Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
need help solving 6 a) b) c) d) the answer for b) should come out to 395,328 use info below if needed to solve here
need help solving 6 a) b) c) d) 
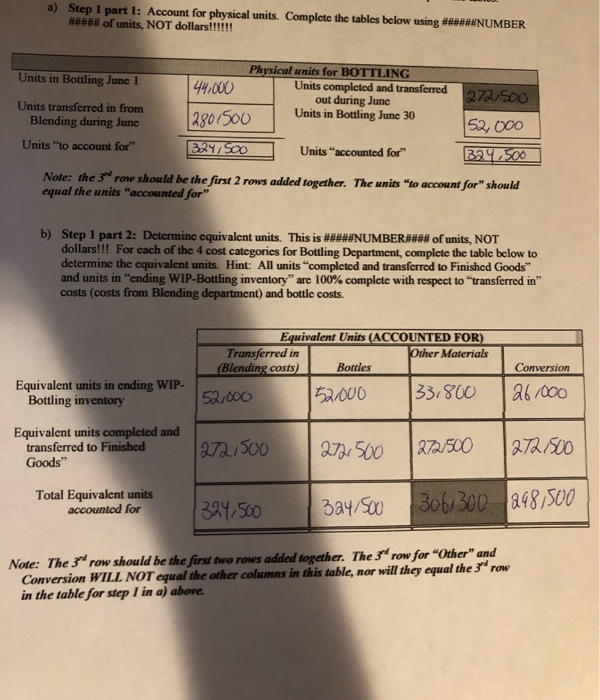
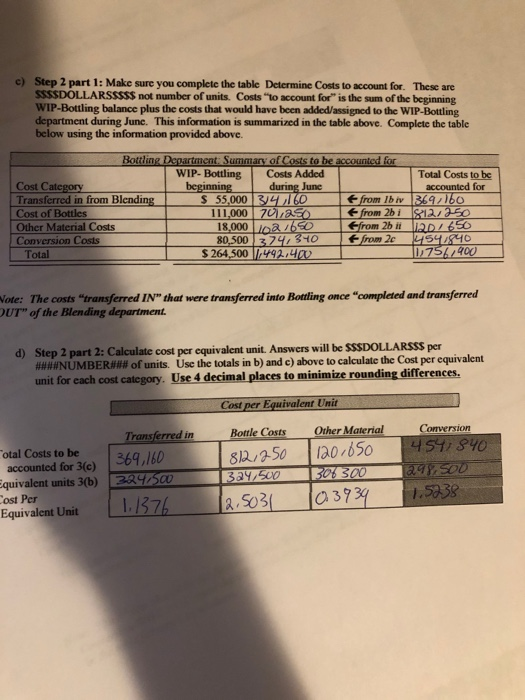
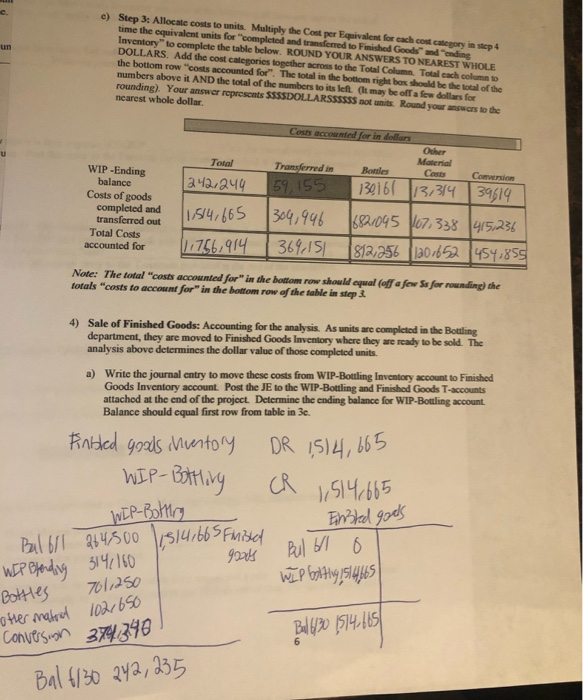
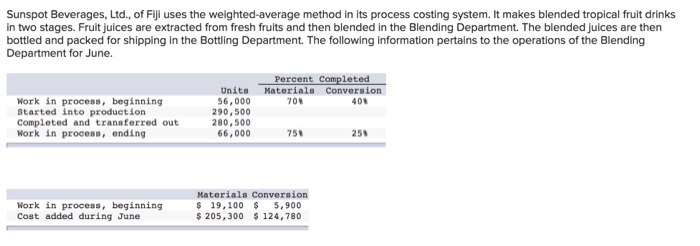
the answer for b) should come out to 395,328 


use info below if needed to solve




here are more clear photos below 
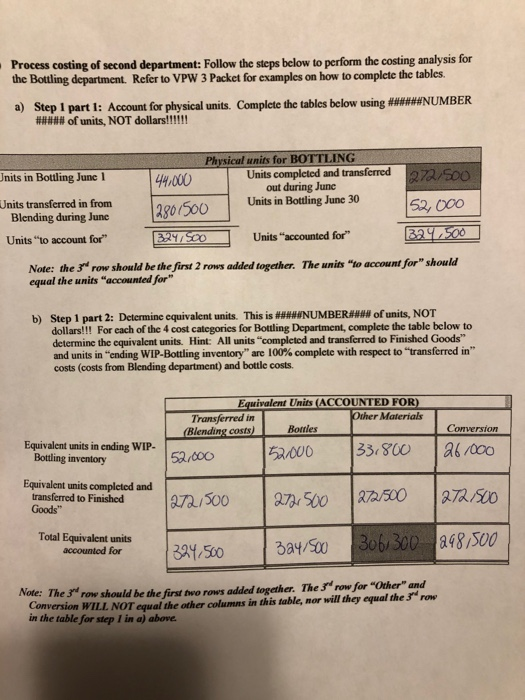
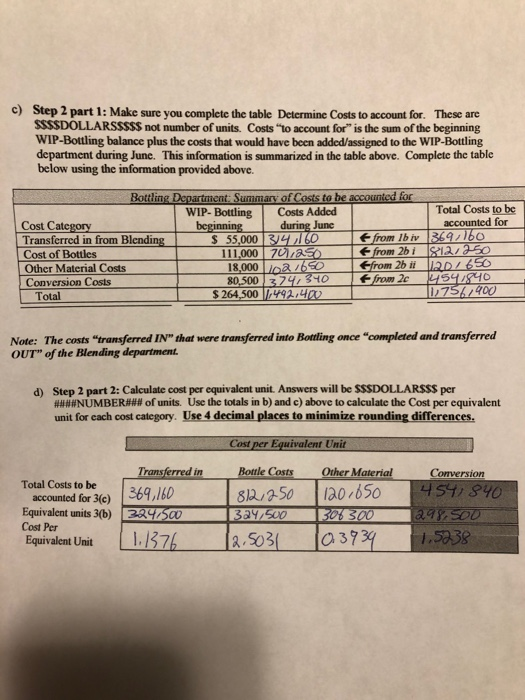
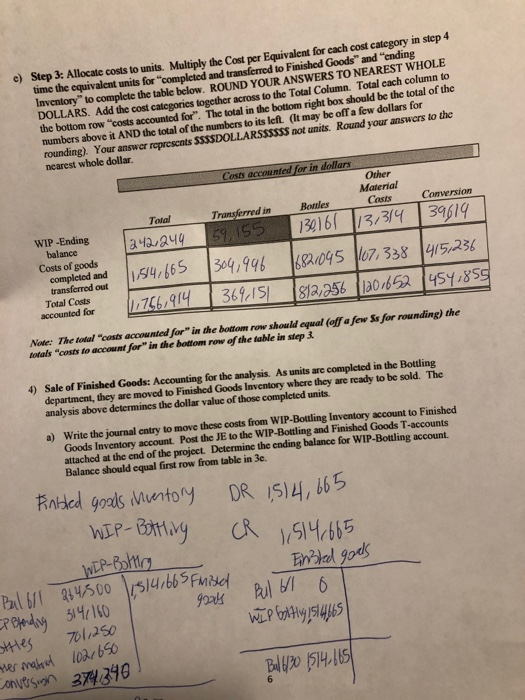
b) Assume the Finished Goods Inventory was zero at the beginning of June and zero at the end of Junc. How many units did they sell during June? 272,500 c) If Sunspot Beverages, Ltd. sold cach unit for $12.00 what would their sales revenue be? 3,2707000_Write the journal entry to record the sales revenue for June d) How much is their expense (COGS)? 1,514,665 Write the journal entry to record the COGS for June. Post this entry to the Finished Goods account attached at the end of the project. 5) Raw Material: The company uses no indirect material and the Raw Material Inventory began the month with $120,000 and ending the month with $98,000. How much raw material inventory did the company purchase during June? 284,450 Write the summary journal entry to record the purchase. Post the journal entry to the T-account provided at the end of the attachment 6) Financial Statement Analysis: Use Chapter 14 concepts for this requirement For Sunspot Beverages; a) What is the value of Inventory they would record on their Balance Sheet at the beginning of June? At the end of June? Remember, Inventory on the balance sheet includes ALL inventory accounts. b) What is their "average" inventory for June? c) Using the formulas provided in Chapter 14 of your text (Pg. 678), calculate the following: Gross Margin percentage: Inventory turnover Average sales period for June. Note: Remember you are calculating ratios for a month not a year. You will need to annualize your turnover (multiply by 12 months) and/or use 30 days rather than 365 days for your sales period. d) Assume the industry leader has an inventory Turnover of 55 and average sales period of 7 days. How does Sunspot Beverages compare to the industry leader? Your answer and comment should be 20 to 50 words. a) Step 1 part 1: Account for physical units. Complete the tables below using #****#NUMBER ##### of units, NOT dollars!!!!!! Physical units for BOTTLING Units in Bottling June 1 44.000 Units completed and transferred out during June 272.500 Units transferred in from Blending during June Units in Bottling June 30 12801500 52,000 Units "to account for" 324/ 500 Units "accounted for B2.500 Note: the 3 row should be the first 2 rows added together. The units "to account for" should equal the units "accounted for" b) Step 1 part 2: Determine equivalent units. This is #####NUMBER#**# of units, NOT dollars!!! For each of the 4 cost categories for Bottling Department, complete the table below to determine the equivalent units. Hint: All units "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and units in ending WIP-Bottling inventory" are 100% complete with respect to transferred in" costs (costs from Blending department) and bottle costs. Equivalent Units (ACCOUNTED FOR) Transferred in Other Materials (Blending costs) Bottles 52.000 52.000 33.800 Conversion 26/000 Equivalent units in ending WIP- Bottling inventory Equivalent units completed and transferred to Finished Goods" 272/500 272,500 272/500 272500 Total Equivalent units accounted for 1324,500 3a4/500 306, 300 298,500 Note: The 3d row should be the first two rows added together. The 3rd row for "Other" and Conversion WILL NOT equal the other columns in this table, nor will they equal the 3 row in the table for step 1 in a) above. c) Step 2 part 1: Make sure you complete the table Determine Costs to account for. These are SSSSDOLLARSSSSS not number of units. Costs "to account for" is the sum of the beginning WIP-Bottling balance plus the costs that would have been added/assigned to the WIP-Bottling department during June. This information is summarized in the table above. Complete the table below using the information provided above. Bottling Department: Summary of Costs to be accounted for WIP- Bottling Costs Added Total Costs to be Cost Category beginning during June accounted for Transferred in from Blending $ 55,000 34 160 from lb iv 369,160 Cost of Bottles 111,000 70,00 from 2bi 812/250 Other Material Costs 18,000 102/650 &from 2bit 12D/ 650 Conversion Costs 80,500 3740340 from 2c 14541840 Total $ 264,500 1,492.40 10756.400 Wote: The costs "transferred IN" that were transferred into Bottling once "completed and transferred OUT" of the Blending department. d) Step 2 part 2: Calculate cost per equivalent unit. Answers will be SSSDOLLARSSS per ###WNUMBER### of units. Use the totals in b) and c) above to calculate the Cost per equivalent unit for each cost category. Use 4 decimal places to minimize rounding differences. Cost per Equivalent Unit Other Material Conversion 4547840 120.650 Total Costs to be accounted for 3(e) Equivalent units 3(b) Cost Per Equivalent Unit Transferred in 369,160 3247500 1.1376 Bottle Costs 812,250 324,500 12.5031 30% 300 0,3939 1.5238 e. c) Step 3: Allocate costs to units. Multiply the Cost per Equivalent for each cost category in step 4 time the equivalent units for completed and transferred to Finished Goods and ending Inventory to complete the table below. ROUND YOUR ANSWERS TO NEAREST WHOLE DOLLARS. Add the cost categories together across to the Total Column. Totalcachomto the bottom row costs accounted for". The total in the bottom right box should be the total of the numbers above it AND the total of the numbers to its left. (It may be off a few dollars for rounding). Your answer represents SSSSDOLLARSSSSSS not units. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar Cosis accounted for in dollar U Other Material Costs Total Transferred in Bandles Comercio WIP -Ending balance 242,244 59,155 130161 13,314 39619 Costs of goods completed and 11,514,665 304,946 5821045 107.338 415,236 transferred out Total Costs accounted for [11756,914 369, 151 812,256 120-652 454,855 Note: The total "costs accounted for in the bottom row should equal (off few Ss for rounding the totals "costs to account for in the bottom row of the table in step 4) Sale of Finished Goods: Accounting for the analysis. As units are completed in the Bottling department, they are moved to Finished Goods Inventory where they are ready to be sold. The analysis above determines the dollar value of those completed units. a) Write the journal entry to move these costs from WIP-Bottling Inventory account to Finished Goods Inventory account. Post the Je to the WIP-Bottling and Finished Goods T-accounts attached at the end of the project. Determine the ending balance for WIP-Bottling account. Balance should cqual first row from table in 3e. Finbled goods inventory WIP- Bottling DR 1514,665 CR 1,514,665 WIP-Bottury Bulbol 264,500 1,514,665 Finished 9000 Einsted goods Bul bllo WIP bolting, sl 4465 WIP Bfending 314,160 Bottles 701,250 otter matoul 102.650 conversion 374,340 Bal +130 242, 235 Bell 6/30 1514.605 6 Sunspot Beverages, Ltd., of Fiji uses the weighted-average method in its process costing system. It makes blended tropical fruit drinks in two stages. Fruit juices are extracted from fresh fruits and then blended in the Blending Department. The blended juices are then bottled and packed for shipping in the Bottling Department. The following information pertains to the operations of the Blending Department for June. Percent Completed Materials Conversion 700 400 Work in process, beginning Started into production Completed and transferred out Work in process, ending Units 56,000 290,500 280,500 66,000 750 251 Work in process, beginning Cost added during June Materials Conversion $ 19,100 $ 5,900 $ 205,300 $ 124,780 Process costing of second department: Follow the steps below to perform the costing analysis for the Bottling department. Refer to VPW 3 Packet for examples on how to complete the tables. a) Step 1 part 1: Account for physical units. Complete the tables below using ######NUMBER ##### of units, NOT dollars!!!!!! Physical units for BOTTLING Units in Bottling June 1 44.000 Units completed and transferred 272/500 out during June Units transferred in from Units in Bottling June 30 12801500 Blending during June 52,000 Units "to account for" 3:24/500 Units "accounted for 329,500 Note: the 3 row should be the first 2 rows added together. The units "to account for" should equal the units "accounted for b) Step 1 part 2: Determine equivalent units. This is #WWWWNUMBER#WW of units, NOT dollars!!! For each of the 4 cost categories for Bottling Department, complete the table below to determine the equivalent units. Hint: All units "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and units in "ending WIP-Bottling inventory" are 100% complete with respect to transferred in" costs (costs from Blending department) and bottle costs. Equivalent Units (ACCOUNTED FOR) Transferred in Other Materials (Blending costs) Bottles 52.000 52/000 33.800 Conversion Equivalent units in ending WIP- Bottling inventory 26/000 Equivalent units completed and transferred to Finished Goods" 272/500 272,500 272/500 1272,500 Total Equivalent units accounted for 1324,500 3a4/500 306,300 298,500 Note: The 3"row should be the first two rows added together. The 3 row for "Other" and Conversion WILL NOT equal the other columns in this table, nor will they equal the 3 row in the table for step 1 in a) above c) Step 2 part 1: Make sure you complete the table Determine Costs to account for. These are SSSSDOLLARSSSSS not number of units. Costs to account for" is the sum of the beginning WIP-Bottling balance plus the costs that would have been added/assigned to the WIP-Bottling department during June. This information is summarized in the table above. Complete the table below using the information provided above. Bottling Department: Summary of Costs to be accounted for WIP- Bottling Costs Added Total Costs to be Cost Category beginning during June accounted for Transferred in from Blending $ 55,000 34160 from Ibiv 369,160 Cost of Bottles 111.000 70,250 from 251 812/250 Other Material Costs 18,000 102 1650 Efrom 26 i 20/650 Conversion Costs 80,5003747340 from 2c 4541840 Total $ 264,500 1,492.400 ID 757,400 Note: The costs "transferred IN" that were transferred into Bottling once "completed and transferred OUT" of the Blending department. d) Step 2 part 2: Calculate cost per equivalent unit. Answers will be SSSDOLLARSSS per ####NUMBER### of units. Use the totals in b) and c) above to calculate the Cost per equivalent unit for each cost category. Use 4 decimal places to minimize rounding differences. Cost per Equivalent Unit Bottle Costs Other Material Transferred in Total Costs to be accounted for 3(e) 369,160 Equivalent units 3(b) 2247500 Cost Per Equivalent Unit 11376 812 250 324,500 12.5031 120.650 30% 300 10.3939 Conversion 454,840 298,500 1.5238 c) Step 3: Allocate costs to units. Multiply the Cost per Equivalent for cach cost category in step 4 time the equivalent units for "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and "ending Inventory to complete the table below. ROUND YOUR ANSWERS TO NEAREST WHOLE DOLLARS. Add the cost categories together across to the Total Column. Total cach column to the bottom row "costs accounted for". The total in the bottom right box should be the total of the numbers above it AND the total of the numbers to its left. (It may be off a few dollars for rounding). Your answer represents SSSSDOLLARSSSSSS not units. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar Total 1242,244 Costs accounted for in dollars Other Material Transferred in Bottles Costs Conversion 130161 13,314 39619 304,996 |6821045 107,338 415,236 369,151 812,256 1201652 454.859 59,155 WIP -Ending balance Costs of goods completed and transferred out Total Costs accounted for 11,514,665 111756,914 Note: The total costs accounted for" in the bottom row should equal (off a few Ss for rounding) the totals "costs to account for" in the bottom row of the table in step 3 4) Sale of Finished Goods: Accounting for the analysis. As units are completed in the Bottling department, they are moved to Finished Goods Inventory where they are ready to be sold. The analysis above determines the dollar value of those completed units. a) Write the journal entry to move these costs from WIP-Bottling Inventory account to Finished Goods Inventory account. Post the JE to the WIP-Bottling and Finished Goods T-accounts attached at the end of the project. Determine the ending balance for WIP-Bottling account. Balance should equal first row from table in 3e. 1514, 665 Finbled goods inventory WIP-Botting goods DR CR WIP-Botting 1,514.665 Bulboll 264,500 1,514,665 FMikel Einsted goals EP Blonding 314,160 Bulbo ottles 7011250 ther matrol conversion 374,340 Ball8/20 1514.805 WIP byltingisi4885 102.650 b) Assume the Finished Goods Inventory was zero at the beginning of June and zero at the end of Junc. How many units did they sell during June? 272,500 c) If Sunspot Beverages, Ltd. sold cach unit for $12.00 what would their sales revenue be? 3,2707000_Write the journal entry to record the sales revenue for June d) How much is their expense (COGS)? 1,514,665 Write the journal entry to record the COGS for June. Post this entry to the Finished Goods account attached at the end of the project. 5) Raw Material: The company uses no indirect material and the Raw Material Inventory began the month with $120,000 and ending the month with $98,000. How much raw material inventory did the company purchase during June? 284,450 Write the summary journal entry to record the purchase. Post the journal entry to the T-account provided at the end of the attachment 6) Financial Statement Analysis: Use Chapter 14 concepts for this requirement For Sunspot Beverages; a) What is the value of Inventory they would record on their Balance Sheet at the beginning of June? At the end of June? Remember, Inventory on the balance sheet includes ALL inventory accounts. b) What is their "average" inventory for June? c) Using the formulas provided in Chapter 14 of your text (Pg. 678), calculate the following: Gross Margin percentage: Inventory turnover Average sales period for June. Note: Remember you are calculating ratios for a month not a year. You will need to annualize your turnover (multiply by 12 months) and/or use 30 days rather than 365 days for your sales period. d) Assume the industry leader has an inventory Turnover of 55 and average sales period of 7 days. How does Sunspot Beverages compare to the industry leader? Your answer and comment should be 20 to 50 words. a) Step 1 part 1: Account for physical units. Complete the tables below using #****#NUMBER ##### of units, NOT dollars!!!!!! Physical units for BOTTLING Units in Bottling June 1 44.000 Units completed and transferred out during June 272.500 Units transferred in from Blending during June Units in Bottling June 30 12801500 52,000 Units "to account for" 324/ 500 Units "accounted for B2.500 Note: the 3 row should be the first 2 rows added together. The units "to account for" should equal the units "accounted for" b) Step 1 part 2: Determine equivalent units. This is #####NUMBER#**# of units, NOT dollars!!! For each of the 4 cost categories for Bottling Department, complete the table below to determine the equivalent units. Hint: All units "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and units in ending WIP-Bottling inventory" are 100% complete with respect to transferred in" costs (costs from Blending department) and bottle costs. Equivalent Units (ACCOUNTED FOR) Transferred in Other Materials (Blending costs) Bottles 52.000 52.000 33.800 Conversion 26/000 Equivalent units in ending WIP- Bottling inventory Equivalent units completed and transferred to Finished Goods" 272/500 272,500 272/500 272500 Total Equivalent units accounted for 1324,500 3a4/500 306, 300 298,500 Note: The 3d row should be the first two rows added together. The 3rd row for "Other" and Conversion WILL NOT equal the other columns in this table, nor will they equal the 3 row in the table for step 1 in a) above. c) Step 2 part 1: Make sure you complete the table Determine Costs to account for. These are SSSSDOLLARSSSSS not number of units. Costs "to account for" is the sum of the beginning WIP-Bottling balance plus the costs that would have been added/assigned to the WIP-Bottling department during June. This information is summarized in the table above. Complete the table below using the information provided above. Bottling Department: Summary of Costs to be accounted for WIP- Bottling Costs Added Total Costs to be Cost Category beginning during June accounted for Transferred in from Blending $ 55,000 34 160 from lb iv 369,160 Cost of Bottles 111,000 70,00 from 2bi 812/250 Other Material Costs 18,000 102/650 &from 2bit 12D/ 650 Conversion Costs 80,500 3740340 from 2c 14541840 Total $ 264,500 1,492.40 10756.400 Wote: The costs "transferred IN" that were transferred into Bottling once "completed and transferred OUT" of the Blending department. d) Step 2 part 2: Calculate cost per equivalent unit. Answers will be SSSDOLLARSSS per ###WNUMBER### of units. Use the totals in b) and c) above to calculate the Cost per equivalent unit for each cost category. Use 4 decimal places to minimize rounding differences. Cost per Equivalent Unit Other Material Conversion 4547840 120.650 Total Costs to be accounted for 3(e) Equivalent units 3(b) Cost Per Equivalent Unit Transferred in 369,160 3247500 1.1376 Bottle Costs 812,250 324,500 12.5031 30% 300 0,3939 1.5238 e. c) Step 3: Allocate costs to units. Multiply the Cost per Equivalent for each cost category in step 4 time the equivalent units for completed and transferred to Finished Goods and ending Inventory to complete the table below. ROUND YOUR ANSWERS TO NEAREST WHOLE DOLLARS. Add the cost categories together across to the Total Column. Totalcachomto the bottom row costs accounted for". The total in the bottom right box should be the total of the numbers above it AND the total of the numbers to its left. (It may be off a few dollars for rounding). Your answer represents SSSSDOLLARSSSSSS not units. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar Cosis accounted for in dollar U Other Material Costs Total Transferred in Bandles Comercio WIP -Ending balance 242,244 59,155 130161 13,314 39619 Costs of goods completed and 11,514,665 304,946 5821045 107.338 415,236 transferred out Total Costs accounted for [11756,914 369, 151 812,256 120-652 454,855 Note: The total "costs accounted for in the bottom row should equal (off few Ss for rounding the totals "costs to account for in the bottom row of the table in step 4) Sale of Finished Goods: Accounting for the analysis. As units are completed in the Bottling department, they are moved to Finished Goods Inventory where they are ready to be sold. The analysis above determines the dollar value of those completed units. a) Write the journal entry to move these costs from WIP-Bottling Inventory account to Finished Goods Inventory account. Post the Je to the WIP-Bottling and Finished Goods T-accounts attached at the end of the project. Determine the ending balance for WIP-Bottling account. Balance should cqual first row from table in 3e. Finbled goods inventory WIP- Bottling DR 1514,665 CR 1,514,665 WIP-Bottury Bulbol 264,500 1,514,665 Finished 9000 Einsted goods Bul bllo WIP bolting, sl 4465 WIP Bfending 314,160 Bottles 701,250 otter matoul 102.650 conversion 374,340 Bal +130 242, 235 Bell 6/30 1514.605 6 Sunspot Beverages, Ltd., of Fiji uses the weighted-average method in its process costing system. It makes blended tropical fruit drinks in two stages. Fruit juices are extracted from fresh fruits and then blended in the Blending Department. The blended juices are then bottled and packed for shipping in the Bottling Department. The following information pertains to the operations of the Blending Department for June. Percent Completed Materials Conversion 700 400 Work in process, beginning Started into production Completed and transferred out Work in process, ending Units 56,000 290,500 280,500 66,000 750 251 Work in process, beginning Cost added during June Materials Conversion $ 19,100 $ 5,900 $ 205,300 $ 124,780 Process costing of second department: Follow the steps below to perform the costing analysis for the Bottling department. Refer to VPW 3 Packet for examples on how to complete the tables. a) Step 1 part 1: Account for physical units. Complete the tables below using ######NUMBER ##### of units, NOT dollars!!!!!! Physical units for BOTTLING Units in Bottling June 1 44.000 Units completed and transferred 272/500 out during June Units transferred in from Units in Bottling June 30 12801500 Blending during June 52,000 Units "to account for" 3:24/500 Units "accounted for 329,500 Note: the 3 row should be the first 2 rows added together. The units "to account for" should equal the units "accounted for b) Step 1 part 2: Determine equivalent units. This is #WWWWNUMBER#WW of units, NOT dollars!!! For each of the 4 cost categories for Bottling Department, complete the table below to determine the equivalent units. Hint: All units "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and units in "ending WIP-Bottling inventory" are 100% complete with respect to transferred in" costs (costs from Blending department) and bottle costs. Equivalent Units (ACCOUNTED FOR) Transferred in Other Materials (Blending costs) Bottles 52.000 52/000 33.800 Conversion Equivalent units in ending WIP- Bottling inventory 26/000 Equivalent units completed and transferred to Finished Goods" 272/500 272,500 272/500 1272,500 Total Equivalent units accounted for 1324,500 3a4/500 306,300 298,500 Note: The 3"row should be the first two rows added together. The 3 row for "Other" and Conversion WILL NOT equal the other columns in this table, nor will they equal the 3 row in the table for step 1 in a) above c) Step 2 part 1: Make sure you complete the table Determine Costs to account for. These are SSSSDOLLARSSSSS not number of units. Costs to account for" is the sum of the beginning WIP-Bottling balance plus the costs that would have been added/assigned to the WIP-Bottling department during June. This information is summarized in the table above. Complete the table below using the information provided above. Bottling Department: Summary of Costs to be accounted for WIP- Bottling Costs Added Total Costs to be Cost Category beginning during June accounted for Transferred in from Blending $ 55,000 34160 from Ibiv 369,160 Cost of Bottles 111.000 70,250 from 251 812/250 Other Material Costs 18,000 102 1650 Efrom 26 i 20/650 Conversion Costs 80,5003747340 from 2c 4541840 Total $ 264,500 1,492.400 ID 757,400 Note: The costs "transferred IN" that were transferred into Bottling once "completed and transferred OUT" of the Blending department. d) Step 2 part 2: Calculate cost per equivalent unit. Answers will be SSSDOLLARSSS per ####NUMBER### of units. Use the totals in b) and c) above to calculate the Cost per equivalent unit for each cost category. Use 4 decimal places to minimize rounding differences. Cost per Equivalent Unit Bottle Costs Other Material Transferred in Total Costs to be accounted for 3(e) 369,160 Equivalent units 3(b) 2247500 Cost Per Equivalent Unit 11376 812 250 324,500 12.5031 120.650 30% 300 10.3939 Conversion 454,840 298,500 1.5238 c) Step 3: Allocate costs to units. Multiply the Cost per Equivalent for cach cost category in step 4 time the equivalent units for "completed and transferred to Finished Goods" and "ending Inventory to complete the table below. ROUND YOUR ANSWERS TO NEAREST WHOLE DOLLARS. Add the cost categories together across to the Total Column. Total cach column to the bottom row "costs accounted for". The total in the bottom right box should be the total of the numbers above it AND the total of the numbers to its left. (It may be off a few dollars for rounding). Your answer represents SSSSDOLLARSSSSSS not units. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar Total 1242,244 Costs accounted for in dollars Other Material Transferred in Bottles Costs Conversion 130161 13,314 39619 304,996 |6821045 107,338 415,236 369,151 812,256 1201652 454.859 59,155 WIP -Ending balance Costs of goods completed and transferred out Total Costs accounted for 11,514,665 111756,914 Note: The total costs accounted for" in the bottom row should equal (off a few Ss for rounding) the totals "costs to account for" in the bottom row of the table in step 3 4) Sale of Finished Goods: Accounting for the analysis. As units are completed in the Bottling department, they are moved to Finished Goods Inventory where they are ready to be sold. The analysis above determines the dollar value of those completed units. a) Write the journal entry to move these costs from WIP-Bottling Inventory account to Finished Goods Inventory account. Post the JE to the WIP-Bottling and Finished Goods T-accounts attached at the end of the project. Determine the ending balance for WIP-Bottling account. Balance should equal first row from table in 3e. 1514, 665 Finbled goods inventory WIP-Botting goods DR CR WIP-Botting 1,514.665 Bulboll 264,500 1,514,665 FMikel Einsted goals EP Blonding 314,160 Bulbo ottles 7011250 ther matrol conversion 374,340 Ball8/20 1514.805 WIP byltingisi4885 102.650 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


