
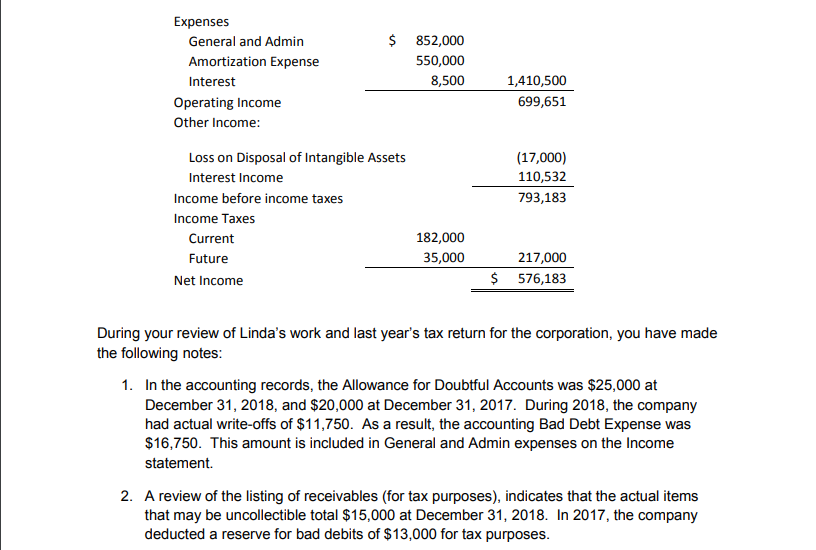
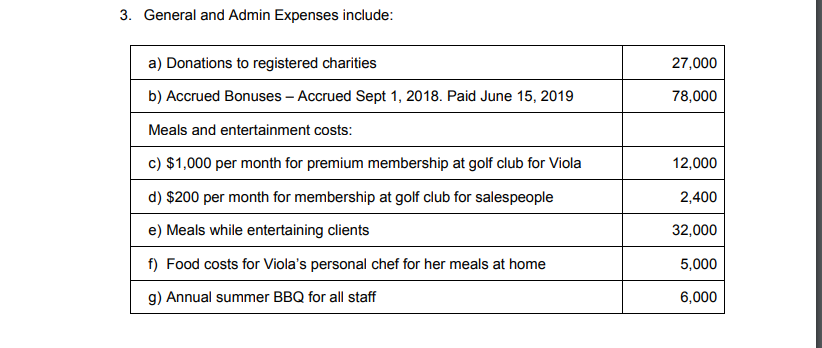
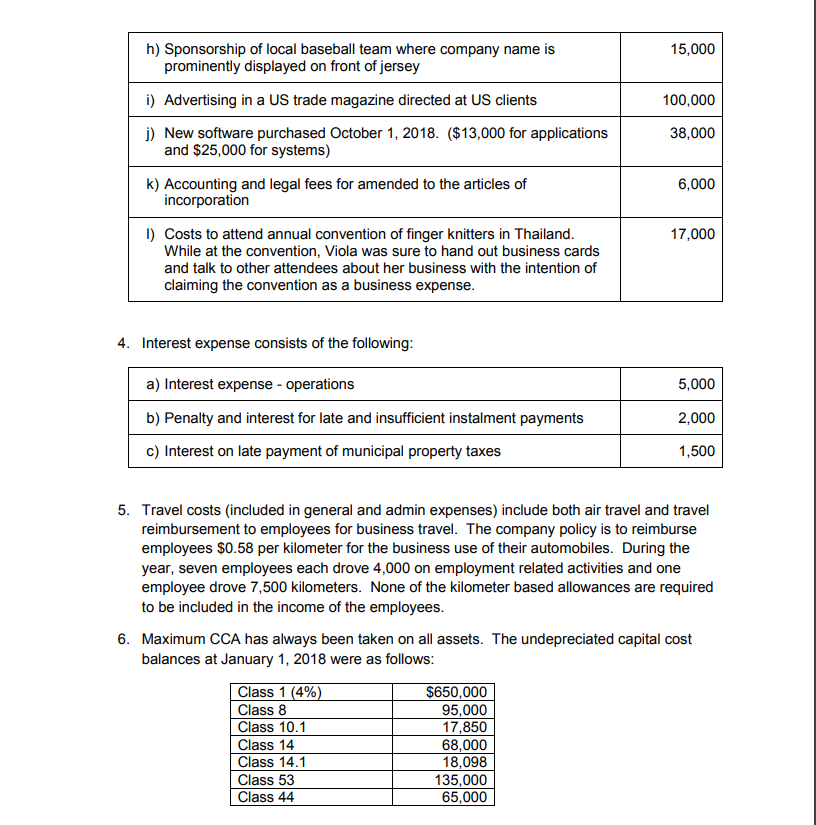

Morton Forms Excel Problem Morton Forms is a Canadian controlled private corporation specializing in designing and printing custom business forms. It is owned by Viola Morton. For the taxation year ended December 31, 2018, Ms. Morton's daughter, Linda, who works in the business, has calculated a Net Income for Morton Forms of $576,183. In calculating this figure, Linda used generally accepted accounting principles Linda has produced the following Income Statement for the year ended December 31, 2018: Morton Forms Inc. Income Statement Year ending December 31, 2018 $7,578,903 Sales 5,468,752 Cost of Goods Sold 2,110,151 Gross Profit Expenses 852,000 General and Admin 550,000 Amortization Expense 8,500 1,410,500 Interest 699,651 Operating Income Other Income: Loss on Disposal of Intangible Assets (17,000) 110,532 Interest Income 793,183 Income before income taxes Income Taxes 182,000 Current 35,000 217,000 Future 576,183 Net Income During your review of Linda's work and last year's tax return for the corporation, you have made the following notes: 1. In the accounting records, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts was $25,000 at December 31, 2018, and $20,000 at December 31, 2017. During 2018, the company had actual write-offs of $11,750. As a result, the accounting Bad Debt Expense was $16,750. This amount is included in General and Admin expenses on the Income statement 2. A review of the listing of receivables (for tax purposes), indicates that the actual items that may be uncollectible total $15,000 at December 31, 2018. In 2017, the company deducted a reserve for bad debits of $13,000 for tax purposes 3. General and Admin Expenses include: a) Donations to registered charities 27,000 b) Accrued Bonuses - Accrued Sept 1, 2018. Paid June 15, 2019 78,000 Meals and entertainment costs: c) $1,000 per month for premium membership at golf club for Viola 12,000 d) $200 per month for membership at golf club for salespeople 2,400 e) Meals while entertaining clients 32,000 f) Food costs for Viola's personal chef for her meals at home 5,000 g) Annual summer BBQ for all staff 6,000 h) Sponsorship of local baseball team where company name is prominently displayed on front of jersey 15,000 i) Advertising in a US trade magazine directed at US clients 100,000 j) New software purchased October 1, 2018. ($13,000 for applications and $25,000 for systems) 38,000 k) Accounting and legal fees for amended to the articles of incorporation 6,000 ) Costs to attend annual convention of finger knitters in Thailand. While at the convention, Viola was sure to hand out business cards 17,000 and talk to other attendees about her business with the intention of claiming the convention as a business expense. 4. Interest expense consists of the following: a) Interest expense operations 5,000 b) Penalty and interest for late and insufficient instalment payments 2,000 c) Interest on late payment of municipal property taxes 1,500 5. Travel costs (included in general and admin expenses) include both air travel and travel reimbursement to employees for business travel. The company policy is to reimburse employees $0.58 per kilometer for the business use of their automobiles. During the year, seven employees each drove 4,000 on employment related activities and one employee drove 7,500 kilometers. None of the kilometer based allowances are required to be included in the income of the employees. 6. Maximum CCA has always been taken on all assets. The undepreciated capital cost balances at January 1, 2018 were as follows: Class 1 (4% $650,000 95,000 17,850 68,000 18,098 135,000 65,000 Class 8 Class 10.1 Class 14 Class 14.1 Class 53 Class 44 7. There was a loss on disposal of a limited life license to produce copyrighted materials for a major distributor. This license originally cost the company $95,000, and it was sold for $63,000 in 2018. The book value of the license at the time of sale was $80,000. When the license was sold, it was the only asset in its CCA class. The loss was claimed as a loss on disposal of intangible assets on the Income Statement 8. Purchases and sales of equipment and other capital assets made during 2018 were as follows. (Note: any items discussed in other sections are included in this list as well) a. The company purchased land and constructed a new building on it during the year. The building was used 95% for manufacturing and process ing. The cost of the land was $350,000, and the building cost $475,000 to construct b. The company purchased a new set of furniture for the reception area for $1,200 c. Some outdated desks used by the finance department with a cost of $5,000 were sold for proceeds of $3,500. d. Landscaping of grounds around the new building cost $35,000. This amount was capitalized for accounting purposes. e. A company car for use by the president of the company was purchased for $90,000. This car replaced the only other existing company car, which was purchased in 2013 for $95,000. The old car was sold for $60,000 f. A fence around the new building cost $52,000. g. New software was purchased: $13,000 for Applications and $25,000 for Systems 9. The company sold some shares that had been purchased several years ago. The capital gain on these shares was $152,708. Linda didn't know how to account for this, so she credited the entire amount to retained earnings. Morton Forms Excel Problem Morton Forms is a Canadian controlled private corporation specializing in designing and printing custom business forms. It is owned by Viola Morton. For the taxation year ended December 31, 2018, Ms. Morton's daughter, Linda, who works in the business, has calculated a Net Income for Morton Forms of $576,183. In calculating this figure, Linda used generally accepted accounting principles Linda has produced the following Income Statement for the year ended December 31, 2018: Morton Forms Inc. Income Statement Year ending December 31, 2018 $7,578,903 Sales 5,468,752 Cost of Goods Sold 2,110,151 Gross Profit Expenses 852,000 General and Admin 550,000 Amortization Expense 8,500 1,410,500 Interest 699,651 Operating Income Other Income: Loss on Disposal of Intangible Assets (17,000) 110,532 Interest Income 793,183 Income before income taxes Income Taxes 182,000 Current 35,000 217,000 Future 576,183 Net Income During your review of Linda's work and last year's tax return for the corporation, you have made the following notes: 1. In the accounting records, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts was $25,000 at December 31, 2018, and $20,000 at December 31, 2017. During 2018, the company had actual write-offs of $11,750. As a result, the accounting Bad Debt Expense was $16,750. This amount is included in General and Admin expenses on the Income statement 2. A review of the listing of receivables (for tax purposes), indicates that the actual items that may be uncollectible total $15,000 at December 31, 2018. In 2017, the company deducted a reserve for bad debits of $13,000 for tax purposes 3. General and Admin Expenses include: a) Donations to registered charities 27,000 b) Accrued Bonuses - Accrued Sept 1, 2018. Paid June 15, 2019 78,000 Meals and entertainment costs: c) $1,000 per month for premium membership at golf club for Viola 12,000 d) $200 per month for membership at golf club for salespeople 2,400 e) Meals while entertaining clients 32,000 f) Food costs for Viola's personal chef for her meals at home 5,000 g) Annual summer BBQ for all staff 6,000 h) Sponsorship of local baseball team where company name is prominently displayed on front of jersey 15,000 i) Advertising in a US trade magazine directed at US clients 100,000 j) New software purchased October 1, 2018. ($13,000 for applications and $25,000 for systems) 38,000 k) Accounting and legal fees for amended to the articles of incorporation 6,000 ) Costs to attend annual convention of finger knitters in Thailand. While at the convention, Viola was sure to hand out business cards 17,000 and talk to other attendees about her business with the intention of claiming the convention as a business expense. 4. Interest expense consists of the following: a) Interest expense operations 5,000 b) Penalty and interest for late and insufficient instalment payments 2,000 c) Interest on late payment of municipal property taxes 1,500 5. Travel costs (included in general and admin expenses) include both air travel and travel reimbursement to employees for business travel. The company policy is to reimburse employees $0.58 per kilometer for the business use of their automobiles. During the year, seven employees each drove 4,000 on employment related activities and one employee drove 7,500 kilometers. None of the kilometer based allowances are required to be included in the income of the employees. 6. Maximum CCA has always been taken on all assets. The undepreciated capital cost balances at January 1, 2018 were as follows: Class 1 (4% $650,000 95,000 17,850 68,000 18,098 135,000 65,000 Class 8 Class 10.1 Class 14 Class 14.1 Class 53 Class 44 7. There was a loss on disposal of a limited life license to produce copyrighted materials for a major distributor. This license originally cost the company $95,000, and it was sold for $63,000 in 2018. The book value of the license at the time of sale was $80,000. When the license was sold, it was the only asset in its CCA class. The loss was claimed as a loss on disposal of intangible assets on the Income Statement 8. Purchases and sales of equipment and other capital assets made during 2018 were as follows. (Note: any items discussed in other sections are included in this list as well) a. The company purchased land and constructed a new building on it during the year. The building was used 95% for manufacturing and process ing. The cost of the land was $350,000, and the building cost $475,000 to construct b. The company purchased a new set of furniture for the reception area for $1,200 c. Some outdated desks used by the finance department with a cost of $5,000 were sold for proceeds of $3,500. d. Landscaping of grounds around the new building cost $35,000. This amount was capitalized for accounting purposes. e. A company car for use by the president of the company was purchased for $90,000. This car replaced the only other existing company car, which was purchased in 2013 for $95,000. The old car was sold for $60,000 f. A fence around the new building cost $52,000. g. New software was purchased: $13,000 for Applications and $25,000 for Systems 9. The company sold some shares that had been purchased several years ago. The capital gain on these shares was $152,708. Linda didn't know how to account for this, so she credited the entire amount to retained earnings











