Mr. T makes a good recovery and is discharged from the hospital, but a few weeks later you meet him again in the outpatient clinic
Mr. T makes a good recovery and is discharged from the hospital, but a few weeks later you meet him again in the outpatient clinic complaining of headache, blurred vision, and pinkeye. His eyes are certainly bloodshot, but there isn't any sign of discharge from them. His face is flushed and his blood pressure is 160/108 mm Hg, his heart rate is 58 beats/minute, and his respiration rate is 18 breaths/minute. His blood glucose is a little high at 128 mg/dL. He denies any alcohol or drug use in the past week, and says he does not normally have high blood pressure. His problems came on in the last few hours.
This client has high blood pressure and a low heart rate. How does high blood pressure lead to a low heart rate?
Drag the labels onto the figure to create a flow chart of how the baroreceptor reflex would respond to increased mean arterial pressure.
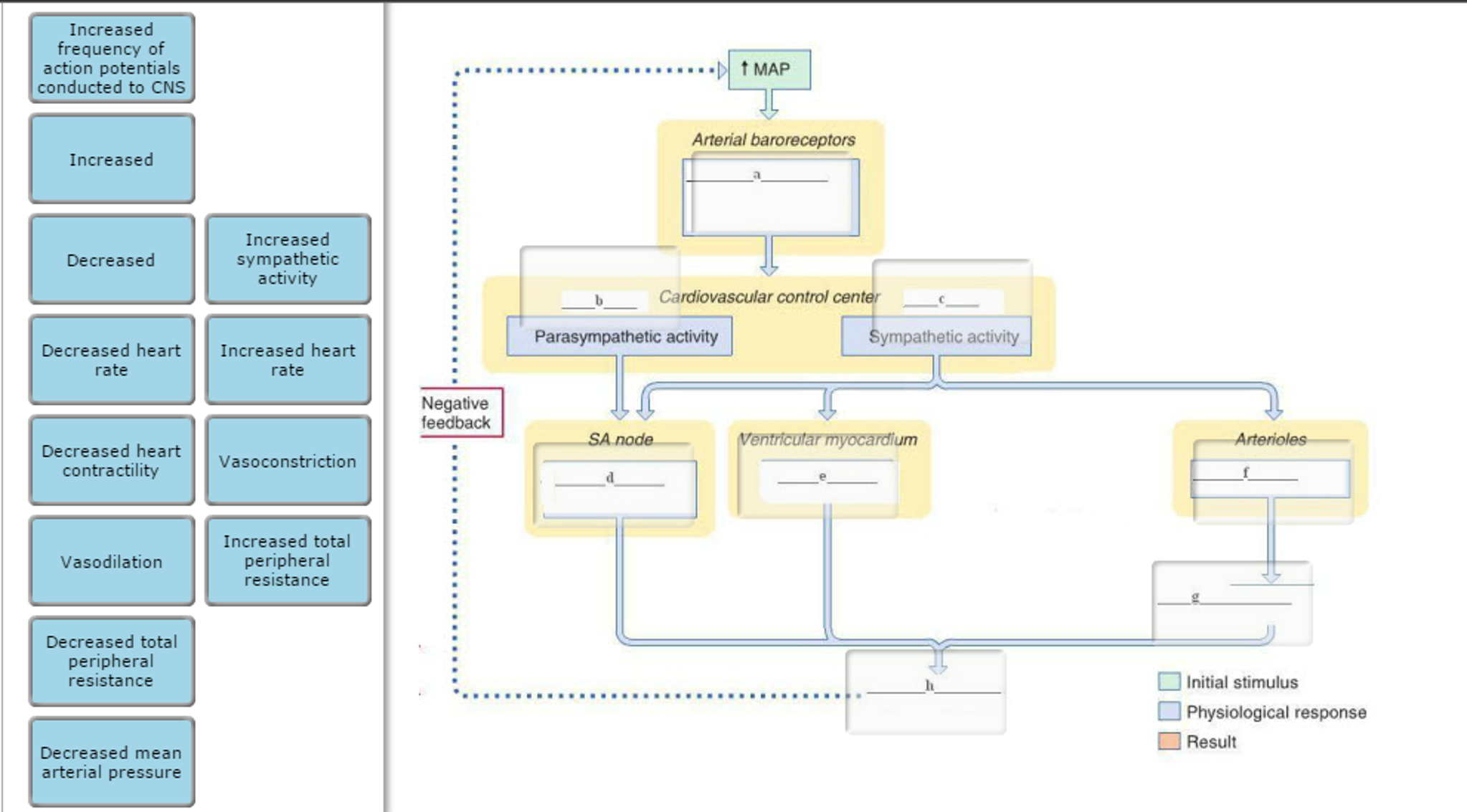
Increased frequency of action potentials conducted to CNS Increased Decreased Decreased heart rate Decreased heart contractility Vasodilation Decreased total peripheral resistance Decreased mean arterial pressure Increased sympathetic activity Increased heart rate Vasoconstriction Increased total peripheral resistance Negative feedback SA node MAP Arterial baroreceptors Parasympathetic activity Cardiovascular control center Sympathetic activity Ventricular myocardium Arterioles Initial stimulus Physiological response Result
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
SOLUTION aincreased total peripheral resi...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


