Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
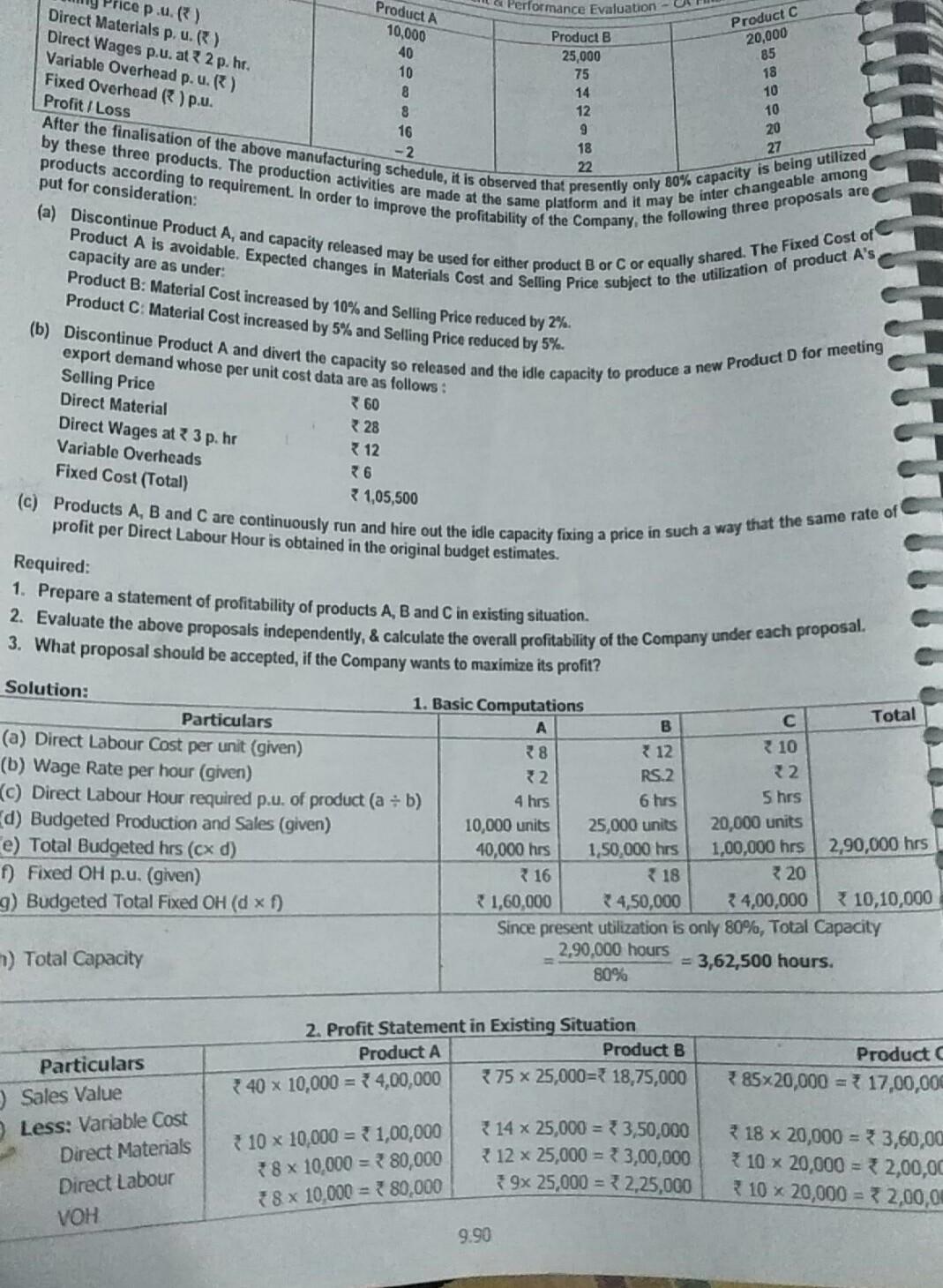
need note Performance Evaluation - Product A 10,000 ice p.u.) Direct Materials p. u.) Direct Wages p.u. at 2 p.hr. Variable Overhead p. u. (
need note
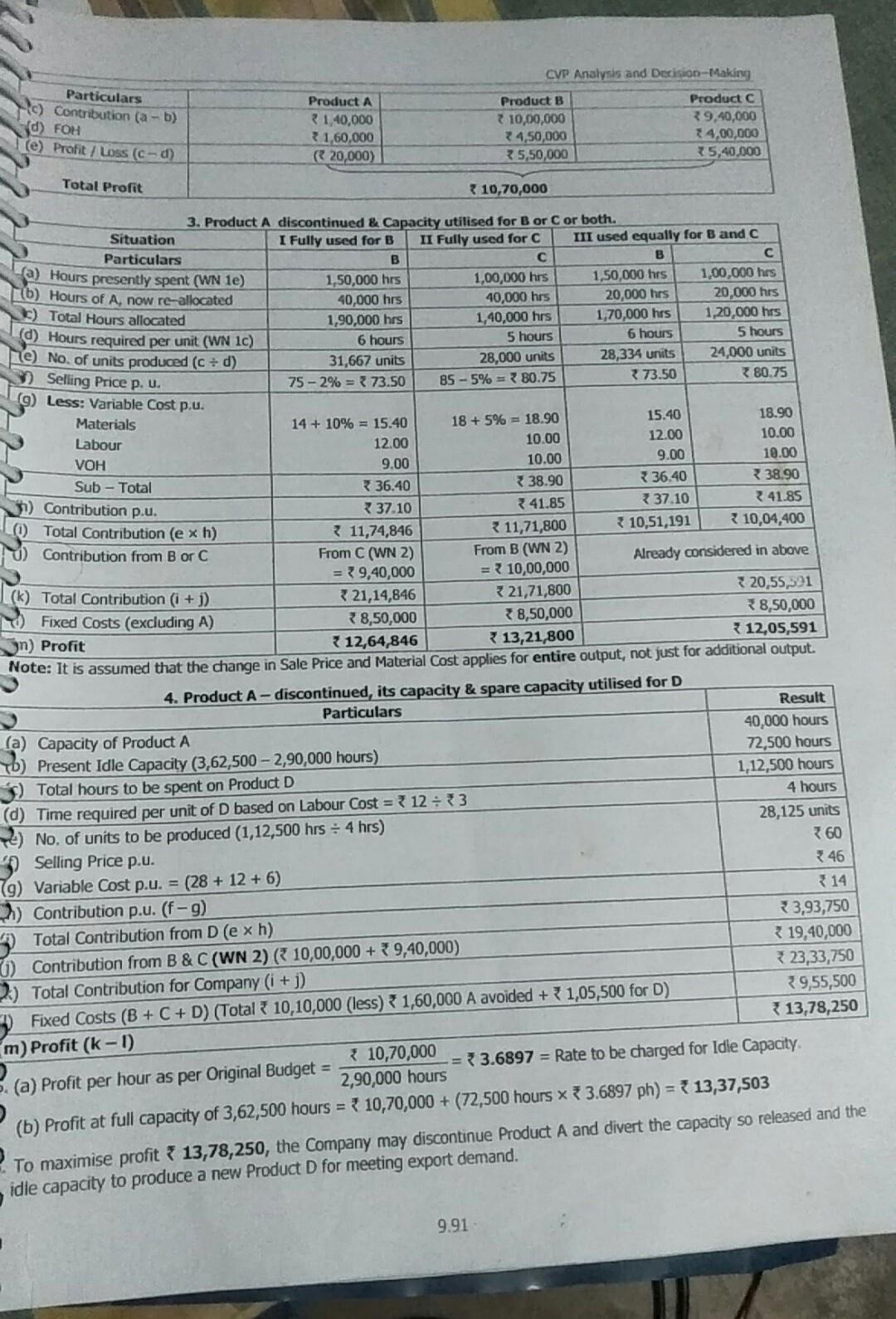
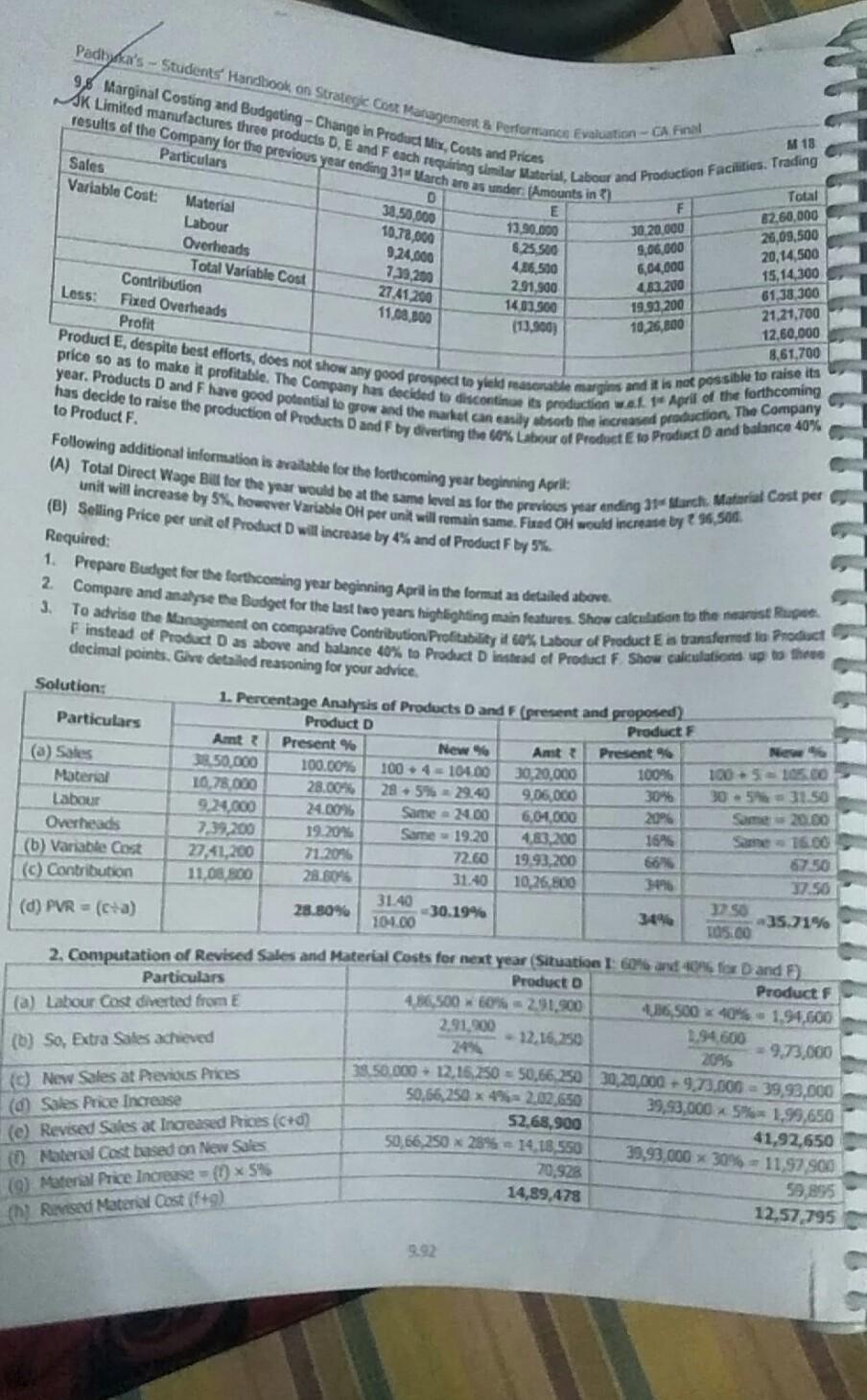
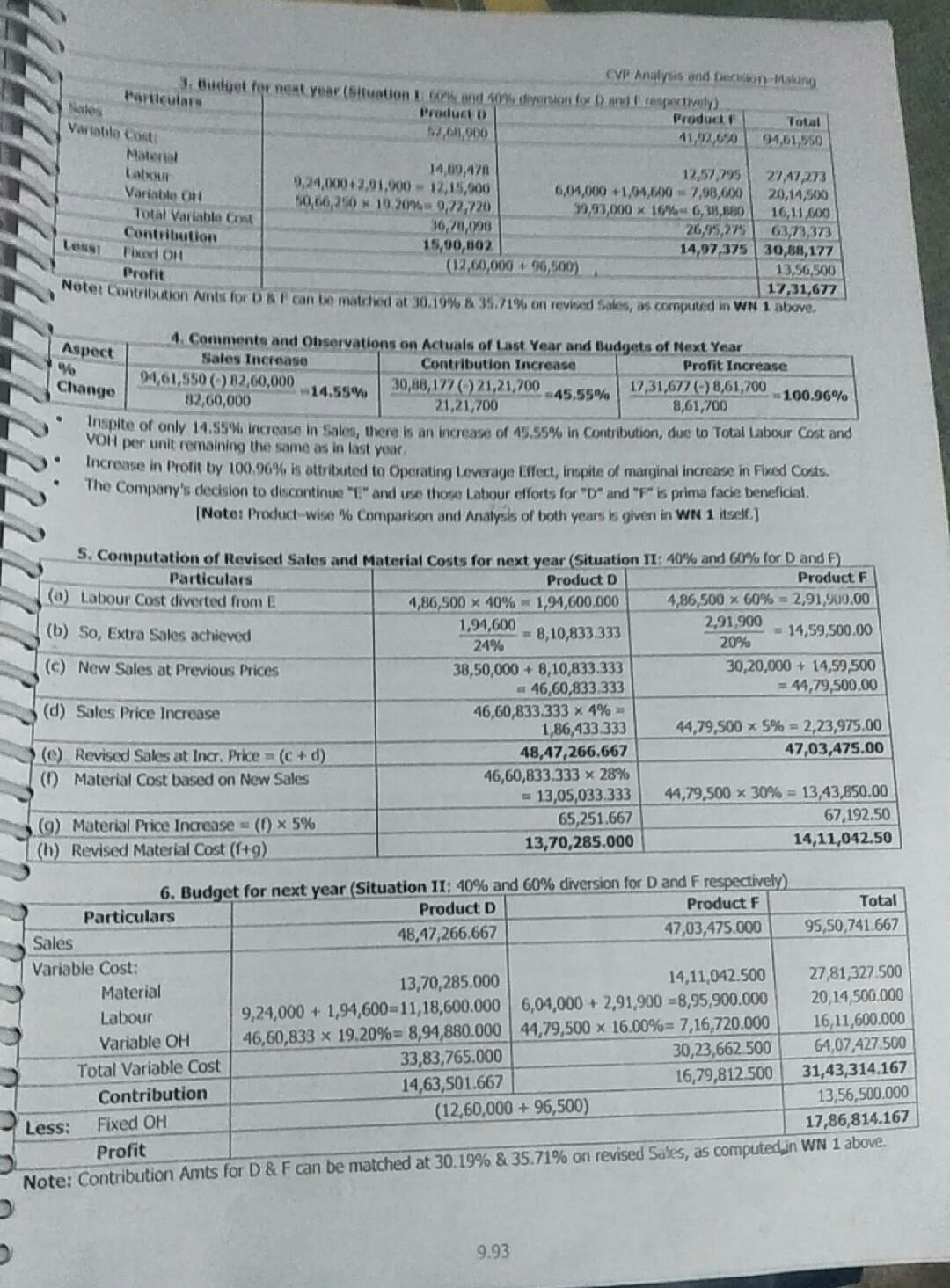
Performance Evaluation - Product A 10,000 ice p.u.) Direct Materials p. u.) Direct Wages p.u. at 2 p.hr. Variable Overhead p. u. ( ) Fixed Overhead ( ) p.u. Profit I Loss 40 10 8 8 16 -2 Product B 25,000 75 14 12 9 After the finalisation of the above manufacturing schedule, it is observed that presently only 80% capacity is being utilized 18 by these three products. The production activities are made at the same platform and it may be inter changeable among 22 products according to requirement. In order to improve the profitability of the Company, the following three proposals are (a) Discontinue Product A, and capacity released may be used for either product B or C or equally shared. The Fixed Cost of Product A is avoidable. Expected changes in Materials Cost and Selling Price subject to the utilization of product A's Product C 20,000 85 18 10 10 20 27 put for consideration: capacity are as under: Product B: Material Cost increased by 10% and Selling Price reduced by 2%. Product C. Material Cost increased by 5% and Selling Price reduced by 5%. (b) Discontinue Product A and divert the capacity so released and the idle capacity to produce a new Product D for meeting export demand whose per unit cost data are as follows: Selling Price 360 Direct Material Direct Wages at 3 p.hr Variable Overheads Fixed Cost (Total) 31,05,500 28 12 6 (c) Products A, B and C are continuously run and hire out the idle capacity foxing a price in such a way that the same rate of profit per Direct Labour Hour is obtained in the original budget estimates. Required: 1. Prepare a statement of profitability of products A, B and C in existing situation. Total 2. Evaluate the above proposals independently, & calculate the overall profitability of the Company under each proposal. 3. What proposal should be accepted, if the Company wants to maximize its profit? Solution: 1. Basic Computations Particulars B C (a) Direct Labour Cost per unit (given) 38 712 10 (b) Wage Rate per hour (given) 2 RS.2 22 (C) Direct Labour Hour required p.u. of product (a - b) 4 hrs 6 hrs 5 hrs d) Budgeted Production and Sales (given) 10,000 units 25,000 units 20,000 units e) Total Budgeted hrs (cx d) 40,000 hrs 1,50,000 hrs 1,00,000 hrs 2,90,000 hrs f) Fixed OH p.u. (given) 16 18 320 9) Budgeted Total Fixed OH (d * 1) 1,60,000 4,50,000 34,00,000 10,10,000 Since present utilization is only 80%, Total Capacity 2,90,000 hours ) Total Capacity = 3,62,500 hours. 80% 2. Profit Statement in Existing Situation Product A Product B 40 x 10,000 = 7 4,00,000 375 x 25,000= 18,75,000 Product 85x20,000 = 17,00,000 Particulars ) Sales Value Less: Variable Cost Direct Materials Direct Labour VOH 10 x 10,000 = 1,00,000 8 x 10,000 = 380,000 38 x 10,000 = 80,000 14 x 25,000 = 33,50,000 12 25,000 = 3,00,000 9x 25,000 = 2,25,000 18 x 20,000 = 33,60,00 * 10 x 20,000 = 32,00,00 10 x 20,000 = 2,00,0 9.90 CVP Analysis and Derision-Making Particulars HC) Contribution (a - b) d) FOH (e) Profit Loss (C-d Product A 21.40,000 21,60,000 ( 20,000) Product B 10,00,000 24,50,000 35,50,000 Product C 39,40,000 74,00,000 25,40.000 Total Profit 310,70,000 a) Hours presently spent (WN 1e) 15.40 12.00 3. Product A discontinued & Capacity utilised for B or C or both. Situation I Fully used for B II Fully used for C III used equally for B and C Particulars B B 1,50,000 hrs 1,00,000 hrs 1,50,000 hrs [(b) Hours of A, now re-allocated 1,00,000 hes 40,000 hrs 40,000 hrs 20,000 hrs 20,000 hrs $) Total Hours allocated 1,90,000 hrs 1,40,000 hrs 1,70,000 hrs 1,20,000 hrs (d) Hours required per unit (WN 1c) 6 hours 5 hours 6 hours 5 hours e) No. of units produced (Cd) 31,667 units 28,000 units 28,334 units 24,000 units Selling Price p. u. 75 -2% = 73.50 85 - 5% = 780.75 73.50 380.75 (9) Less: Variable Cost p.u. Materials 14 + 10% = 15.40 18 + 5% = 18.90 18.90 Labour 12.00 10.00 10.00 VOH 9.00 10.00 9.00 10.00 Sub - Total 36.40 3 38.90 36.40 38.90 ) Contribution p.u. 337.10 341.85 737.10 241.85 Total Contribution (e xh) 3 11,74,846 11,71,800 10,51,191 10,04,400 Contribution from B or C From C (WN 2) From B (WN 2) Already considered in above = 39,40,000 = 10,00,000 (k) Total Contribution (i + 3) 21,14,846 321,71,800 320,55,591 Fixed Costs (excluding A) 8,50,000 8,50,000 8,50,000 in) Profit 12,64,846 13,21,800 312,05,591 Note: It is assumed that the change in Sale Price and Material Cost applies for entire output, not just for additional output. 4. Product A-discontinued, its capacity & spare capacity utilised for D Result Particulars 40,000 hours (a) Capacity of Product A 72,500 hours TO) Present Idle Capacity (3,62,500 - 2,90,000 hours) 1,12,500 hours Total hours to be spent on Product D 4 hours (d) Time required per unit of D based on Labour Cost = 7 12:33 28,125 units 4) No. of units to be produced (1,12,500 hrs = 4 hrs) 360 Selling Price p.u. 46 (9) Variable Cost p.u. = (28 + 12 + 6) 14 2) Contribution p.u. (f-9) 3,93,750 Total Contribution from D (e x h) 19,40,000 6) Contribution from B & C (WN 2) ( 10,00,000 + 39,40,000) 323,33,750 2.) Total Contribution for Company (i + 1) 39,55,500 Fixed Costs (B + C + D) (Total 10,10,000 (less) 1,60,000 A avoided + 1,05,500 for D) 13,78,250 m) Profit (k-1) 10,70,000 = 3.6897 = Rate to be charged for Idle Capacity (a) Profit per hour as per Original Budget 2,90,000 hours (b) Profit at full capacity of 3,62,500 hours = { 10,70,000 + (72,500 hours x 3.6897 ph) = { 13,37,503 To maximise profit * 13,78,250, the Company may discontinue Product A and divert the capacity so released and the idle capacity to produce a new Product D for meeting export demand. 9.91 9,8 Marginal Costing and Budgeting - Change in Product Mix, Corts and Prices Padhya's - Student Handbook on Strategic Cost Management & Performance Evaluation - CA Final SK Limited manufactures three products D, E and F each requiring similar Material, Labour and Production Facilities. Trading results of the Company for the previous year ending 31 March areas under Amounts in ) M 18 Total E 30.20.000 9,06,000 406,500 15,14,300 2.91,500 14 01.500 21.21,700 113.900) F Particulars Sales Variable Cost: Material Labour Overheads Total Variable Cost Contribution Less: Fixed Overheads Profit O 38.50,000 10,78,000 9,24,000 7.39,200 27.41.200 11.08,300 13.90.000 6.25.500 62,60,000 26,09,500 20,14,500 6,04,000 182.200 19.99 200 10 26,000 61,38,300 12.60.000 8.61,700 Product E, despite best efforts, does not show any good prospect to yield reasonable margins and it is not possible to raise its year. Products D and F have good potential to grow and the market can easily absorb the increased production The Company price so as to make it profitable. The Company has decided to discontinue is production war April of the forthcoming has decide to raise the production of Products and F by diverting the Labour of Product E to Product D and balance 40% to Product F. Following additional information is available for the forthcoming year beginning Aprik: (A) Total Direct Wage Bill for the year would be at the same level as for the previous year ending 31 arch. Material Cost per unit will increase by 5%, however Variable OH per unit will remain same, Fured OH would increase by 96 Sod (B) Selling Price per unit of Product D will increase by 4% and of Product F by 5%. Required: 1. Prepare Budget for the forthcoming year beginning April in the format as detailed above. 3. Solution: 2. Compare and analyse the Budget for the last two years highlighting main features Show calculation to the nearest Rapod. To advise the Management on comparative Contribution Profitability it Go Labour of Product is transferred to Product Finstead of Product Das above and balance 40% to Product Dinstead of Product F Show calculations up to the decimal points. Give detailed reasoning for your advice. 1. Percentage Analysis of Products and F (present and proposed) Particulars Product D Products Amt: Present % New Amt (a) Sales Present New 50.000 100.00% 100 4 = 104.00 30,20,000 100% 1005 -15.00 Material 10,78.000 28.00% 28.5% = 29.40 9,06,000 30% 30.5 31.50 Labour 9.24,000 24.00% Same - 24.00 6,04,000 20% Same 20.00 Overheads 232.200 19.20% Same 19.20 4,87,200 16% Sam 16.00 (b) Variable Cost 27,41,200 71.2096 22.60 19.93,200 66% 750 (c) Contribution 11.08 800 28.50% 31.40 10,26 800 3097 37.50 31.40 (D) PVR = (ca) 28.80% 30.19% 1256 104.00 -35.21% TOS.00 2. Computation of Revised Sales and Material Costs for next year (Situation : 60% and 40% for D and 5) Particulars Producto Product 416.500 60% = 291.900 4,36,500 40% 1,94,600 (a) Labour Cost diverted from E 2.91,500 - 12.16.250 1.94,600 (1) So, Extra Sales achieved 24% -9,73,000 2096 13.50.000 - 12,15.250 = 50,66.250 30,20,000 - 9.73.000 - 39.93.000 50,56,250 x 4% 202,650 39,93,000 x 5% = 1,99,650 52.68,900 41,92,650 50,66,250 x 289 14.18.550 39,93 000 x 3096 - 11,97 900 70,928 59,995 14,89,478 12.57.795 (c) New Sales at Previous Prices (0) Sales Price Increase (e) Revised Sales at Increased Prices (c+d) (0) Material Cost based on New Sales (9) Material Price Increase = ( x 5% (h) Revised Material Cost (f+) 9.92 CVP Analysis and Dersion Making 3. Budget for next year (situation I Grond a diarionfo and respectively) Particulars Product Produce Sales Total 11,92.00 94,51,550 Vartable costi Material 14,69 478 12,57,795 27,47,273 Lalo 9,24,000+2,01,60 = 12,15,000 6,04,000 +1,04,64% 7,98,600 20,14,500 Variable O 50,60,290 * 10.20% 0,22,720 39,93,000 x 16% 6,38,680 16,11,600 Total Variable Chat 36,281,1996 26,95,275 63,13,373 Contribution 15,90,802 14,97,375 30,88,177 Lessi Fixed on 13,56,500 (12,60,000 196,500) Profit 17,31,677 Noter Contribution Ants for a can be matdied at 30.19% 35.71%, on revised Sakers, as computed in WN 1 above. Aspect y Change 4.Comments and Observations on Actuals of Last Year and Budgets of Next Year Sales Increase Contribution Increase Profit Increase 94,61,550 () 82,60,000 14.55% 30,88,17221.21,700 17,31,677) 8,61,700 -45.55% 100.96% 82,60,000 21,21,700 8,61,700 Inspite of only 14.55% increase in Soles, there is an increase of 45.55% in Contribution, due to Total Labour Cost and VOH per unit remaining the same as in last year Increase in Pront by 100,96% is attributed to Operating Leverage Effect, inspite of marginal increase in Fixed Costs. The Company's decision to discontinue and use those Labour efforts for "D" and "F" is prima facie beneficial INote: Product wise % Comparison and Analysis of both years is given in WN 1 itself. S. Computation of Revised Sales and Material Costs for next year (Situation II: 40% and 60% for D and F). Particulars Product D Product F (a) Labour Cost diverted from E 4,86,500 x 40% 1,94,600.000 4,86,500 x 60% = 2,91,900.00 (b) So, Extra Sales achieved 1,94,600 2,91,900 8,10,833 333 - 14,59,500.00 24% 20% (c) New Sales at Previous Prices 38,50,000 + 8,10,833.333 30,20,000 + 14,59,500 = 46,60,833,333 = 44,79,500.00 (d) Sales Price Increase 46,60,833.333 x 4% 1,86,433.333 44,79,500 x 5% = 2,23,975.00 (e) Revised Sales at Inar. Price = (c + d) 48,47,266.667 47,03,475.00 0 Material Cost based on New Sales 46,60,833.333 x 28% = 13,05,033 333 44,79,500 x 30% = 13,43,850.00 (9) Material Price Increase (0) x 5% 65,251.667 67,192.50 (h) Revised Material Cost (1+9) 13,70,285.000 14,11,042.50 6. Budget for next year (Situation II: 40% and 60% diversion for D and F respectively) Particulars Product D Product F Total Sales 48,47,266,667 47,03,475.000 95,50,741.667 Variable Cost: Material 13,70,285.000 14,11,042.500 27,81,327.500 Labour 9,24,000 + 1,94,600=11,18,600.000 6,04,000 + 2,91,900 =8,95,900.000 20.14,500,000 Variable OH 46,60,833 x 19.20%= 8,94,880.000 44,79,500 x 16.00%= 7,16,720.000 16,11,600.000 Total Variable Cost 33,83,765.000 30,23,662.500 64,07,427.500 Contribution 14,63,501.667 16,79,812.500 31,43,314.167 Less: Fixed OH (12,60,000+ 96,500) 13,56,500.000 Profit 17,86,814.167 Note: Contribution Amts for D & F can be matched at 30.19% & 35.71% on revised Sales, as computed in WN 1 above. 9.93Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


