Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Motor 15cm Shaft 2 Pulley t V belt driver Gear B Pulley F Shaft #1 L Table 1: Gears & Pulleys diameter Son Gear
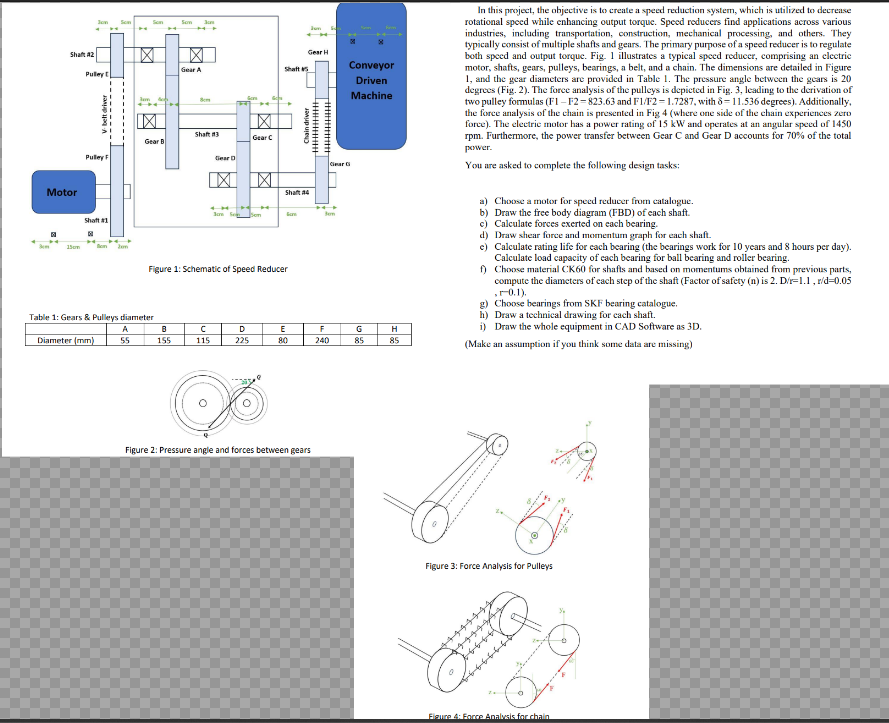
Motor 15cm Shaft 2 Pulley t V belt driver Gear B Pulley F Shaft #1 L Table 1: Gears & Pulleys diameter Son Gear H Gear A Shaft s Shaft #3 Gear C Chain driver Gear D Shaft #4 Figure 1: Schematic of Speed Reducer Clear G Conveyor Driven Machine In this project, the objective is to create a speed reduction system, which is utilized to decrease rotational speed while enhancing output torque. Speed reducers find applications across various industries, including transportation, construction, mechanical processing, and others. They typically consist of multiple shafts and gears. The primary purpose of a speed reducer is to regulate both speed and output torque. Fig. 1 illustrates a typical speed reducer, comprising an electric motor, shafts, gears, pulleys, bearings, a belt, and a chain. The dimensions are detailed in Figure 1, and the gear diameters are provided in Table 1. The pressure angle between the gears is 20 degrees (Fig. 2). The force analysis of the pulleys is depicted in Fig. 3, leading to the derivation of two pulley formulas (F1-F2-823.63 and F1/F2=1.7287, with 8-11.536 degrees). Additionally, the force analysis of the chain is presented in Fig 4 (where one side of the chain experiences zero force). The electric motor has a power rating of 15 kW and operates at an angular speed of 1450 rpm. Furthermore, the power transfer between Gear C and Gear D accounts for 70% of the total power. You are asked to complete the following design tasks: a) Choose a motor for speed reducer from catalogue. b) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of each shaft. c) Calculate forces exerted on each bearing. d) Draw shear force and momentum graph for each shaft. e) Calculate rating life for each bearing (the bearings work for 10 years and 8 hours per day). Calculate load capacity of each bearing for ball bearing and roller bearing. f) Choose material CK60 for shafts and based on momentums obtained from previous parts, compute the diameters of each step of the shaft (Factor of safety (n) is 2. Dir=1.1, r/d=0.05 .-0.1). g) Choose bearings from SKF bearing catalogue. h) Draw a technical drawing for each shaft. i) Draw the whole equipment in CAD Software as 3D. (Make an assumption if you think some data are missing) A B C D E F G H Diameter (mm) 55 155 115 225 80 240 85 85 Figure 2: Pressure angle and forces between gears Figure 3: Force Analysis for Pulleys 14444 Figure 4: Force Analysis for chain
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


