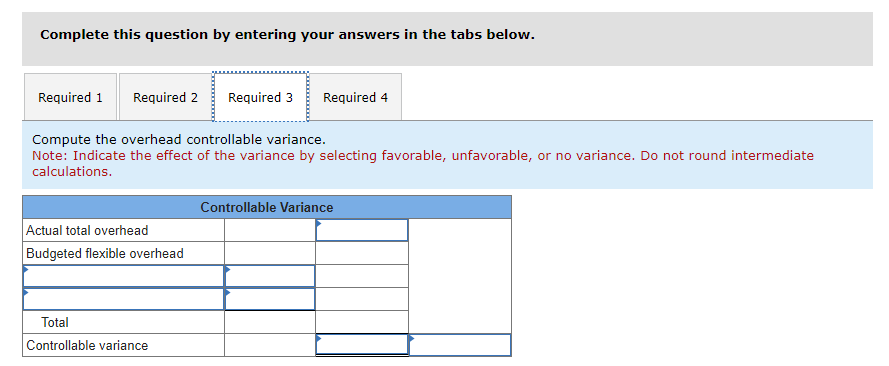
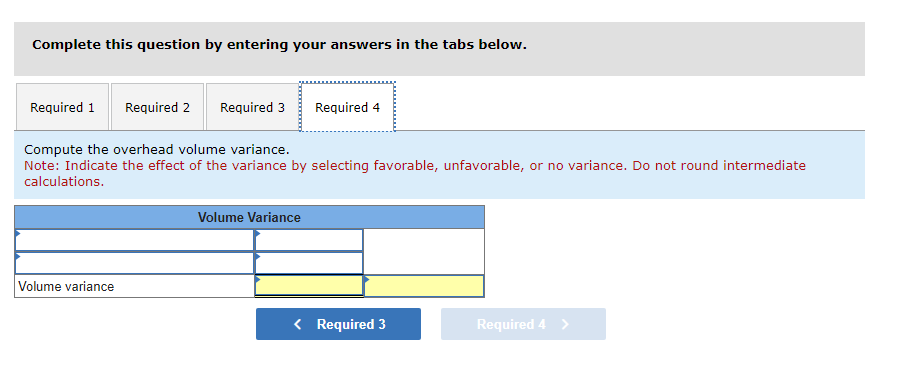
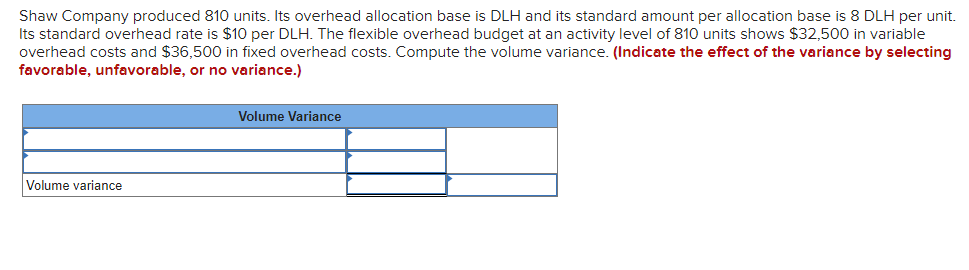
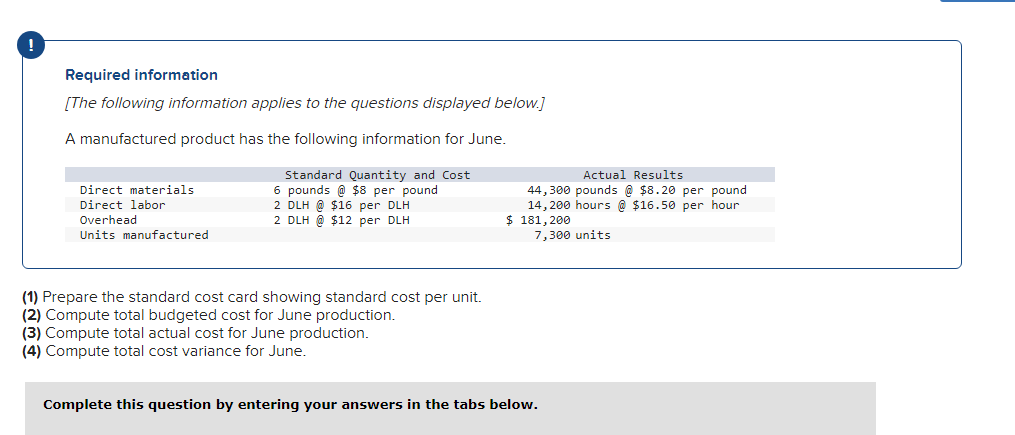
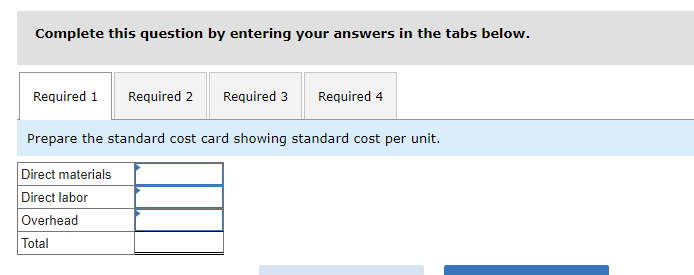
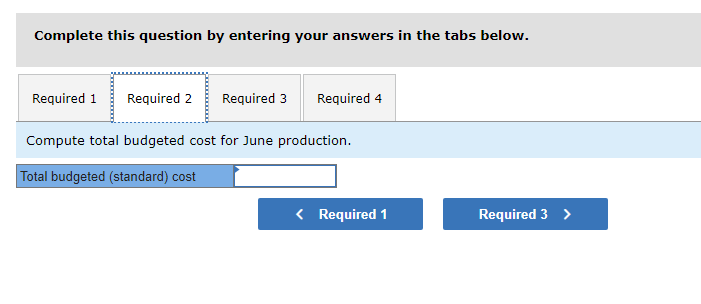
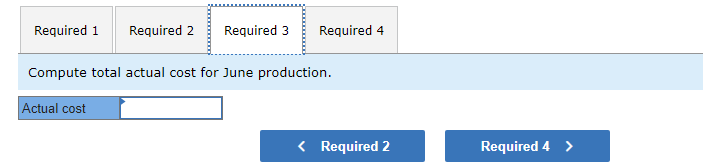
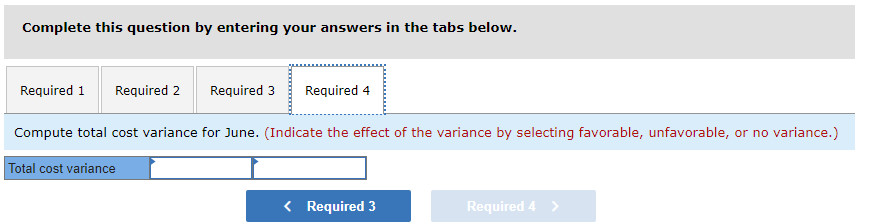

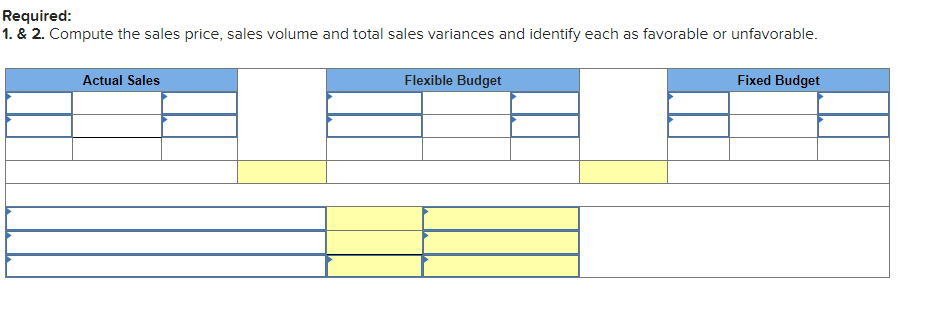
Mia Wiz sells computers. During May, it sold 400 computers at a $1,000 per unit price. The fixed budget for May predicted sales of 450 computers at an per unit price of $970. AQ = Actual Quantity SQ = Standard Quantity AP = Actual Price SP = Standard Price 1&2. Compute the sales price variance and the sales volume variance for May. Identify it as favorable or unfavorable. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Actual Sales Flexible Budget Budgeted Sales Complete the following partial flexible budget performance report, and indicate whether each variance is favorable or unfavorable. The company budgets a selling price of $80 per unit and variable costs of $36 per unit. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Flexible Budget Performance Report For Month Ended June 30 Sales Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Income Flexible Budget (11,500 units) Actual Results (11,500 units) Variances Favorable/Unfavorable $ 35,000 Favorable 358,000 506,000 277,000 292,000 Javon Company set standards of 3 hours of direct labor per unit at a rate of $16.60 per hour. During October, the company actually uses 21,000 hours of direct labor at a $352,800 total cost to produce 7,200 units. In November, the company uses 25,000 hours of direct labor at a $421,250 total cost to produce 7,600 units of product. AH = Actual Hours SH = Standard Hours AR = Actual Rate SR Standard Rate (1) Compute the direct labor rate variance, the direct labor efficiency variance, and the total direct labor variance for each of these two months. (2) Javon investigates variances of more than 5% of actual direct labor cost. Which direct labor variances will the company investigate further? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 1 Required 2 Compute the direct labor rate variance, the direct labor efficiency variance, and the total direct labor variance for each of these two months. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Actual Cost October Standard Cost Actual Cost November < Required 1 Required 2 > Standard Cost (2) Javon investigates variances of more than 5% of actual direct labor cost. Which direct labor variances will the company investigate further? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Javon investigates variances of more than 5% of actual direct labor cost. Which direct labor variances will the company investigate further? Which direct labor variances will the company investigate further? < Required 1 Required 2 > The following information relates to production activities of Mercer Manufacturing for the year. Actual direct materials used Actual direct labor used Actual units produced Standard quantity and price per unit for direct materials Standard quantity and rate per unit for direct labor AR Actual Rate SR = Standard Rate AQ = Actual Quantity SQ = Standard Quantity AP = Actual Price SP Standard Price (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. (2) Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances. 17,800 pounds at $4.95 per pound 18,435 hours at $37 per hour 33,600 0.50 pound at $4.90 per pound 0.50 hour at $38 per hour Required 1 Required 2 Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Actual Cost Standard Cost < Required 1 Required 2 > Required 1 Required 2 Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Actual Cost Standard Cost < Required 1 Required 2 > Blaze Corporation allocates overhead on the basis of DLH and the standard amount per allocation base is 3.00 DLH per unit. For March, the company planned production of 10,000 units (80% of its production capacity of 12,500 units) and prepared the following budget. The company actually operated at 90% capacity (11,250 units) in March and incurred actual total overhead costs of $121,600. Overhead Budget Production in units Budgeted variable overhead Budgeted fixed overhead 80% Operating Levels 10,000 $ 51,000 $ 66,000 1. Compute the standard overhead rate. Hint. Standard allocation base at 80% capacity is 30,000 DLH, computed as 10,000 units 3.00 DLH per unit. 2. Compute the total overhead variance. 3. Compute the overhead controllable variance. 4. Compute the overhead volume variance. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute the standard overhead rate. Hint: Standard allocation base at 80% capacity is 30,000 DLH, computed as 10,000 units x 3.00 DLH per unit. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Standard overhead rate < Required 1 Required 2 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute the total overhead variance. Note: Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance. Do not round intermediate calculations. Overhead variance Overhead variance < Required 1 Required 3 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute the overhead controllable variance. Note: Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance. Do not round intermediate calculations. Actual total overhead Budgeted flexible overhead Total Controllable variance Controllable Variance Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute the overhead volume variance. Note: Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance. Do not round intermediate calculations. Volume variance Volume Variance < Required 3 Required 4 Shaw Company produced 810 units. Its overhead allocation base is DLH and its standard amount per allocation base is 8 DLH per unit. Its standard overhead rate is $10 per DLH. The flexible overhead budget at an activity level of 810 units shows $32,500 in variable overhead costs and $36,500 in fixed overhead costs. Compute the volume variance. (Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Volume variance Volume Variance Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] A manufactured product has the following information for June. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Units manufactured Standard Quantity and Cost 6 pounds @ $8 per pound 2 DLH @ $16 per DLH 2 DLH @ $12 per DLH (1) Prepare the standard cost card showing standard cost per unit. (2) Compute total budgeted cost for June production. (3) Compute total actual cost for June production. (4) Compute total cost variance for June. Actual Results 44,300 pounds @ $8.20 per pound 14,200 hours @ $16.50 per hour $ 181,200 7,300 units Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Prepare the standard cost card showing standard cost per unit. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Total Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute total budgeted cost for June production. Total budgeted (standard) cost < Required 1 Required 3 > Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute total actual cost for June production. Actual cost < Required 2 Required 4 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Compute total cost variance for June. (Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Total cost variance < Required 3 Required 4 > Samsung offers sales price discounts on some products. Samsung can use sales variance analysis to assess the effects of these sales discounts. Assumed data for one model of a Samsung television follow. AQ = Actual Quantity AP = Actual Price SP=Standard Price SQ = Standard Quantity TV Sales (units) Sales price per unit Budgeted 2,000 units $ 1,800 Actual 3,000 units $ 1,100 Required: 1. & 2. Compute the sales price, sales volume and total sales variances and identify each as favorable or unfavorable. Required: 1. & 2. Compute the sales price, sales volume and total sales variances and identify each as favorable or unfavorable. Actual Sales Flexible Budget Fixed Budget
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


