Question: Need to answer a-e thank you - There are two ways for locals to earn income in the DRC, mining and farming. - A large

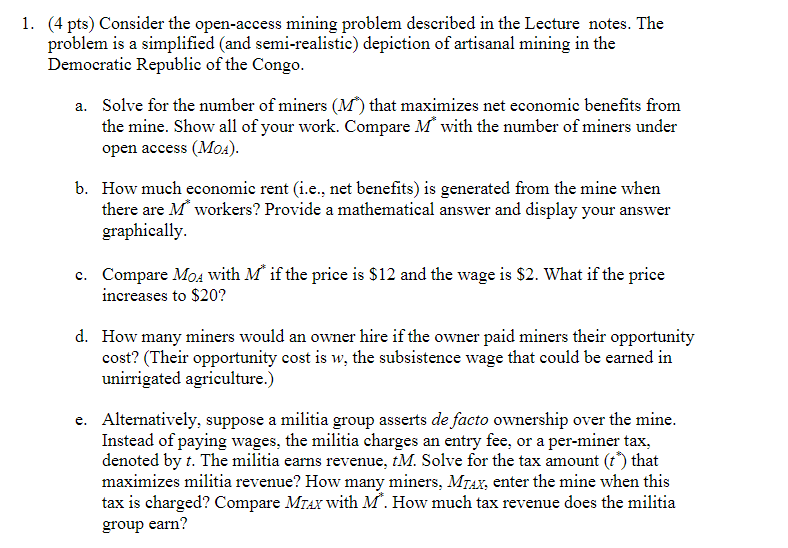
Need to answer a-e thank you
- There are two ways for locals to earn income in the DRC, mining and farming. - A large number of homogenous laborers could be miners (M) or farmers (F) such that L=F+M. Unirrigated farm land is sufficiently abundant such that that each laborer can earn a subsistence wage of whe - Earnings from the mining site are pY, where p>0 is the price of minerals and Y is the output. - Productivity at the mining site is given by Y=M1/2. (4 pts) Consider the open-access mining problem described in the Lecture notes. The problem is a simplified (and semi-realistic) depiction of artisanal mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. a. Solve for the number of miners (M) that maximizes net economic benefits from the mine. Show all of your work. Compare M with the number of miners under open access (MOA). b. How much economic rent (i.e., net benefits) is generated from the mine when there are M workers? Provide a mathematical answer and display your answer graphically. c. Compare MOA with M if the price is $12 and the wage is $2. What if the price increases to $20 ? d. How many miners would an owner hire if the owner paid miners their opportunity cost? (Their opportunity cost is w, the subsistence wage that could be earned in unirrigated agriculture.) e. Alternatively, suppose a militia group asserts de facto ownership over the mine. Instead of paying wages, the militia charges an entry fee, or a per-miner tax, denoted by t. The militia earns revenue, tM. Solve for the tax amount (t) that maximizes militia revenue? How many miners, MTAX, enter the mine when this tax is charged? Compare MTAX with M. How much tax revenue does the militia group earn? - There are two ways for locals to earn income in the DRC, mining and farming. - A large number of homogenous laborers could be miners (M) or farmers (F) such that L=F+M. Unirrigated farm land is sufficiently abundant such that that each laborer can earn a subsistence wage of whe - Earnings from the mining site are pY, where p>0 is the price of minerals and Y is the output. - Productivity at the mining site is given by Y=M1/2. (4 pts) Consider the open-access mining problem described in the Lecture notes. The problem is a simplified (and semi-realistic) depiction of artisanal mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. a. Solve for the number of miners (M) that maximizes net economic benefits from the mine. Show all of your work. Compare M with the number of miners under open access (MOA). b. How much economic rent (i.e., net benefits) is generated from the mine when there are M workers? Provide a mathematical answer and display your answer graphically. c. Compare MOA with M if the price is $12 and the wage is $2. What if the price increases to $20 ? d. How many miners would an owner hire if the owner paid miners their opportunity cost? (Their opportunity cost is w, the subsistence wage that could be earned in unirrigated agriculture.) e. Alternatively, suppose a militia group asserts de facto ownership over the mine. Instead of paying wages, the militia charges an entry fee, or a per-miner tax, denoted by t. The militia earns revenue, tM. Solve for the tax amount (t) that maximizes militia revenue? How many miners, MTAX, enter the mine when this tax is charged? Compare MTAX with M. How much tax revenue does the militia group earn
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


