Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
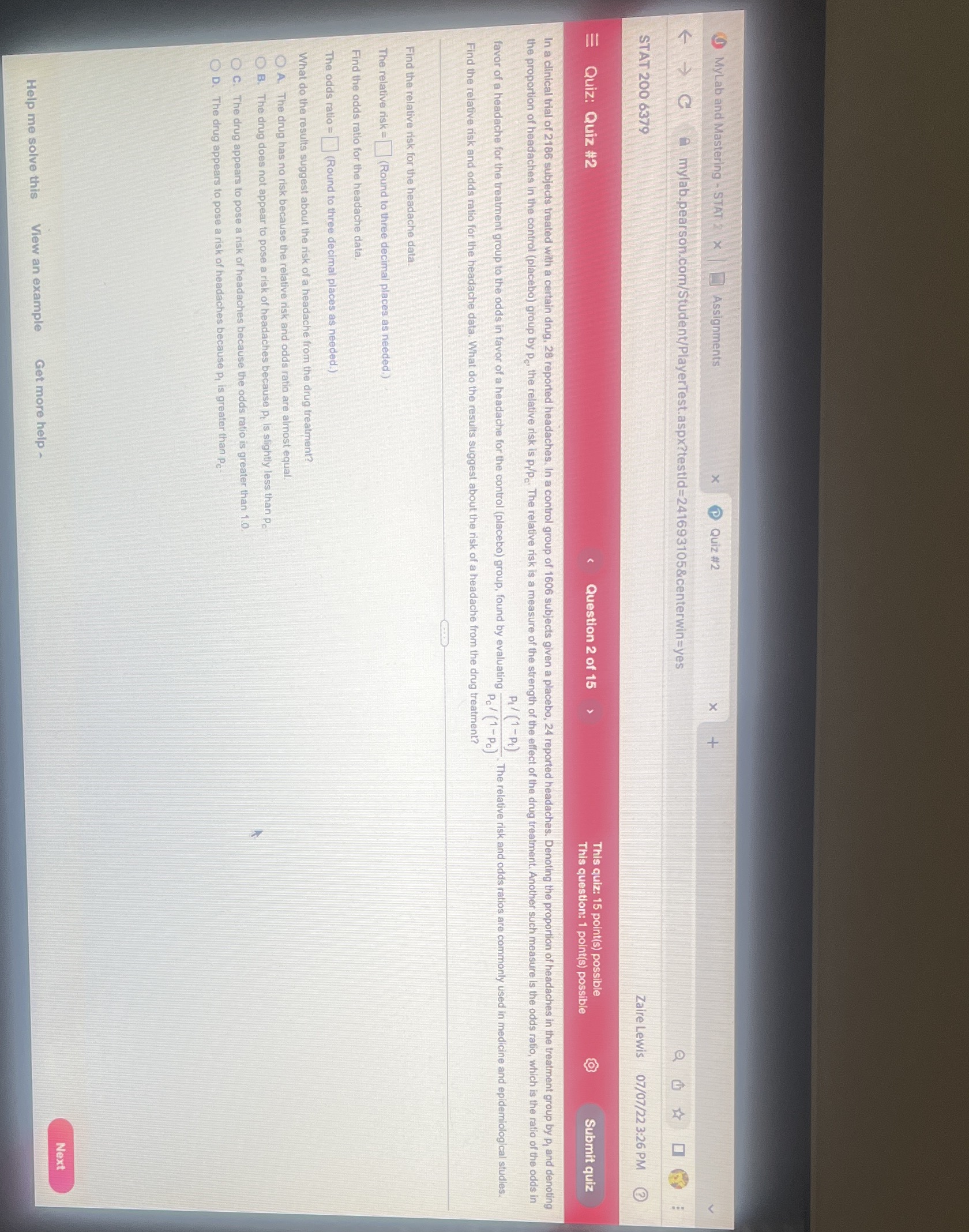
MyLab and Mastering - STAT 2 x Assignments x Quiz #2 X G mylab.pearson.com/Student/PlayerTest.aspx?testid=241693105¢erwin=yes STAT 200 6379 Zaire Lewis 07/07/22 3:26 PM = Quiz: Quiz
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


