Question
Need help with the following program: Complete a program that has a user enter a pollutant choice, a number of grams of the pollutant emitted
Need help with the following program:
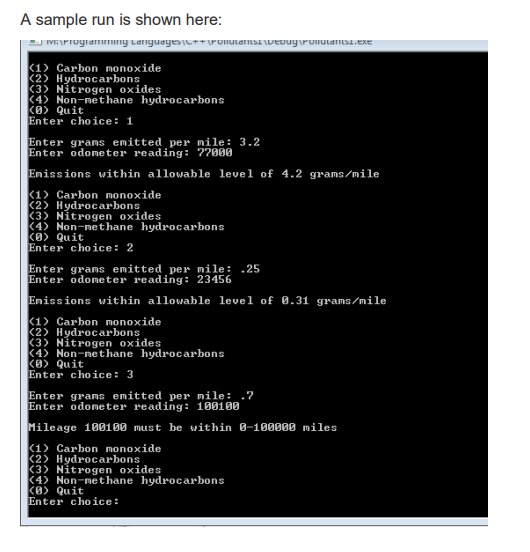
Complete a program that has a user enter a pollutant choice, a number of grams of the pollutant emitted per mile, and an odometer reading (0-100000). Output an indication of whether or not they are compliant with the following regulations:

1. Not change any of the given code.
2. Use the defined constant variables for any constant values in your program.
3. Create additional constant variables to use when checking the mileage boundaries (50000 miles and 100000 miles).
4. Output an indication that an invalid odometer reading has been entered (outside of the range of 0-100000).
5. Use the switch statement started in the program for your decision structure.
6. Have at least one other user defined function.
One possibility is the following function that determines the allowable level for a particular pollutant: double getAllowableLevel (double gramsPerMileAllowed1, double gramsPerMileAllowed2, int odometer);
Beginning Code:
#include
#include
const int FIRST_STAGE_MILEAGE = 50000;
const int CARBON_MONOXIDE = 1;
const int HYDROCARBON = 2;
const int NITROGEN_OXIDE = 3;
const int NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON = 4;
const double CARBON_MONOXIDE_ALLOWED1 = 3.4;
const double CARBON_MONOXIDE_ALLOWED2 = 4.2;
const double HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED1 = 0.31;
const double HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED2 = 0.39;
const double NITROGEN_OXIDE_ALLOWED1 = 0.4;
const double NITROGEN_OXIDE_ALLOWED2= 0.5;
const double NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED1 = 0.25;
const double NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED2 = 0.31;
using namespace std;
void outputMenu ();
//function prototypes to get allowable level and determine if within bounds
double getAllowableLevel (double gramsPerMileAllowed1, double gramsPerMileAllowed2, int odometer);
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pollutant;
double gramsPerMile;
int odometer;
bool compliant;
double allowableGramsPerMile;
outputMenu();
cout
cin >> pollutant;
cout
cin >> gramsPerMile;
cout
cin >> odometer;
switch (pollutant)
{
case CARBON_MONOXIDE:
allowableGramsPerMile = getAllowableLevel(CARBON_MONOXIDE_ALLOWED1, CARBON_MONOXIDE_ALLOWED2, odometer);
break;
case HYDROCARBON:
allowableGramsPerMile = getAllowableLevel(HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED1, HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED2, odometer);
break;
case NITROGEN_OXIDE:
allowableGramsPerMile = getAllowableLevel(NITROGEN_OXIDE_ALLOWED1, NITROGEN_OXIDE_ALLOWED2, odometer);
break;
case NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON:
allowableGramsPerMile = getAllowableLevel(NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED1, NONMETHANE_HYDROCARBON_ALLOWED2, odometer);
break;
}
string compliance;
compliant = gramsPerMile
if (compliant)
compliance = "within";
else
compliance = "exceeds";
cout
cin.ignore();
cin.get();
}
void outputMenu ()
{
cout
cout
cout
cout
}
//Given an odometer reading, returns the allowable level
double getAllowableLevel (double gramsPerMileAllowed1, double gramsPerMileAllowed2, int odometer)
{
if (odometer
{
return gramsPerMileAllowed1;
}
else
{
return gramsPerMileAllowed2;
}
}
carbon monoxide hydrocarbons nitogen oxides first 50,000 miles second 50,000 miles 3.4 grams/mile 4.2 grams/mile 0.31 grams/mile 0.39 grams/mile 0.4 grams/mile 0.5 grams/mile
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


