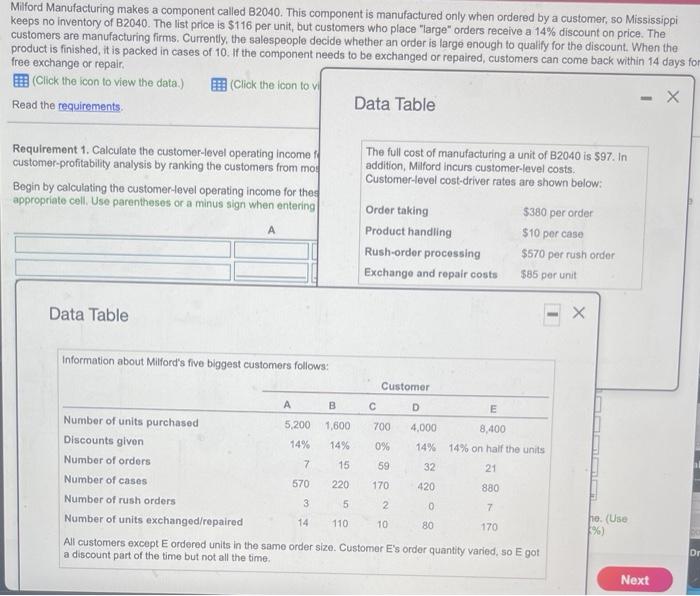
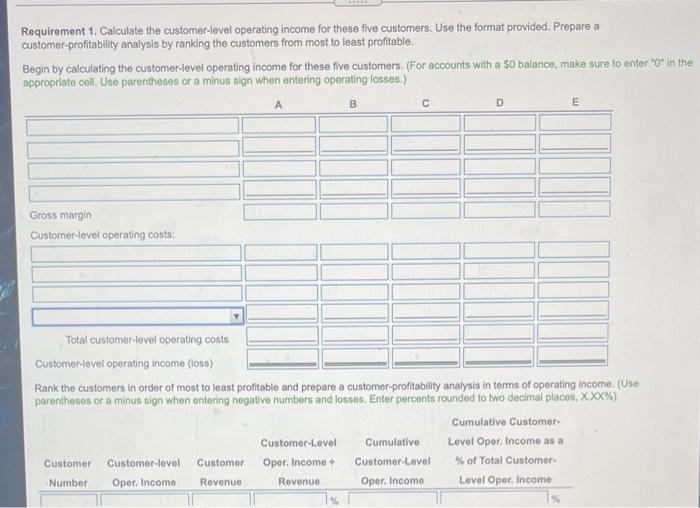
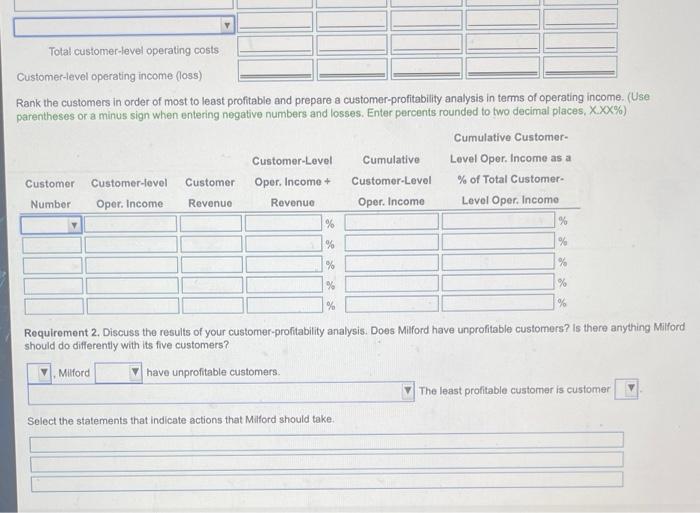
Milford Manufacturing makes a component called B2040. This component is manufactured only when ordered by a customer, so Mississippi keeps no inventory of B2040. The list price is $116 per unit, but customers who place "large" orders receive a 14% discount on price. The customers are manufacturing firms. Currently, the salespeople decide whether an order is large enough to qualify for the discount. When the product is finished, it is packed in cases of 10. If the component needs to be exchanged or repaired, customers can come back within 14 days for free exchange or repair (Click the icon to view the data.) Click the icon to Data Table Read the requirements Requirement 1. Calculate the customer-level operating income customer-profitability analysis by ranking the customers from mo Begin by calculating the customer-level operating income for the appropriate coll. Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering The full cost of manufacturing a unit of B2040 is $97. In addition, Milford Incurs customer-level costs. Customer-level cost-driver rates are shown below: A Order taking Product handling Rush-order processing Exchange and repair costs $380 per order $10 per case $570 per rush order $85 per unit Data Table Information about Milford's five biggest customers follows: Customer A B C D E Number of units purchased 5,200 1,600 700 4,000 8,400 Discounts given 14% 14% 0% 14% 14% on half the units Number of orders 7 15 59 32 21 Number of cases 570 220 170 420 880 Number of rush orders 3 5 2 7 Number of units exchanged/repaired 14 110 10 80 170 All customers except E ordered units in the same order size. Customer E's order quantity varied, so E got a discount part of the time but not all the time, 0 ho (Use %) Dr Next Requirement 1. Calculate the customer-level operating income for these five customers. Use the format provided. Prepare a customer-profitability analysis by ranking the customers from most to least profitable. Begin by calculating the customer-level operating income for these five customers. (For accounts with a $0 balance, make sure to enter "o" in the appropriate cell. Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering operating losses.) A B D E Gross margin Customer-level operating costs Total customer-level operating costs Customer-lovel operating incomo (loss) Rank the customers in order of most to least profitable and prepare a customer-profitability analysis in terms of operating income (Une parentheses or a minus sign when entering negative numbers and lossos. Enter percents rounded to two decimal places, XXX%) Cumulative Customer Customer-Level Cumulative Level Opor. Income as a Customer Customer lovel Customer Oper. Income Customer Level % of Total Customer Number Oper. Income Revenue Revenue Oper. Income Level Oper. Income Total customer-level operating costs Customer-level operating income (loss) Rank the customers in order of most to least profitable and prepare a customer-profitability analysis in terms of operating income. (Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering negative numbers and losses. Enter perounts rounded to two decimal places, X.XX%) Cumulative Customer Customer-Level Cumulative Level Oper. Income as a Customer Customer-level Customer Oper. Income + Customer-Level % of Total Customer Number Oper. Income Revenuo Revenue Oper. Income Level Oper. Income % % % % % % % % Requirement 2. Discuss the results of your customer-profitability analysis. Does Milford have unprofitable customers? Is there anything Milford should do differently with its five customers? V. Milford have unprofitable customers. The least profitable customer is customer Select the statements that indicate actions that Milford should take Customer Customer-level Customer Oper. Income customer-Level Number Oper. Income Revenue Revenue Oper. Income % of Total Customer- Level Oper. Income If customer B were not being given price discounts, B would be profitable. Discounts should be offered for large orders only. of customer C were not being given price discounts, C would be profitable. Discounts should be offered for large orders. The cost of rush order processing is high. The company should work to reduce theses costs or the number of rush orders. The cost of product handling is high. The company should work to reduce these costs. The most profitable customers (A and E) are valued customers and should receive the highest level of customer service. The most profitable customers (B and D) are valued customers and should receive the highest level of customer service, NOXE ope ab Cost of goods sold ng ga Exchange and repair Order taking Price discounts Product handling Revenues at actual prices Revenues at list price Rush order processing Milford Manufacturing makes a component called B2040. This component is manufactured only when ordered by a customer, so Mississippi keeps no inventory of B2040. The list price is $116 per unit, but customers who place "large" orders receive a 14% discount on price. The customers are manufacturing firms. Currently, the salespeople decide whether an order is large enough to qualify for the discount. When the product is finished, it is packed in cases of 10. If the component needs to be exchanged or repaired, customers can come back within 14 days for free exchange or repair (Click the icon to view the data.) Click the icon to Data Table Read the requirements Requirement 1. Calculate the customer-level operating income customer-profitability analysis by ranking the customers from mo Begin by calculating the customer-level operating income for the appropriate coll. Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering The full cost of manufacturing a unit of B2040 is $97. In addition, Milford Incurs customer-level costs. Customer-level cost-driver rates are shown below: A Order taking Product handling Rush-order processing Exchange and repair costs $380 per order $10 per case $570 per rush order $85 per unit Data Table Information about Milford's five biggest customers follows: Customer A B C D E Number of units purchased 5,200 1,600 700 4,000 8,400 Discounts given 14% 14% 0% 14% 14% on half the units Number of orders 7 15 59 32 21 Number of cases 570 220 170 420 880 Number of rush orders 3 5 2 7 Number of units exchanged/repaired 14 110 10 80 170 All customers except E ordered units in the same order size. Customer E's order quantity varied, so E got a discount part of the time but not all the time, 0 ho (Use %) Dr Next Requirement 1. Calculate the customer-level operating income for these five customers. Use the format provided. Prepare a customer-profitability analysis by ranking the customers from most to least profitable. Begin by calculating the customer-level operating income for these five customers. (For accounts with a $0 balance, make sure to enter "o" in the appropriate cell. Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering operating losses.) A B D E Gross margin Customer-level operating costs Total customer-level operating costs Customer-lovel operating incomo (loss) Rank the customers in order of most to least profitable and prepare a customer-profitability analysis in terms of operating income (Une parentheses or a minus sign when entering negative numbers and lossos. Enter percents rounded to two decimal places, XXX%) Cumulative Customer Customer-Level Cumulative Level Opor. Income as a Customer Customer lovel Customer Oper. Income Customer Level % of Total Customer Number Oper. Income Revenue Revenue Oper. Income Level Oper. Income Total customer-level operating costs Customer-level operating income (loss) Rank the customers in order of most to least profitable and prepare a customer-profitability analysis in terms of operating income. (Use parentheses or a minus sign when entering negative numbers and losses. Enter perounts rounded to two decimal places, X.XX%) Cumulative Customer Customer-Level Cumulative Level Oper. Income as a Customer Customer-level Customer Oper. Income + Customer-Level % of Total Customer Number Oper. Income Revenuo Revenue Oper. Income Level Oper. Income % % % % % % % % Requirement 2. Discuss the results of your customer-profitability analysis. Does Milford have unprofitable customers? Is there anything Milford should do differently with its five customers? V. Milford have unprofitable customers. The least profitable customer is customer Select the statements that indicate actions that Milford should take Customer Customer-level Customer Oper. Income customer-Level Number Oper. Income Revenue Revenue Oper. Income % of Total Customer- Level Oper. Income If customer B were not being given price discounts, B would be profitable. Discounts should be offered for large orders only. of customer C were not being given price discounts, C would be profitable. Discounts should be offered for large orders. The cost of rush order processing is high. The company should work to reduce theses costs or the number of rush orders. The cost of product handling is high. The company should work to reduce these costs. The most profitable customers (A and E) are valued customers and should receive the highest level of customer service. The most profitable customers (B and D) are valued customers and should receive the highest level of customer service, NOXE ope ab Cost of goods sold ng ga Exchange and repair Order taking Price discounts Product handling Revenues at actual prices Revenues at list price Rush order processing