Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need all only (k) Return on Decision: Since ROI under Alternative 34 Alternative means of using Idle Capacity - Evaluation and Profitability Analysis XYZ Ltd

need all only
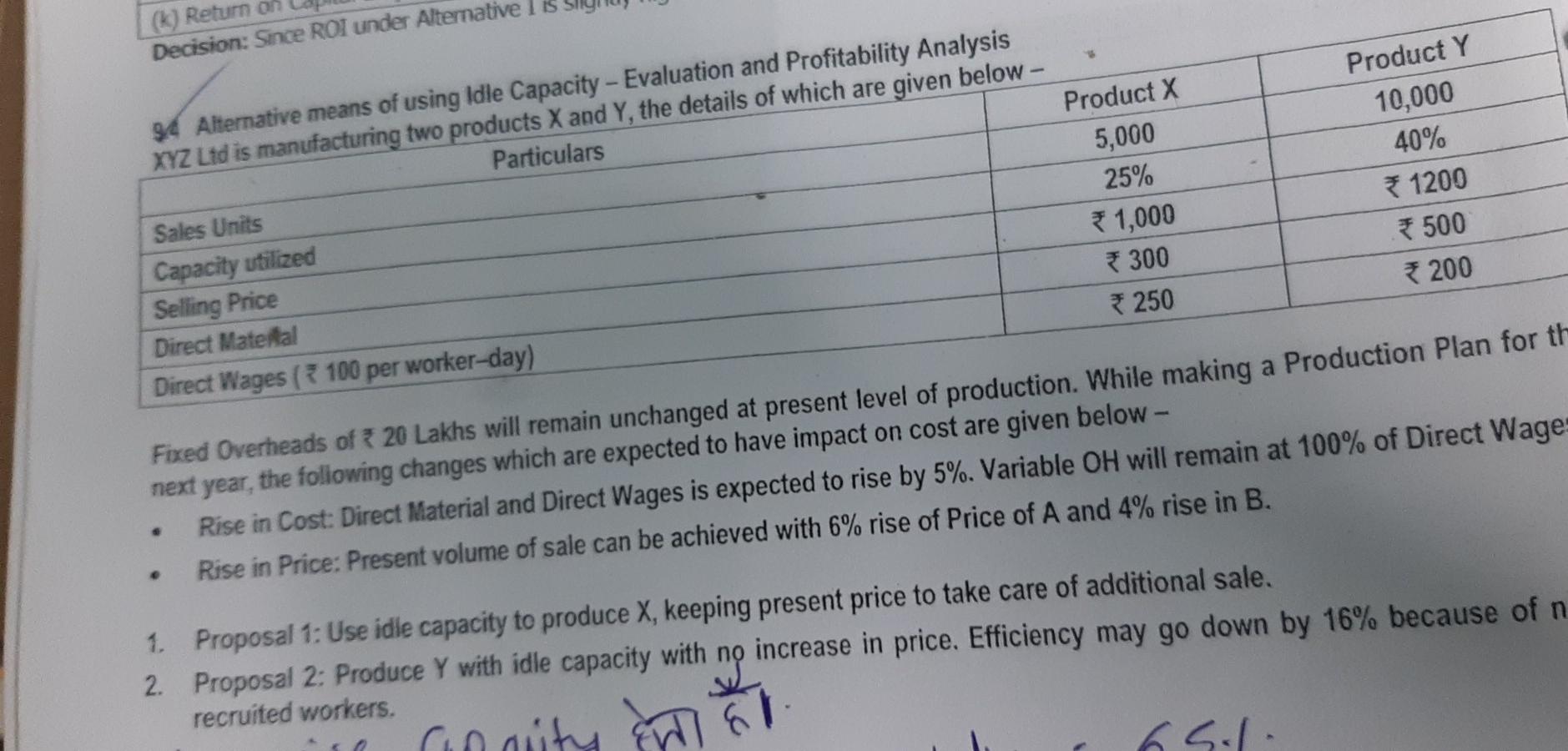
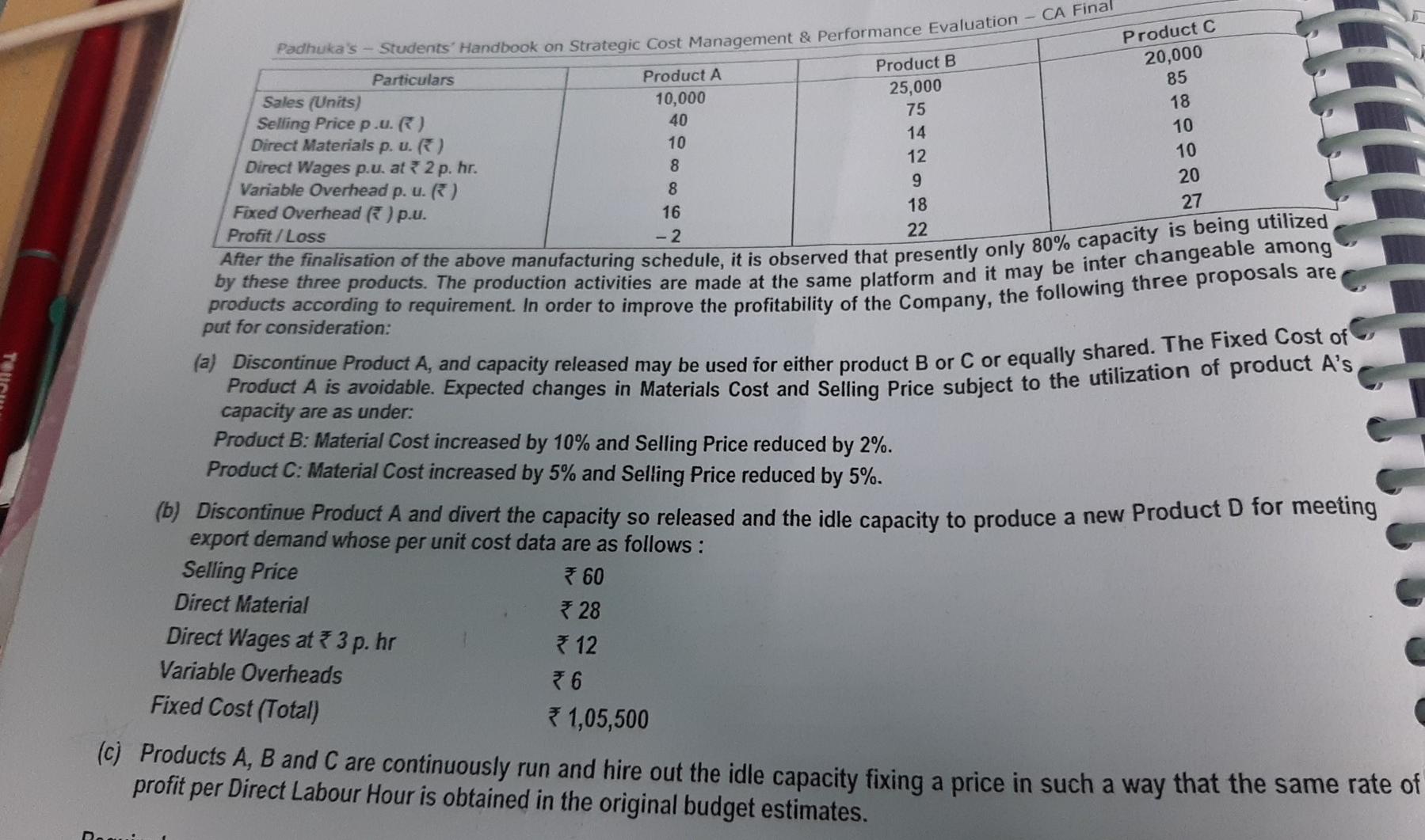
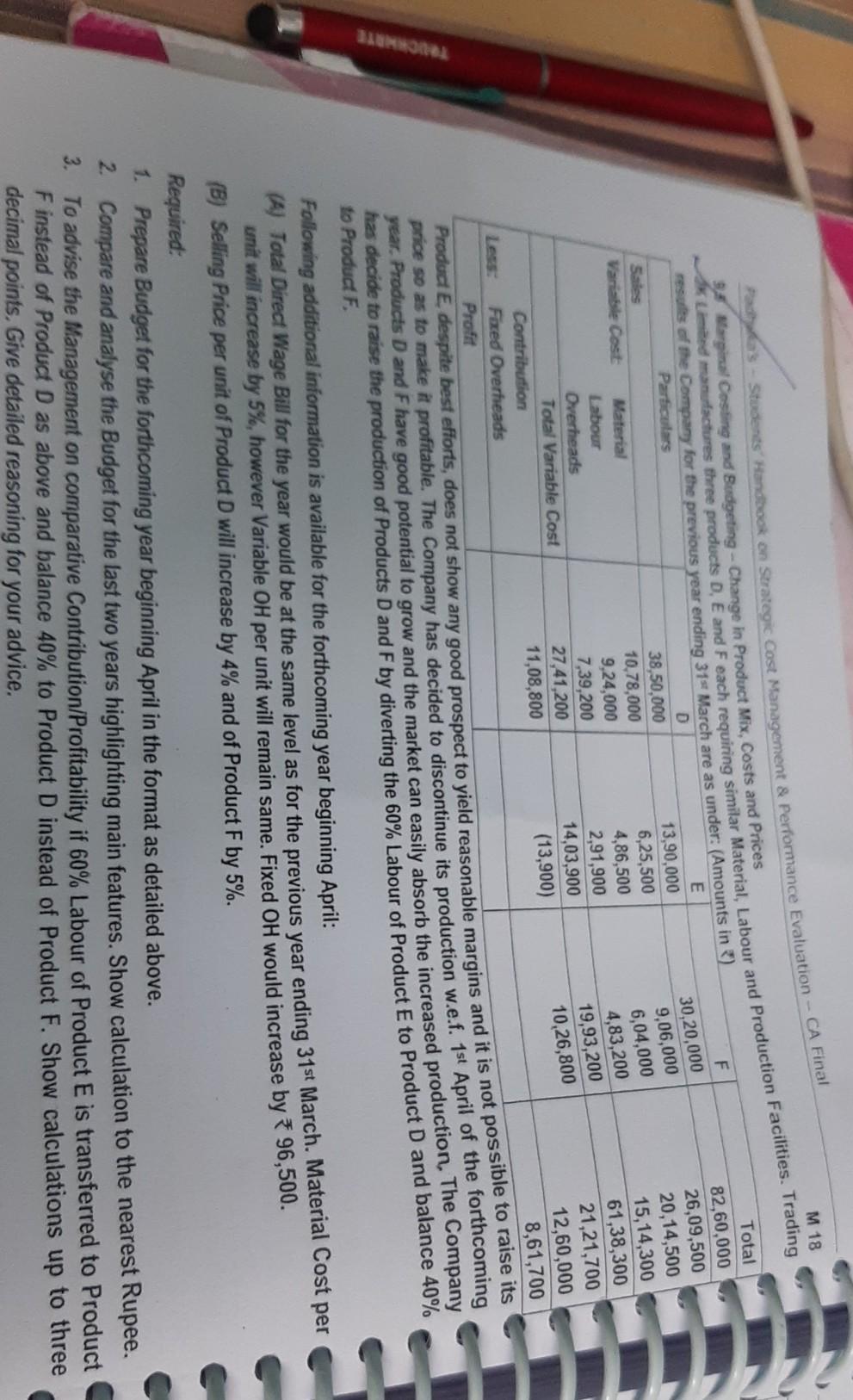
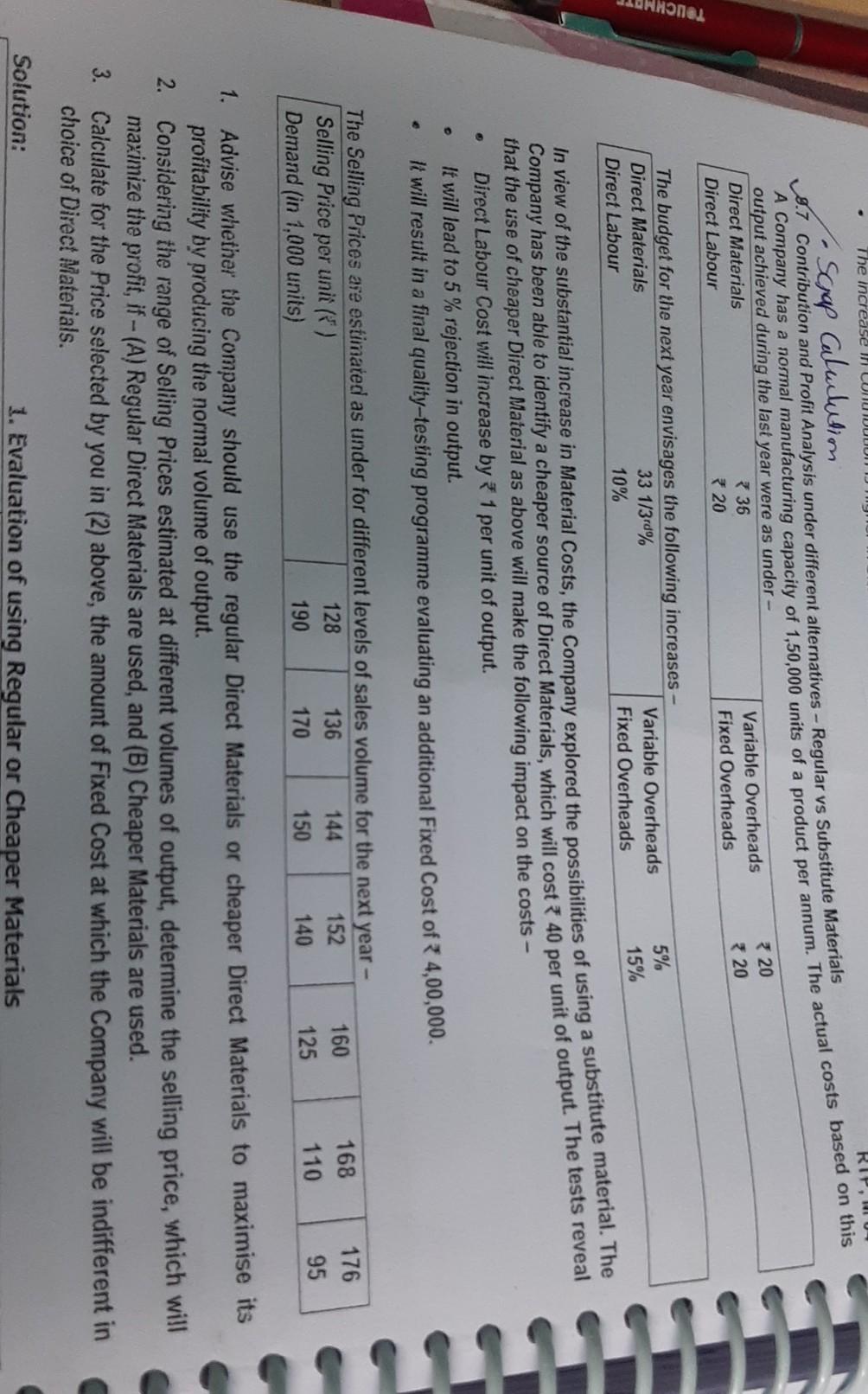
(k) Return on Decision: Since ROI under Alternative 34 Alternative means of using Idle Capacity - Evaluation and Profitability Analysis XYZ Ltd is manufacturing two products X and Y, the details of which are given below - Particulars Sales Units Capacity utilized Selling Price Direct Material Direct Wages (* 100 per worker-day) Product X 5,000 25% 1,000 300 *250 Product Y 10,000 40% 1200 * 500 200 Fixed Overheads of * 20 Lakhs will remain unchanged at present level of production. While making a Production Plan for th next year, the following changes which are expected to have impact on cost are given below - Rise in Cost: Direct Material and Direct Wages is expected to rise by 5%. Variable OH will remain at 100% of Direct Wage Rise in Price: Present volume of sale can be achieved with 6% rise of Price of A and 4% rise in B. 1. Proposal 1: Use idle capacity to produce X, keeping present price to take care of additional sale. 2. Proposal 2: Produce Y with idle capacity with no increase in price. Efficiency may go down by 16% because of n recruited workers. AL cindity & El 5 2. Revised Labour Costs of Y under Proposal 2 (after 16% efficiency fall) = 84% of Y = Materials 525 + Labour * 250 + VOH * 250 = 1,025 p.u. Contribution p.u. of Z under Proposal 3 = 11,350 - (400 +315 + 315)] = 3 320 p.u. Conclusion: Proposal 3 should be accepted, to maximize profits. 2.5 Evaluation of Alternative Proposals - Profitability Analysis E Ltd is engaged in the manufacturing of three products in its factory. The following budget estimates are pre 9.89 Product B 25,000 75 Padhuka's - Students' Handbook on Strategic Cost Management & Performance Evaluation - CA Final Particulars Product A Sales (Units) 10,000 Selling Price p.u.) 40 Direct Materials p. u.) 10 14 Direct Wages p.u. at 2 p.hr. 8 12 Variable Overhead p. u.) 8 9 Fixed Overhead ) p.u. 16 18 Profit/Loss -2 22 After the finalisation of the above manufacturing schedule, it is observed that presently only 80% capacity is being utilized products according to requirement. In order to improve the profitability of the Company, the following three proposals are by these three products. The production activities are made at the same platform and it may be inter changeable among put for consideration: (a) Discontinue Product A, and capacity released may be used for either product B or C or equally shared. The Fixed Cost of capacity are as under: Product C 20,000 85 18 10 10 20 27 Tour Product A is avoidable. Expected changes in Materials cost and Selling Price subject to the utilization of product A's Product B: Material Cost increased by 10% and Selling Price reduced by 2%. Product C: Material Cost increased by 5% and Selling Price reduced by 5%. (b) Discontinue Product A and divert the capacity so released and the idle capacity to produce a new Product D for meeting export demand whose per unit cost data are as follows: Selling Price 60 Direct Material 28 Direct Wages at 3 p.hr & 12 Variable Overheads 6 Fixed Cost (Total) 1,05,500 (c) Products A, B and C are continuously run and hire out the idle capacity fixing a price in such a way that the same rate of profit per Direct Labour Hour is obtained in the original budget estimates. M 18 Kuctures three products D, E and F each requiring similar Material, Labour and Production Facilities. Trading Students' Handbook on Strategic Case Management & Performance Evaluation - CA Final 3,5 Marginal Costing and Budgeting - Change in Product Mix, Costs and Prices Total results of the Company for the previous year ending 31s March are as under: (Amounts in ) Particulars D 82,60,000 Sales 38,50,000 13,90,000 26,09,500 Variable Cost Material 10,78,000 6,25,500 20,14,500 Labour 9,24,000 4,86,500 15,14,300 Overheads 7,39,200 2,91,900 61,38,300 Total Variable Cost 27,41,200 14,03,900 21,21,700 Contribution 11,08,800 (13,900) 12,60,000 Less Fixed Overheads 8,61,700 Profit Product E. despite best efforts, does not show any good prospect to yield reasonable margins and it is not possible to raise its Price so as to make it profitable. The Company has decided to discontinue its production w.e.f. 1st April of the forthcoming year Products D and Fhave good potential to grow and the market can easily absorb the increased production. The Company has decide to raise the production of Products D and F by diverting the 60% Labour of Product E to Product D and balance 40% to Product F F 30,20,000 9,06,000 6,04,000 4,83,200 19,93,200 10,26,800 TUERTE Following additional information is available for the forthcoming year beginning April: (A) Total Direct Wage Bill for the year would be at the same level as for the previous year ending 31st March. Material Cost per unit will increase by 5%, however Variable OH per unit will remain same. Fixed OH would increase by 96,500. (B) Selling Price per unit of Product D will increase by 4% and of Product F by 5%. Required: 1. Prepare Budget for the forthcoming year beginning April in the format as detailed above. 2. Compare and analyse the Budget for the last two years highlighting main features. Show calculation to the nearest Rupee. To advise the Management on comparative Contribution/Profitability if 60% Labour of Product E is transferred to Product Finstead of Product D as above and balance 40% to Product D instead of Product F. Show calculations up to three decimal points. Give detailed reasoning for your advice. 3. The increase I LUNU RIP, WI Schap Calulution 9.7 Contribution and Profit Analysis under different alternatives - Regular vs Substitute Materials A Company has a normal manufacturing capacity of 1,50,000 units of a product per annum. The actual costs based on this output achieved during the last year were as under - Direct Materials * 36 Direct Labour 20 Variable Overheads Fixed Overheads 320 * 20 ARHInel The budget for the next year envisages the following increases Direct Materials 33 1/3.8% Direct Labour 10% Variable Overheads Fixed Overheads 5% 15% In view of the substantial increase in Material Costs, the Company explored the possibilities of using a substitute material. The Company has been able to identify a cheaper source of Direct Materials, which will cost 40 per unit of output. The tests reveal that the use of cheaper Direct Material as above will make the following impact on the costs - Direct Labour Cost will increase by 1 per unit of output. It will lead to 5% rejection in output. It will result in a final quality-testing programme evaluating an additional Fixed Cost of 4,00,000. The Selling Prices are estimated as under for different levels of sales volume for the next year - Selling Price per unit() 128 136 144 152 Demand (in 1,000 units) 190 170 150 140 160 125 168 110 176 95 1. Advise whether the Company should use the regular Direct Materials or cheaper Direct Materials to maximise its profitability by producing the normal volume of output. 2. Considering the range of Selling Prices estimated at different volumes of output, determine the selling price, which will maximize the profit, if -(A) Regular Direct Materials are used, and (B) Cheaper Materials are used. 3. Calculate for the Price selected by you in (2) above, the amount of Fixed Cost at which the Company will be indifferent in choice of Direct Materials. Solution: 1. Evaluation of using Regular or Cheaper MaterialsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


