Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need help plz with accounting for these 5 questions Construct and Interpret a Product Profitabaty Report, Allocating Seling and Administrative Expentes Naper Inc. manufactures power
need help plz with accounting for these 5 questions 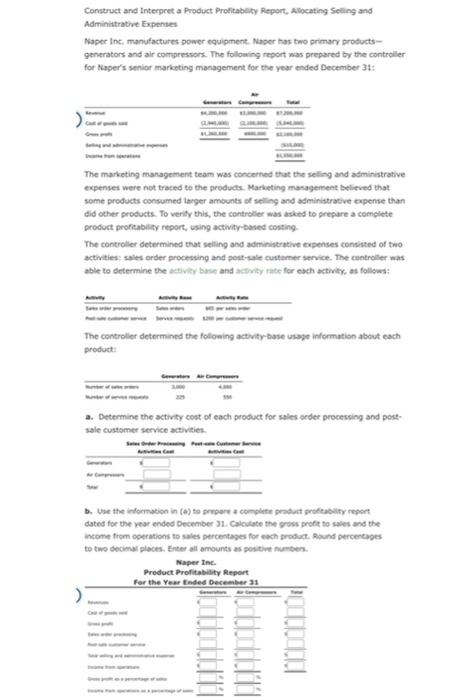

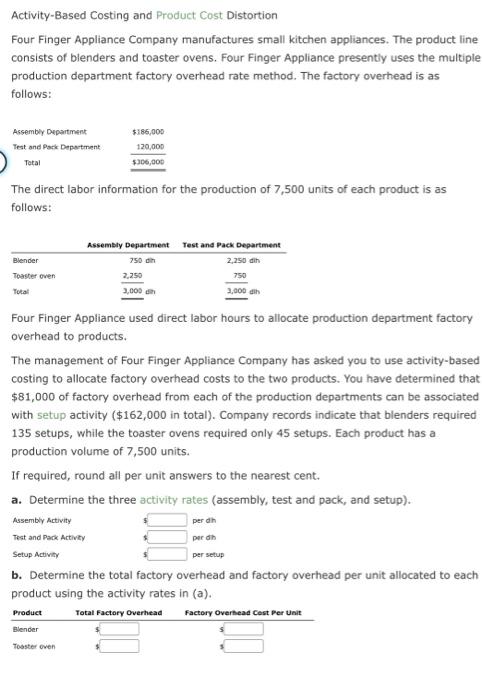
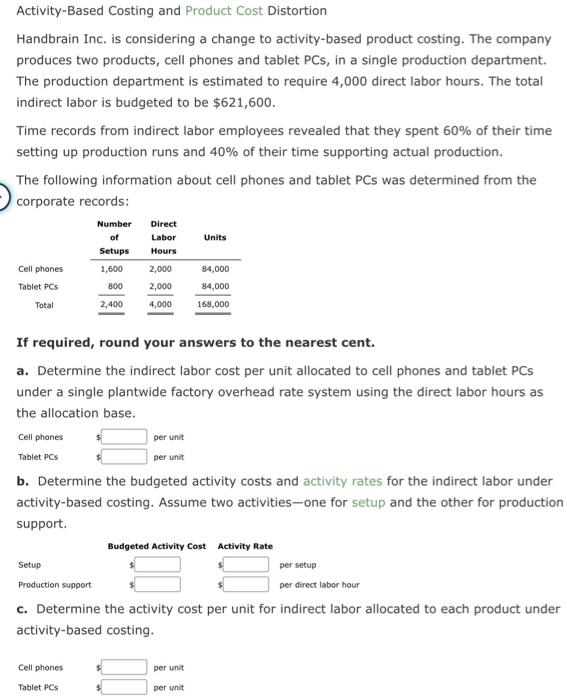
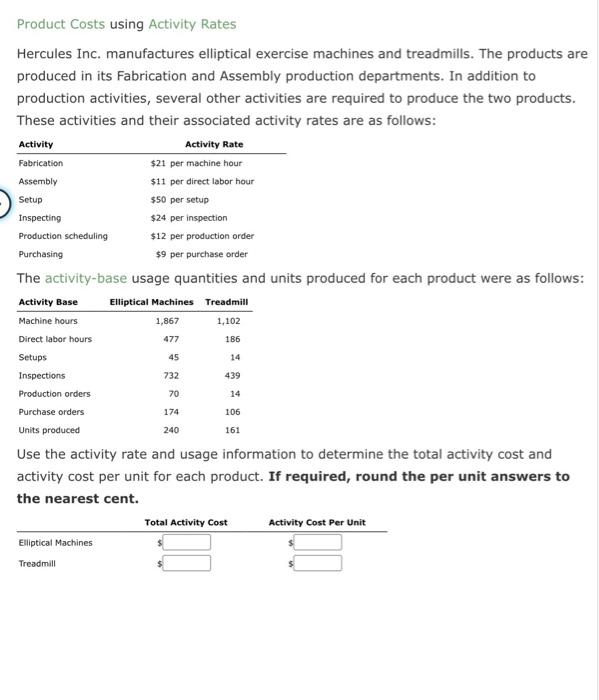
Construct and Interpret a Product Profitabaty Report, Allocating Seling and Administrative Expentes Naper Inc. manufactures power equipment. Naser has two primary productsgenerators and air compressors. The following report was prepared by the controller for Aaper's senior marketing management for the year ended December 31 : The marketing management team was concerned that the selling and asministrative expenues were not traced to the products. Marketing masagement believed that some products consumed targer amounts of seliling and administrative expense than did outer products. To verify this, the centroller was askied to prepare a complete product profeablisy report, wing activity-based costing. The controller determined that selling and administrative expenses consisted of two activities: sales order processing and post-sale custemer service. The centroller was able to determine the activicy base and activiky rate for each activity, as follews: The controller determined the following activity base usage information about each product: a. Determine the activity cost of each product foe sales seder processing and postsale customer service activies. b. Whe the informacion in (a) te prupers a complete praduct profeablity repont dated for the year ended December 31 . Calculate the gross profit to sales and the income from ogerations ts sales percentages for each probuct. Round perceneages to twe decimal placts. Enter all amounts as positive numben. Product Costs and Product Profitability Reports, using a Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate Isaac Engines Inc. produces three products-pistons, valves, and cams-for the heavy equipment industry. Isaac Engines has a very simple production process and product line and uses a single plantwide factory overhead rate to allocate overhead to the three products. The factory overhead rate is based on direct labor hours. Information about the three products for 20r2 is as follows: The estimated direct labor rate is $20 per direct labor hour. Beginning and ending inventories are negligible and are, thus, assumed to be zero. The budgeted factory overhead for Isaac Engines is $235,200. If required, round all per unit answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the plantwide factory overhead rate. 4 per dih b. Determine the factory overhead and direct labor cost per unit for each product. c. Use the information provided to construct a budgeted gross profit report by product line for the year ended December 31, 20Y2. Include the gross profit as a percent of sales in the last line of your report, rounded to one decimal place. Activity-Based Costing and Product Cost Distortion Four Finger Appliance Company manufactures small kitchen appliances. The product line consists of blenders and toaster ovens. Four Finger Appliance presently uses the multiple production department factory overhead rate method. The factory overhead is as follows: The direct labor information for the production of 7,500 units of each product is as follows: Four Finger Appliance used direct labor hours to allocate production department factory overhead to products. The management of Four Finger Appliance Company has asked you to use activity-based costing to allocate factory overhead costs to the two products. You have determined that $81,000 of factory overhead from each of the production departments can be associated with setup activity ( $162,000 in total). Company records indicate that blenders required 135 setups, while the toaster ovens required only 45 setups. Each product has a production volume of 7,500 units. If required, round all per unit answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the three activity rates (assembly, test and pack, and setup). b. Determine the total factory overhead and factory overhead per unit allocated to each product using the activity rates in (a). Activity-Based Costing and Product Cost Distortion Handbrain Inc. is considering a change to activity-based product costing. The company produces two products, cell phones and tablet PCs, in a single production department. The production department is estimated to require 4,000 direct labor hours. The total indirect labor is budgeted to be $621,600. Time records from indirect labor employees revealed that they spent 60% of their time setting up production runs and 40% of their time supporting actual production. The following information about cell phones and tablet PCs was determined from the corporate records: If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the indirect labor cost per unit allocated to cell phones and tablet PCs under a single plantwide factory overhead rate system using the direct labor hours as the allocation base. CellphonesTabletPCs$$perunitperunit b. Determine the budgeted activity costs and activity rates for the indirect labor under activity-based costing. Assume two activities-one for setup and the other for production support. c. Determine the activity cost per unit for indirect labor allocated to each product under activity-based costing. Product Costs using Activity Rates Hercules Inc. manufactures elliptical exercise machines and treadmills. The products are produced in its Fabrication and Assembly production departments. In addition to production activities, several other activities are required to produce the two products. These activities and their associated activity rates are as follows: The activity-base usage quantities and units produced for each product were as follows: Use the activity rate and usage information to determine the total activity cost and activity cost per unit for each product. If required, round the per unit answers to the nearest cent. Construct and Interpret a Product Profitabaty Report, Allocating Seling and Administrative Expentes Naper Inc. manufactures power equipment. Naser has two primary productsgenerators and air compressors. The following report was prepared by the controller for Aaper's senior marketing management for the year ended December 31 : The marketing management team was concerned that the selling and asministrative expenues were not traced to the products. Marketing masagement believed that some products consumed targer amounts of seliling and administrative expense than did outer products. To verify this, the centroller was askied to prepare a complete product profeablisy report, wing activity-based costing. The controller determined that selling and administrative expenses consisted of two activities: sales order processing and post-sale custemer service. The centroller was able to determine the activicy base and activiky rate for each activity, as follews: The controller determined the following activity base usage information about each product: a. Determine the activity cost of each product foe sales seder processing and postsale customer service activies. b. Whe the informacion in (a) te prupers a complete praduct profeablity repont dated for the year ended December 31 . Calculate the gross profit to sales and the income from ogerations ts sales percentages for each probuct. Round perceneages to twe decimal placts. Enter all amounts as positive numben. Product Costs and Product Profitability Reports, using a Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate Isaac Engines Inc. produces three products-pistons, valves, and cams-for the heavy equipment industry. Isaac Engines has a very simple production process and product line and uses a single plantwide factory overhead rate to allocate overhead to the three products. The factory overhead rate is based on direct labor hours. Information about the three products for 20r2 is as follows: The estimated direct labor rate is $20 per direct labor hour. Beginning and ending inventories are negligible and are, thus, assumed to be zero. The budgeted factory overhead for Isaac Engines is $235,200. If required, round all per unit answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the plantwide factory overhead rate. 4 per dih b. Determine the factory overhead and direct labor cost per unit for each product. c. Use the information provided to construct a budgeted gross profit report by product line for the year ended December 31, 20Y2. Include the gross profit as a percent of sales in the last line of your report, rounded to one decimal place. Activity-Based Costing and Product Cost Distortion Four Finger Appliance Company manufactures small kitchen appliances. The product line consists of blenders and toaster ovens. Four Finger Appliance presently uses the multiple production department factory overhead rate method. The factory overhead is as follows: The direct labor information for the production of 7,500 units of each product is as follows: Four Finger Appliance used direct labor hours to allocate production department factory overhead to products. The management of Four Finger Appliance Company has asked you to use activity-based costing to allocate factory overhead costs to the two products. You have determined that $81,000 of factory overhead from each of the production departments can be associated with setup activity ( $162,000 in total). Company records indicate that blenders required 135 setups, while the toaster ovens required only 45 setups. Each product has a production volume of 7,500 units. If required, round all per unit answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the three activity rates (assembly, test and pack, and setup). b. Determine the total factory overhead and factory overhead per unit allocated to each product using the activity rates in (a). Activity-Based Costing and Product Cost Distortion Handbrain Inc. is considering a change to activity-based product costing. The company produces two products, cell phones and tablet PCs, in a single production department. The production department is estimated to require 4,000 direct labor hours. The total indirect labor is budgeted to be $621,600. Time records from indirect labor employees revealed that they spent 60% of their time setting up production runs and 40% of their time supporting actual production. The following information about cell phones and tablet PCs was determined from the corporate records: If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the indirect labor cost per unit allocated to cell phones and tablet PCs under a single plantwide factory overhead rate system using the direct labor hours as the allocation base. CellphonesTabletPCs$$perunitperunit b. Determine the budgeted activity costs and activity rates for the indirect labor under activity-based costing. Assume two activities-one for setup and the other for production support. c. Determine the activity cost per unit for indirect labor allocated to each product under activity-based costing. Product Costs using Activity Rates Hercules Inc. manufactures elliptical exercise machines and treadmills. The products are produced in its Fabrication and Assembly production departments. In addition to production activities, several other activities are required to produce the two products. These activities and their associated activity rates are as follows: The activity-base usage quantities and units produced for each product were as follows: Use the activity rate and usage information to determine the total activity cost and activity cost per unit for each product. If required, round the per unit answers to the nearest cent 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


