Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
mRNA PART B. Answer the following questions on your paper: 1. What is the first step of protein synthesis? 2. What is the second


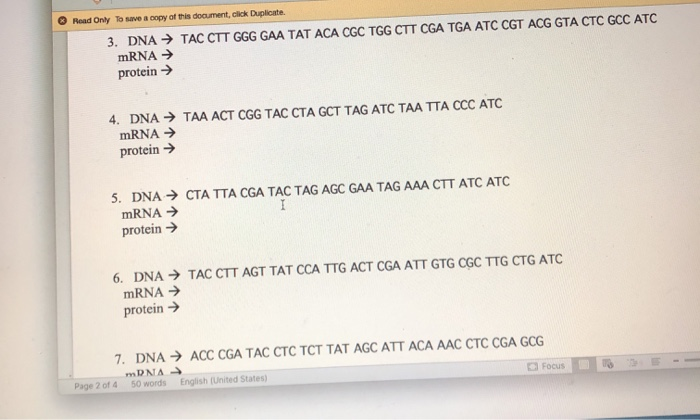


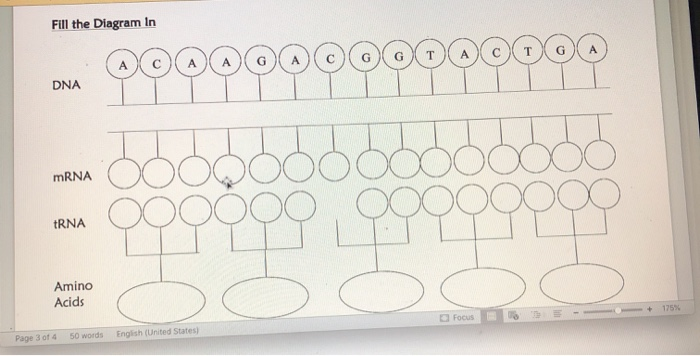



mRNA PART B. Answer the following questions on your paper: 1. What is the first step of protein synthesis? 2. What is the second step of protein synthesis? 3. Where does the first step of protein synthesis occur? 4. Where does the second step of protein synthesis occur? bases at a time. 5. Nitrogen bases are read 6. The bases on the mRNA strand are called 7. The bases on tRNA are called 8. What is the start codon? 9. What are the stop codons? (Use your mRNA chart or pg: 298) 10. A bunch of amino acids attached together is called a PART C. Use your codon chart or the chart on page 298 to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember to read through the strand and ONLY start on AUG and STOP when it tells you to stop. Follow example below: Example: DNAAGA CGG TAC CTC CGG TGG GTG CTT GTC TGT ATC CTT CTC AGT ATC mRNA UCU GCC AUG GAG GCC ACC CAC GAA CAG ACA UAG GAA GAG UCA UAG protein start-glu - ala -thre - hist - asp -glu - threo-stop acid acid 1. DNA CCT CTT TAC ACA CGG AGG GTA CGC TAT TCT ATG ATT ACA CGG TTG CGA TCC ATA ATC mRNA protein 2. DNA AGA ACA TAA TAC CTC TTA ACA CTC TAA AGA CCA GCA CTC CGA TGA ACT GGA GCA mRNA protein 1751 Read Only To save a copy of this document, click Duplicate. 3. DNA TAC CTT GGG GAA TAT ACA CGC TGG CTT CGA TGA ATC CGT ACG GTA CTC GCC ATC mRNA protein 4. DNA TAA ACT CGG TAC CTA GCT TAG ATC TAA TTA CCC ATC mRNA protein 5. DNA CTA TTA CGA TAC TAG AGC GAA TAG AAA CTT ATC ATC mRNA I protein 6. DNA TAC CTT AGT TAT CCA TTG ACT CGA ATT GTG CGC TTG CTG ATC mRNA protein 7. DNA ACC CGA TAC CTC TCT TAT AGC ATT ACA AAC CTC CGA GCG mRNA - 50 words English (United States) Page 2 of 4 Focus 16 8. DNA TAC AGA CGG CAA CTC TGG GTG CTT TGT TCT CTT CTC AGT ATC mRNA protein H Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1-18. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). Focus 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. (mRNA/rRNA) is used to carry the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes. 7. (tRNA/rRNA) makes up the ribosome. Look in the book for this. 8. (DNA/RNA) uses uracil instead of thymine. 9. (RNA/amino) acids make up a protein. 11. Transcription takes place in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 12. tRNA is used in (translation/transcription). 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. Fill the Diagram In DNA mRNA tRNA Amino Acids Page 3 of 4 do A 55 50 words English (United States) G 04 OO O A DOC Focus T G Po 10 + 175% REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION THINKING QUESTIONS 1. DRAW A DNA NUCLEOTIDE & AN RNA NUCLEOTIDE. LABEL EACH OF THE 3 MAJOR PARTS. 2. WHAT ARE THE THREE MAJOR DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DNA & RNA? A) B) 3. WHAT IS THE POINT OF DNA REPLICATION? 4. WHEN & WHERE DOES REPLICATION OCCUR? 5. WHAT IS THE POINT OF TRANSCRIPTION? 6. WHAT ARE THREE NUCLEOTIDES TOGETHER CALLED ON MRNA? (IE: ACA) 7. THE MRNA CODONS CAN BE USED IN A CHART TO FIND: 8. WHAT MOLECULE CONTAINS AN ANTI-CODON? 9. WHY IS THIS (ANSWER TO #13) MOLECULE SO IMPORTANT? 10. TRANSLATION TAKES PLACE IN THE 11. WHAT IS THE POINT OF TRANSLATION? ON A 12. TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION TOGETHER IS THE PROCESS OF 12. TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION TOGETHER IS THE PROCESS OF GRAB A BOOK!!! TURN TO SECTION 11.3 13. WHAT IS ANY CHANGE IN THE DNA SEQUENCE CALLED? 14. ANY AGENT THAT CAUSES A MUTATION WOULD BE CALLED A 15. WHAT ARE SOME EXAMPLES OF THINGS THAT CAUSE MUTATIONS? 16. WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF DNA OR GENE MUTATIONS? GIVE EXAMPLES OF EACH. A. B. 17. WHICH ONE OF THE TWO ABOVE IS MORE DESTRUCTIVE? WHY? 18. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A GENE MUTATION & A CHROMOSOME MUTATION? 19. WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS? EXPLAIN EACH. INCLUDE A PICTURE USE PAGE 306. A. Focus 18. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A GENE MUTATION & A CHROMOSOME MUTATION? 19. WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF CHROMOSOME MUTATIONS? EXPLAIN EACH. INCLUDE A PICTURE USE PAGE 306. A. B. C. D. I 20. ARE MUTATIONS ALWAYS BAD? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER. Cansie
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 The first step in protein synthesis is called Transcription wherein the DNA code is converted into ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


