Need help correcting my mistakes, thanks in advance.
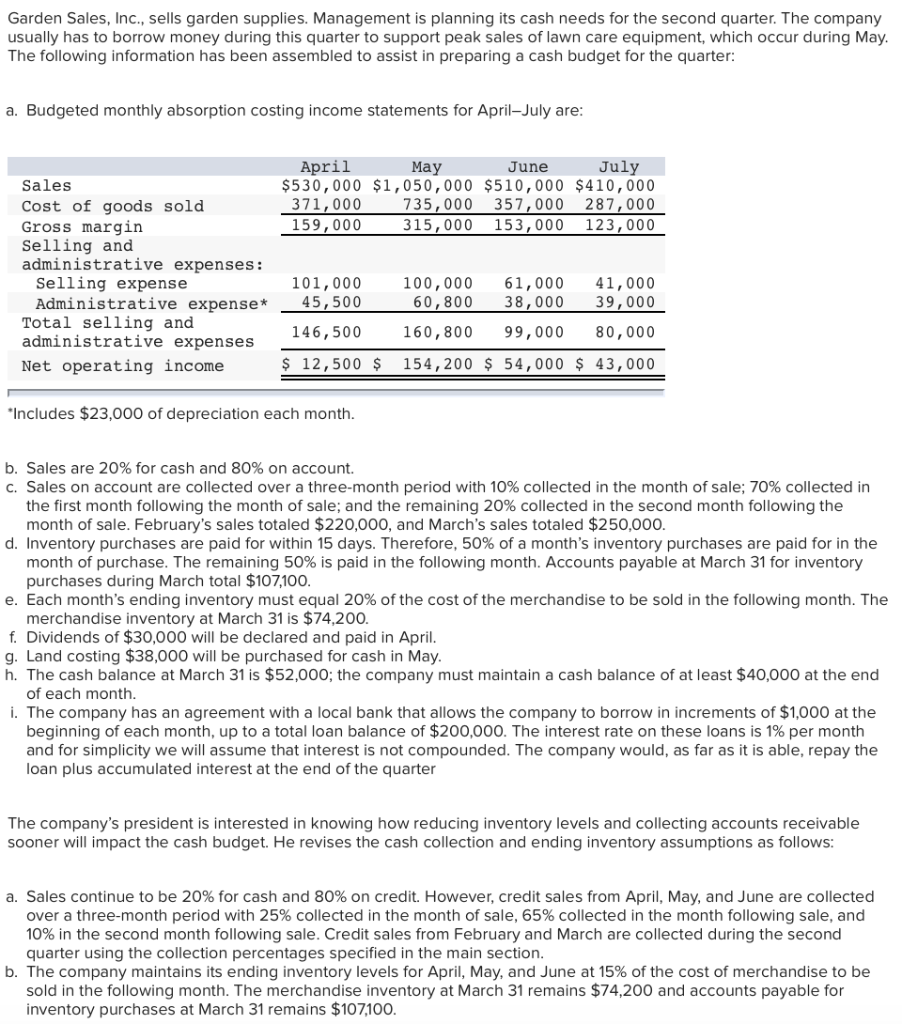
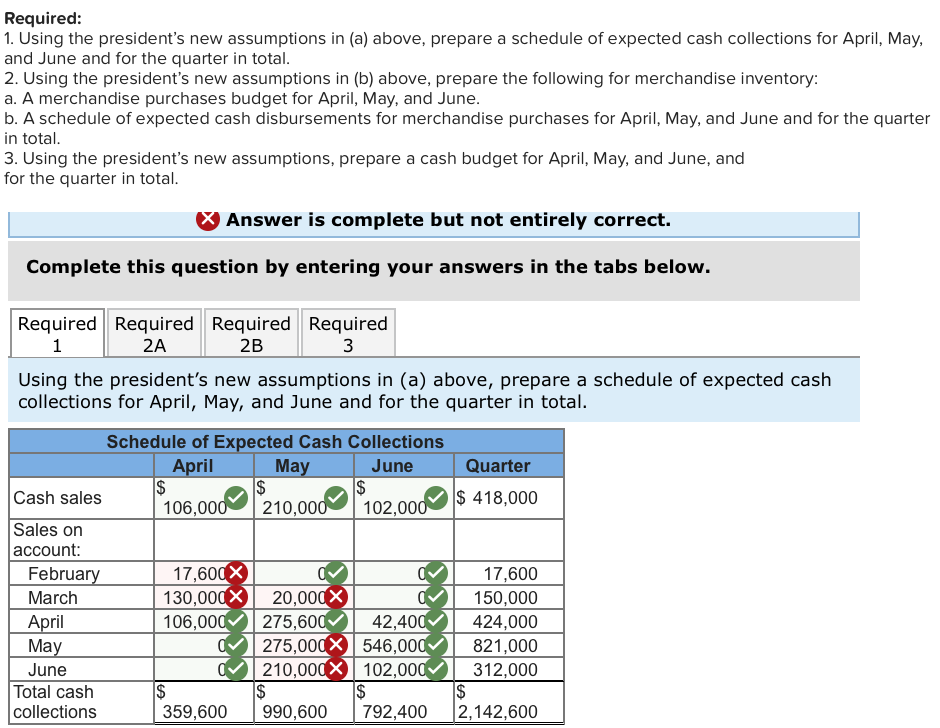
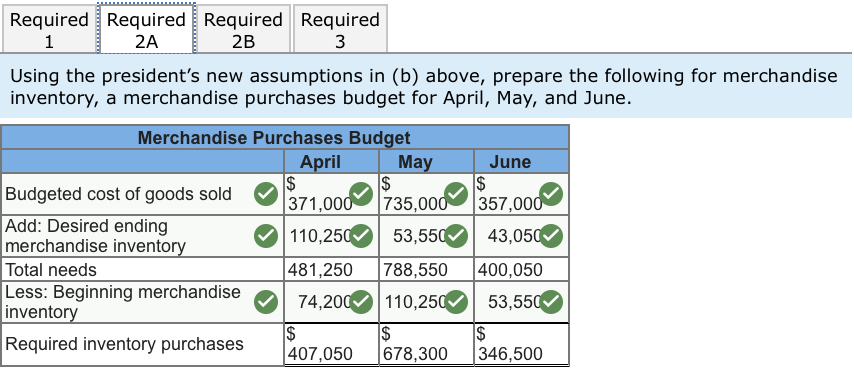
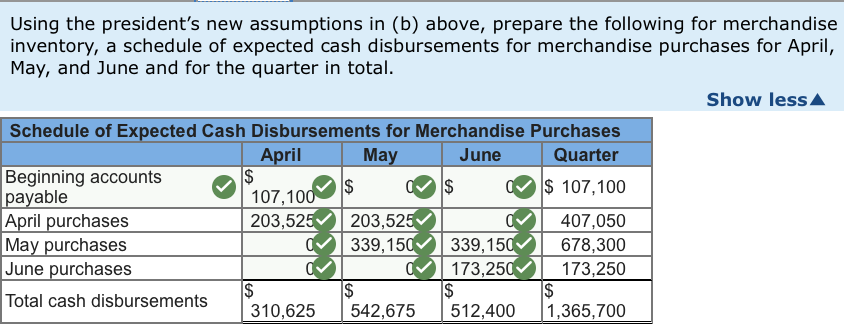
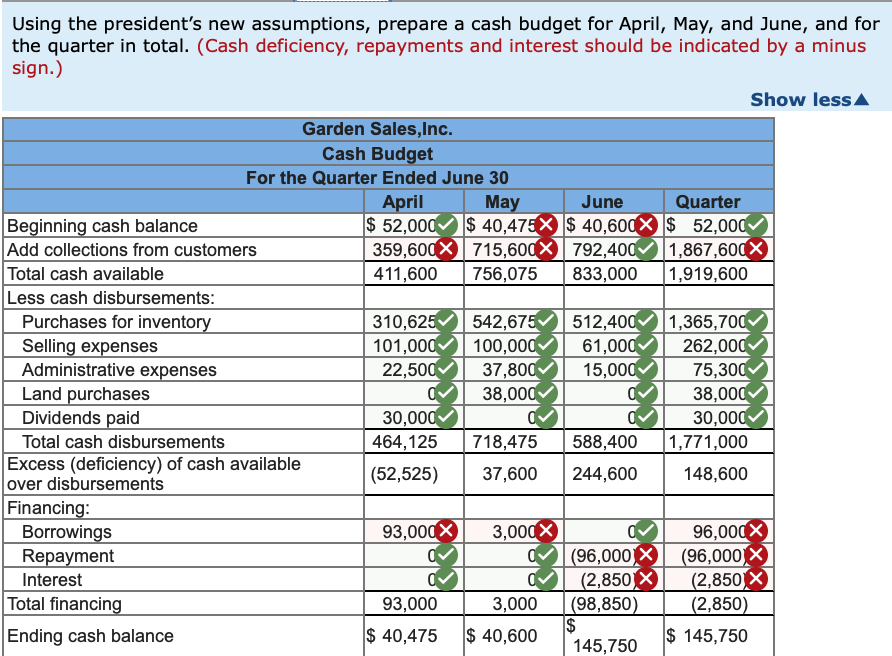
Garden Sales, Inc., sells garden supplies. Management is planning its cash needs for the second quarter. The company usually has to borrow money during this quarter to support peak sales of lawn care equipment, which occur during May. The following information has been assembled to assist in preparing a cash budget for the quarter: a. Budgeted monthly absorption costing income statements for April-July are: April May June July $530,000 $1,050,000 $510,000 $410,000 371,000 735,000 357,000 287,000 159,000 315,000 153,000 123,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: Selling expense Administrative expense* Total selling and administrative expenses Net operating income 101,000 45,500 146,500 $ 12,500 $ 100,000 61,000 41,000 60,800 38,000 39,000 160,800 99,000 80,000 154,200 $ 54,000 $ 43,000 Includes $23,000 of depreciation each month. b. Sales are 20% for cash and 80% on account. C. Sales on account are collected over a three-month period with 10% collected in the month of sale; 70% collected in the first month following the month of sale; and the remaining 20% collected in the second month following the month of sale. February's sales totaled $220,000, and March's sales totaled $250,000 d. Inventory purchases are paid for within 15 days. Therefore, 50% of a month's inventory purchases are paid for in the month of purchase. The remaining 50% is paid in the following month. Accounts payable at March 31 for inventory purchases during March total $107,100. e. Each month's ending inventory must equal 20% of the cost of the merchandise to be sold in the following month. The merchandise inventory at March 31 is $74,200. f. Dividends of $30,000 will be declared and paid in April. g. Land costing $38,000 will be purchased for cash in May. h. The cash balance at March 31 is $52,000; the company must maintain a cash balance of at least $40,000 at the end of each month. i. The company has an agreement with a local bank that allows the company to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $200,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month and for simplicity we will assume that interest is not compounded. The company would, as far as it is able, repay the loan plus accumulated interest at the end of the quarter The company's president is interested in knowing how reducing inventory levels and collecting accounts receivable sooner will impact the cash budget. He revises the cash collection and ending inventory assumptions as follows: a. Sales continue to be 20% for cash and 80% on credit. However, credit sales from April, May, and June are collected over a three-month period with 25% collected in the month of sale, 65% collected in the month following sale, and 10% in the second month following sale. Credit sales from February and March are collected during the second quarter using the collection percentages specified in the main section. b. The company maintains its ending inventory levels for April, May, and June at 15% of the cost of merchandise to be sold in the following month. The merchandise inventory at March 31 remains $74,200 and accounts payable for inventory purchases at March 31 remains $107,100. Required: 1. Using the president's new assumptions in (a) above, prepare a schedule of expected cash collections for April, May, and June and for the quarter in total. 2. Using the president's new assumptions in (b) above, prepare the following for merchandise inventory: a. A merchandise purchases budget for April, May, and June. b. A schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases for April, May, and June and for the quarter in total. 3. Using the president's new assumptions, prepare a cash budget for April, May, and June, and for the quarter in total. X Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required Required Required Required 2A 2B Using the president's new assumptions in (a) above, prepare a schedule of expected cash collections for April, May, and June and for the quarter in total. Quarter $ 418,000 Schedule of Expected Cash Collections April May June Cash sales 106.000 210.000 102.000 Sales on account: February 17, 600x 1 March 130,000 X 20,000 X April 106,000275,600 42,400 May 275,000 546,000 June 210,000 X 102,000 Total cash collections 359,600 990,600 792,400 7600 150,000 424,000 821,000 312,000 2,142,600 Required Required Required Required 2A 2B | 3 Using the president's new assumptions in (b) above, prepare the following for merchandise inventory, a merchandise purchases budget for April, May, and June. June $ Merchandise Purchases Budget April May Budgeted cost of goods sold wold $ $ 371.000 735,000 Add: Desired ending 110,25053,550 merchandise inventory Total needs 481,250 788,550 Less: Beginning merchandisel 74.200110,250 inventory Required inventory purchases 407,050 678.300 357.000 43,050 400,050 53,550 346,500 Using the president's new assumptions in (b) above, prepare the following for merchandise inventory, a schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases for April, May, and June and for the quarter in total. Show less Schedule of Expected Cash Disbursements for Merchandise Purchases April May June Quarter Beginning accounts $ $ $ 107,100 payable April purchases 203,525203,5251 4 07,050 May purchases 339,150339,150 678,300 June purchases 173,250 173,250 IS Total cash disbursements | 310,625 542,675 512,400 1,365,700 Using the president's new assumptions, prepare a cash budget for April, May, and June, and for the quarter in total. (Cash deficiency, repayments and interest should be indicated by a minus sign.) Show less Garden Sales, Inc. Cash Budget For the Quarter Ended June 30 April May June Quarter Beginning cash balance $ 52,000 $ 40,475 X $ 40,600 X $ 52,000 Add collections from customers 359,600X715,600X792,4001,867,600X Total cash available 411,600 756,075 833,000 1,919,600 Less cash disbursements: Purchases for inventory 310,625 542,675512,4001,365,700 Selling expenses 101,000 100,000 61,000 262,000 | Administrative expenses 22,500 37,800 15,000 75,300 Land purchases Q 38,000 38,000 Dividends paid 30,000 VI VI 30,000 Total cash disbursements 464,125 718,475 588,400 1,771,000 Excess (deficiency) of cash available (52,525) 37,600 | 244,600 148,600 over disbursements Financing: Borrowings 93,000X 3,000 W 96,000x Repayment (96,000 (96,000 X Interest (2,850 X (2,850 X Total financing 93,000 3,000 (98,850) | (2,850) Ending cash balance $ 40,475 $ 40,600 145.750 $ 145,750











