Question
Mike's Exhaust Works produces efficient exhaust systems used on custom motorcycles. They sell their systems to other manufacturers, who build customized bikes to clients. Kai
Mike's Exhaust Works produces efficient exhaust systems used on custom motorcycles. They sell their systems to other manufacturers, who build customized bikes to clients. Kai is the sales manager, and she has created the following projected demand schedule for Tom, the production manager.
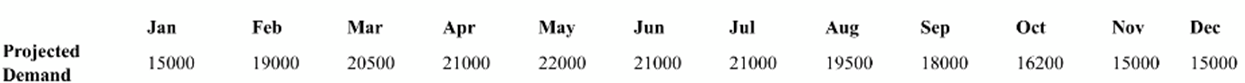 Mike's Exhaust Currently has 50 tradesmen who each work 20 clays a week, an c. produce 15 exhaust systems per day. a) Assuming that the company is only concerned with aggregate yearly demand, should the labor force be changed?
Mike's Exhaust Currently has 50 tradesmen who each work 20 clays a week, an c. produce 15 exhaust systems per day. a) Assuming that the company is only concerned with aggregate yearly demand, should the labor force be changed?
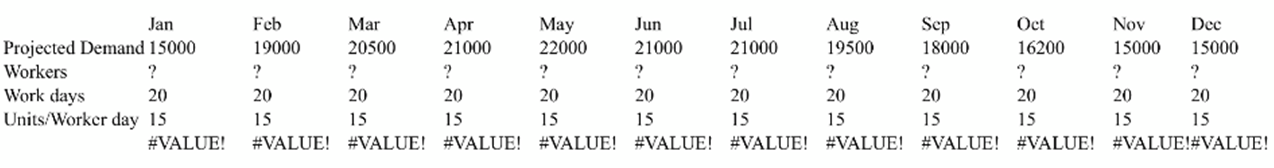 b) Assuming that the company is concerned with aggregate monthly demand, how should the labor force be changed? (round to the nearest whole employee - exact monthly demand must me met, no over or underproduction allowed).
b) Assuming that the company is concerned with aggregate monthly demand, how should the labor force be changed? (round to the nearest whole employee - exact monthly demand must me met, no over or underproduction allowed). 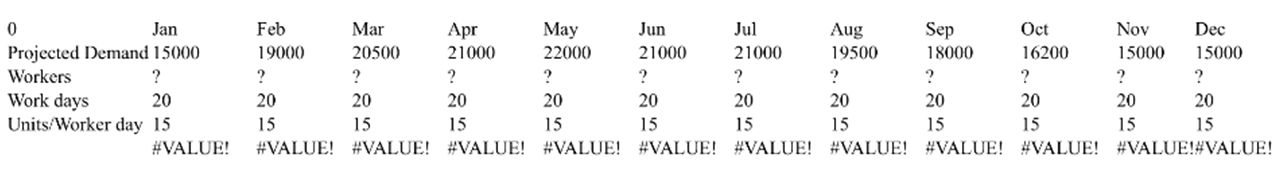
c) Each time the company lays off an employee. the expenses for the layoff are $19,000. In this sear. hots much are the costs of layoffs?
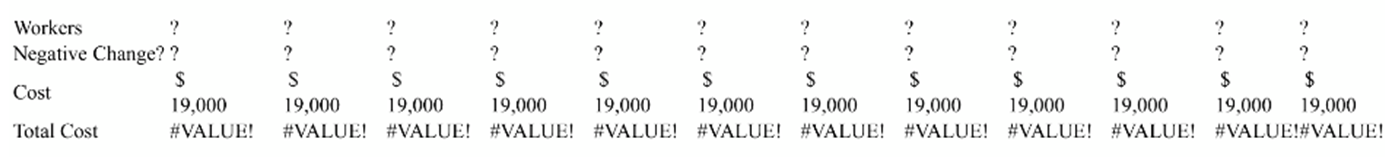
d) During busy times, the tradesmen at Mike's will happily take up to 50% overtime each month. Each worker makes $140 a day and overtime is 50% above standard rate. Using a fixed staff of 50, use overtime to calculate the number of equivalent workers needed per day to fill demand. (Hint: like "b" but do not round)

e) What is the overtime wage cost in the above example (d)? 
f) CCompare this overtime wage cost to the layoff cost in (c). Which is better?
g) The tradesmen at Mike's are in a union, and would like to eliminate the cycle of temporary hires and layoffs. They are will to negotiate their overtime wage so that it does not benefit the company to continue with this process. The current overtime wage is time + 50%. What should the union negotiate to change it to?  h) In your opinion, would the union what to do this?
h) In your opinion, would the union what to do this?
Projected Demand Jan 15000 Feb 19000 Mar 20500 Apr 21000 May 22000 Jun 21000 Jul 21000 Aug 19500 Sep 18000 Oct 16200 Nov 15000 15000 Dec Jan Projected Demand 15000 Workers ? Work days 20 Units/Worker day 15. #VALUE! Feb 19000 Mar 20500 Apr 21000 ? ? 20 20 15 15 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! ? 20 15 May 22000 ? 20 15 #VALUE! Jun 21000 ? 20 15 Jul 21000 ? 20 15 Aug 19500 ? 20 15 Sep 18000 ? 20 15 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! Oct 16200 ? 20 15 Nov 15000 ? 20 15 Dec 15000 ? 20 15 0 Jan Projected Demand 15000 Workers ? Work days 20 Units/Worker day 15 #VALUE! Feb 19000 Mar 20500 Apr 21000 May 22000 Jun 21000 Jul 21000 Aug 19500 Sep 18000 Oct 16200 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! Nov 15000 Dec 15000 ? 20 15 ? 20 15 #VALUE!#VALUE! Workers Negative Change?? Cost Total Cost ? ? ? ? ? ? ? S ? ? S $ $ 19,000 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! S 19,000 S 19,000 S 19,000 19,000 19,000 19,000 19,000 19,000 19,000 ? $ ? ? 2 ? $ $ 19,000 19,000 Jan Projected Demand 15000 Workers ? 20 Work days Units/Worker day 15 #VALUE! Feb 19000 ? 20 15 #VALUE! Mar 20500 ? 20 15 #VALUE! Apr 21000 ? 20 15 #VALUE! May 22000 ? 20 15 Jun 21000 ? 20 15 Jul 21000 ? 20 15 Aug 19500 ? 20 15 Sep 18000 ? 20 15 Oct 16200 ? 20 15 Nov Dec 15000 ? 20 15 15000 ? 20 15 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! Jan Equivalent Workers Actual Workers 50 Variation ? #VALUE! Workdays/month 20 Overtime Cost/day ? Total Overtime cost #VALUE! Equivalent ? Workers Actual Workers 50 Variation #VALUE! Workdays/month 20 Overtime Cost/day ? Total Overtime cost #VALUE! Feb ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? Dec ? 50 #VALUE!#VALUE! 20 ? #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! ? 50 #VALUE! Mar 20 ? ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? ? 50 #VALUE! Apr ? 20 ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? May ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? Jun ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? Sep ? 50 50 50 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! 20 20 20 20 ? ? ? ? Jul ? Aug ? 50 20 ? Oct ? ? ? ? ? 50 50 50 50 50 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! 20 20 ? ? ? ? 50 #VALUE!#VALUE! 20 ? #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! 20 ? Nov ? 50 20 ? 20 ? ? 50 20 ? Jan Equivalent ? Workers Actual Workers 50 Variation #VALUE! Workdays/month 20 Overtime Cost/day? Total Overtime cost Overtime % #VALUE! ? Feb ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? Apr ? 50 50 #VALUE! #VALUE! 20 ? Mar ? May ? 50 #VALUE! 20 ? 20 ? Jun ? Jul ? 50 50 #VALUE! #VALUE! 20 ? 20 ? Aug ? ? 50 #VALUE!#VALUE! 20 ? #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE!#VALUE! Sep ? Oct ? Nov ? 50 50 50 #VALUE! #VALUE! #VALUE! 20 20 20 ? ? ? 50 Dec 20 ?
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


