Need help to solve this worksheet!
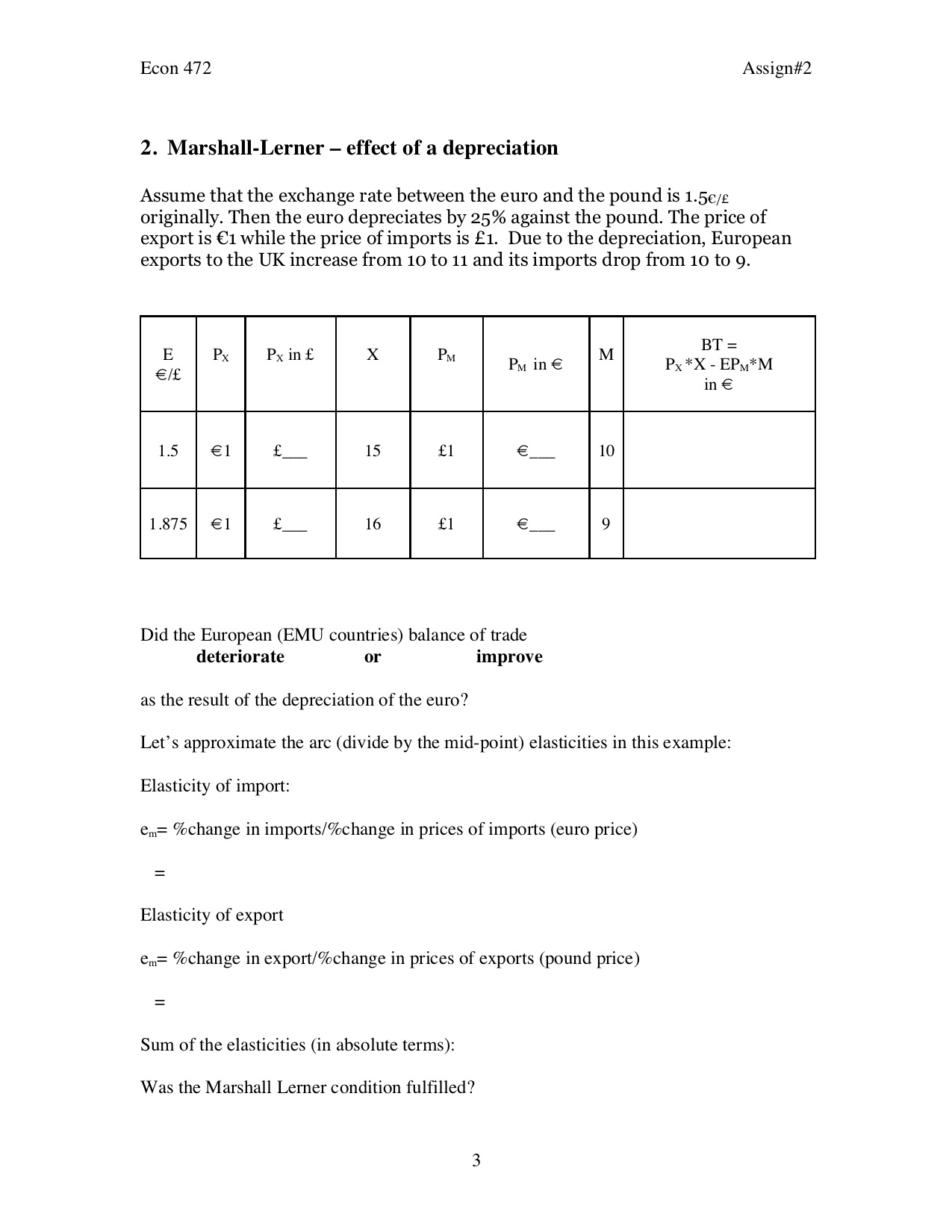
Econ 47 2 Assign#2 2. Marshall-Lerner - effect of a depreciation Assume that the exchange rate between the euro and the pound is 1.559. originally. Then the euro depreciates by 25% against the pound. The price of export is 11 while the price of imports is 1. Due to the depreciation, European exports to the UK increase from 10 to 11 and its imports drop from 10 to 9. BT = Px *X - EPM*M in Did the European (EMU countries) balance of trade deteriorate or improve as the result of the depreciation of the euro? Let' s approximate the arc (divide by the mid-point) elasticities in this example: Elasticity of import: em: %change in imports/%change in prices of imports (euro price) Elasticity of export em: %change in export/%change in prices of exports (pound price) Sum of the elasticities (in absolute terms): Was the Marshall Lerner condition fulfilled? Econ 472 Assign#2 3. Small open economy Assume a small country is characterized by the following equations: Consumption C =220 + .7(Y-T) Investment I = 200 Government spending G = 100 Tax T = 100 Imports M = 100 + .2Y Exports X = 400 a. Calculate equilibrium income Y, the corresponding balance of trade BT, and government saving SG using the usual equilibrium condition Y=C+I+G+X-M. Y= BT = SG = b. Construct the equations for the SN-I line and for the X-M line and equate these two equations to calculate equilibrium income Y (you should get the same result as in a.) SN.I = . X-M = Y = c. We are now going to calculate the impact of a fiscal expansion (an increase in G equal to 100) under fixed and then under flexible exchange rate using the S"-I/X-M approach. i. Fixed exchange rate regime - G increases from 100 to 200 First construct the new equations for SN-I and X-M (if they have changed). Then calculate the new level of output, the balance of trade BT, and government saving SG. = I-NS X-M = Y = BT = SG = Illustrate your results with the SN-I/X-M graph (name all your curves and axes an show the changes).ECON 472 Name: Autumn 2020 ASSIGNMENT #2 Due Tuesday October 27 1. Foreign exchange market equilibrium under exible and xed ER a. Draw the market for foreign exchange (S and D) and show the equilibrium exchange rate and the equilibrium quantity of traded. The supply of foreign exchange is derived from the supply of export of Macs and the demand for foreign exchange is derived from the demand for import of Volkswagen The equilibrium exchange rate is Ea/e = 1 and the quantity traded in equilibrium is 2,400,000 euros E ($/) Qof b. Now assume that, as a result of a change in taste, the European public wants to buy fewer Mac s. Show the impact on the foreign exchange market graph above with exible ER. What happens to the US exchange rate ($/ )? depreciation appreciation stays the same Econ 47 2 Assign#2 c. Let's now change the story and assume that the US and the Europeans agree together to peg their exchange rate at the level calculated in c (xed exchange rate). What happens to the US exchange rate ($/) when the foreign supply shifts as in d (the European public wants to buy fewer Macs). depreciation appreciation stays the same d. If your answer is: \"stays the same\" what does the FED do to achieve that? The FED in the foreign exchange market. From what you read above, does the ECB (European Central Bank) get involved to? Yes No How does the FED intervene to keep its parity with the 8? it buys or it sells How does the ECB (European Central Bank) intervene to keep its parity with the :5? it buys $ or it sells 35 So what is the effect on the FED's foreign reserves? they increase or they decrease Assuming no sterilization from the part of the FED, what are the effects of these changes in the FED foreign reserves i. on the US money supply increases or decreases or no change ii. on US prices on the long run? increase or decrease or no change Finally, the FED could counteract these effects on prices (if any and in whichever direction) by using monetary policy (sterilization). What kind of monetary policy? open market purchase or open market sale