
Need help with screenshots 1 through 7! Each problem is one-parted, and does NOT include multiple parts. Therefore, it should be pretty easy. However, if you think you need any more info, do not hesitate to let me know. THANK YOU!!!!
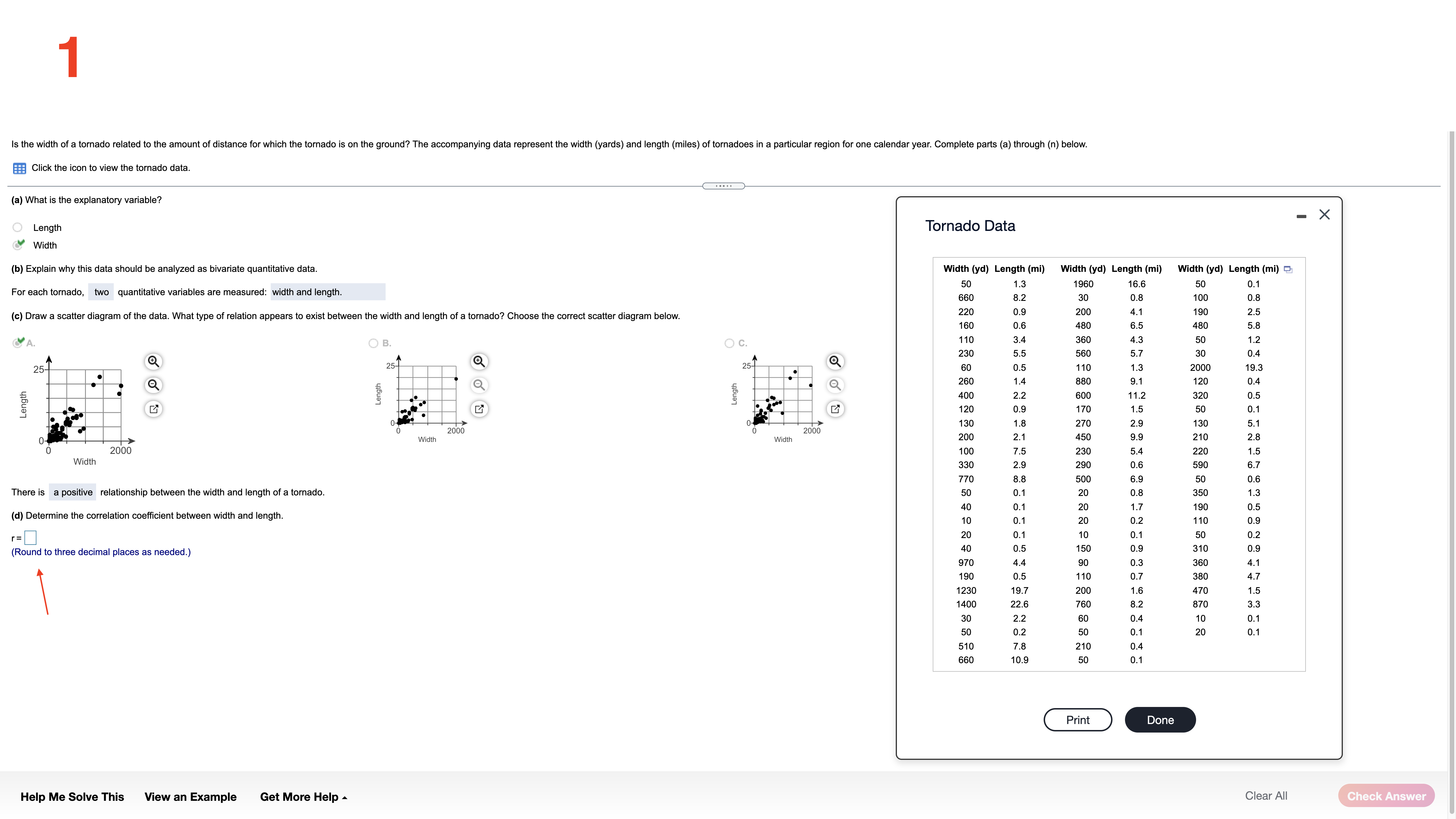
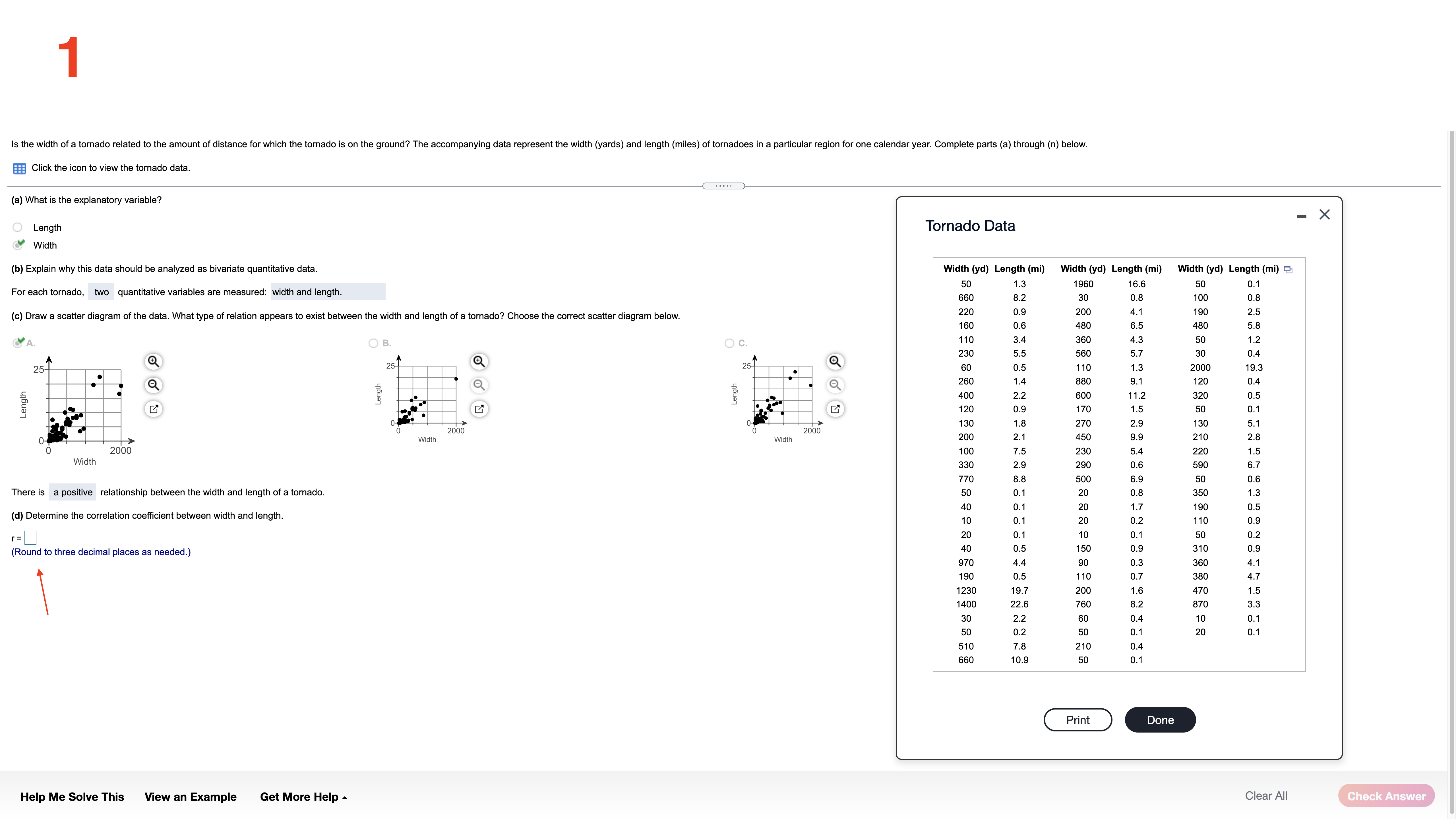
Is the width of a tornado related to the amount of distance for which the tornado is on the ground? The accompanying data represent the width (yards) and length (miles) of tornadoes in a particular region for one calendar year. Complete parts (a) through (n) below. Click the icon to view the tornado data. (a) What is the explanatory variable? - X O Length Tornado Data Width (b) Explain why this data should be analyzed as bivariate quantitative data. Width (yd) Length (mi) Width (yd) Length (mi) Width (yd) Length (mi) 50 1.3 1960 16. 50 0.1 For each tornado, two quantitative variables are measured: width and length. 660 8.2 30 0.8 10 0.8 (c) Draw a scatter diagram of the data. What type of relation appears to exist between the width and length of a tornado? Choose the correct scatter diagram below. 220 0.9 200 4.1 190 2.5 160 0.6 480 6.5 480 5.8 O B. O C. 10 3.4 360 4.3 50 1.2 230 5.5 560 5.7 30 0.4 25- 25-1 25- 60 0.5 110 1.3 2000 19.3 260 1.4 880 9.1 120 0.4 Length Length 400 2.2 600 11.2 320 0.5 Length 20 0.9 170 1.5 50 0.1 30 1.8 270 2.9 130 5.1 2000 2000 0- Width Width 200 2.1 450 9.9 210 2.8 2000 100 7.5 230 5.4 220 1.5 Width 330 2.9 290 0.6 590 6.7 770 8 .8 500 6.9 50 0.6 There is a positive relationship between the width and length of a tornado. 50 0.1 20 0.8 350 1.3 40 0.1 20 1.7 190 0.5 (d) Determine the correlation coefficient between width and length. 10 0.1 20 0.2 110 0.9 r= 20 0.1 10 0.1 50 0.2 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) 10 0.5 150 0.9 310 0.9 970 4.4 90 0.3 360 4.1 190 0.5 110 0.7 380 4.7 123 19.7 200 1.6 470 1.5 1400 22.6 760 8.2 870 3.3 30 2.2 50 0.4 10 0.1 50 0.2 50 0.1 20 0.1 510 7.8 210 0.4 660 10.9 50 Print Done Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help - Clear All Check Answer2 What is the coefficient of determination for Data Set B? The coefficient of determination for Data Set B is %. Full Data Set: (Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest tenth as needed.) Data Set A Data Set B Data Set C X X y X y 3.6 8.9 3.1 8.9 2.8 8.9 8.3 15.0 9.4 15.0 8.1 15.0 0.5 4.8 1.2 4.8 3.0 4.8 1.4 6.0 1.0 6.0 8.3 6.0 8.2 14.9 9.0 8.2 14.9 5.9 11.9 5.0 11.9 1.4 11.9 4.3 9.8 3.4 9.8 1.0 9.8 8.3 15.0 7.4 15.0 7.9 15.0 0.3 4.7 0.1 4.7 5.9 4.7 6.8 13.0 7.5 13.0 5.0 13.0 (This is a reading assessment question. Be certain of your answer because you only get one attempt on this question.) Textbook StatCrunch Get More Help Clear All Check Answer3 A probability experiment is conducted in which the sample space of the experiment is S = (4. 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15), event F = (7. 8, 9, 10, 11), and event G =(11, 12, 13, 14}. Assume that each outcome is equally likely. List the outcomes in F or G. Find P(F or G) by counting the number of outcomes in F or G. Determine P(F or G) using the general addition rule. List the outcomes in F or G. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, ll in the answer box to complete your choice. \"'A- F or G = {7,8,9,1o,11,12,13,14} (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) , 'B. ForG=() Find P(F or G) by counting the number of outcomes in F or G. P(F or G) = (Type an integer or a decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed) Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help . Clear All 4 A probability experiment is conducted in which the sample space of the experiment is S =(4,5,6.7,8.9.10,11.12.13.14.15). Let event E = (7.8.9.10). Assume each outcome is equally likely. List the outcomes in E. Find P (Ec). List the outcomes in E, Select the correct choice below and. if necessary. ll in the answer box to complete your choice. 'VA- E = {4,5,6,11,12,13,14,15} (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) '33- E=() P (E) = (Type an integer or a decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed) Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help . Clear All 5 The data on the right represent the number of live multiple-delivery births (three or more babies) in a particular year for women 15 to 54 years old. Use the data to complete parts (a) through (d) below. Number of Multiple Q1 Age Births 1 5-1 9 89 20-24 506 25-29 1629 30-34 2629 35-39 1844 40-44 375 45-54 1 16 (a) Determine the probability that a randomly selected multiple birth for women 15-54 years old involved a mother 30 to 39 years old. P(30 to 39): 0.633 (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed) (b) Determine the probability that a randomly selected multiple birth for women 15-54 years old involved a mother who was not 30 to 39 years old. P(not 30 to 39) = 0367 (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) (c) Determine the probability that a randomly selected multiple birth for women 15-54 years old involved a mother who was less than 45 years old. P(less than 45) = (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help . Clear All 6 For a parallel structure of identical components, the system can succeed if at least one of the components succeeds. Assume that components fail independently of each other and that each component has a 0.16 probability of failure. Complete parts (a) through ((2) below. (a) Would it be unusual to obsen/e one component fail? Two components? It V be unusual to observe one component fail. since the probability that one component fails, , is V than 0.05. It i be unusual to observe two components fail, since the probability that two components fail, , is : than 0.05. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. \"less\" or \"greater\" H H H H / less or greater \"would\" or \"would not\" \"would\" or \"would not,\" Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help . Clear All 7 Suppose the data to the right represent the survival data for the a certain ship that sank. The males are adult males and the females are adult females. Complete parts (a) through (j). e Female Child Total Survived 272 474 66 812 Died 1,433 153 51 1,637 Total 1,705 627 117 2,449 (a) If a passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the passenger survived? 0.332 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) If a passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the passenger was female? 0.256 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (c) If a passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the passenger was female or a child? 0.304 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (d) If a passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the passenger was female and survived? 0.194 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (e) If a passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the passenger was female or survived? 0.394 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (f) If a female passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that she survived? 0.756 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (g) If a child passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that the child survived? 0.564 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (h) If a male passenger is selected at random, what is the probability that he survived? 0.160 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (i) Do you think the adage "women and children first" was adhered to on this ship? O A. No, because the survival rate for men was about the same as the survival rates for women and children. B. Yes, because the survival rate for men was much lower than the survival rates for women and children. O C. No, because the survival rate for men was higher than the survival rates for women and children. (j) Suppose two females are randomly selected. What is the probability both survived? (Round to four decimal places as needed.) X I' (1,!) More Help Me Solve This View an Example Get More Help - Clear All Check