Question
Modify bakery algorithm in c to include a getThreadCount function. Function specifications: Global variables: code to be modified: // Importing the thread library #include pthread.h
Modify bakery algorithm in c to include a getThreadCount function.
Function specifications:
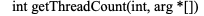

Global variables:

code to be modified:
// Importing the thread library
#include "pthread.h"
#include "stdio.h"
// Importing POSIX Operating System API library
#include "unistd.h"
#include "string.h"
// This is a memory barrier instruction.
// Causes compiler to enforce an ordering
// constraint on memory operations.
// This means that operations issued prior
// to the barrier will be performed
// before operations issued after the barrier.
#define MEMBAR __sync_synchronize()
#define THREAD_COUNT 8
volatile int tickets[THREAD_COUNT];
volatile int choosing[THREAD_COUNT];
// VOLATILE used to prevent the compiler
// from applying any optimizations.
volatile int resource;
void lock(int thread)
{
// Before getting the ticket number
//"choosing" variable is set to be true
choosing[thread] = 1;
MEMBAR;
// Memory barrier applied
int max_ticket = 0;
// Finding Maximum ticket value among current threads
for (int i = 0; i
int ticket = tickets[i];
max_ticket = ticket > max_ticket ? ticket : max_ticket;
}
// Allotting a new ticket value as MAXIMUM + 1
tickets[thread] = max_ticket + 1;
MEMBAR;
choosing[thread] = 0;
MEMBAR;
// The ENTRY Section starts from here
for (int other = 0; other
// Applying the bakery algorithm conditions
while (choosing[other]) {
}
MEMBAR;
while (tickets[other] != 0 && (tickets[other]
|| (tickets[other]
== tickets[thread]
&& other
}
}
}
// EXIT Section
void unlock(int thread)
{
MEMBAR;
tickets[thread] = 0;
}
// The CRITICAL Section
void use_resource(int thread)
{
if (resource != 0) {
printf("Resource was acquired by %d, but is still in-use by %d! ",
thread, resource);
}
resource = thread;
printf("%d using resource... ", thread);
MEMBAR;
sleep(2);
resource = 0;
}
// A simplified function to show the implementation
void* thread_body(void* arg)
{
long thread = (long)arg;
lock(thread);
use_resource(thread);
unlock(thread);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
memset((void*)tickets, 0, sizeof(tickets));
memset((void*)choosing, 0, sizeof(choosing));
resource = 0;
// Declaring the thread variables
pthread_t threads[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i
// Creating a new thread with the function
//"thread_body" as its thread routine
pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, &thread_body, (void*)((long)i));
}
for (int i = 0; i
// Reaping the resources used by
// all threads once their task is completed !
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
}
return 0;
}
int getThreadCount(int, arg *]) int getThreadCount(int, arg *])Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


