NET 363 Homework 3 Due Sunday, February 27, 2022, by 11:59 pm 50 points total 1. A DHCP Server allocates each IPv4 address with

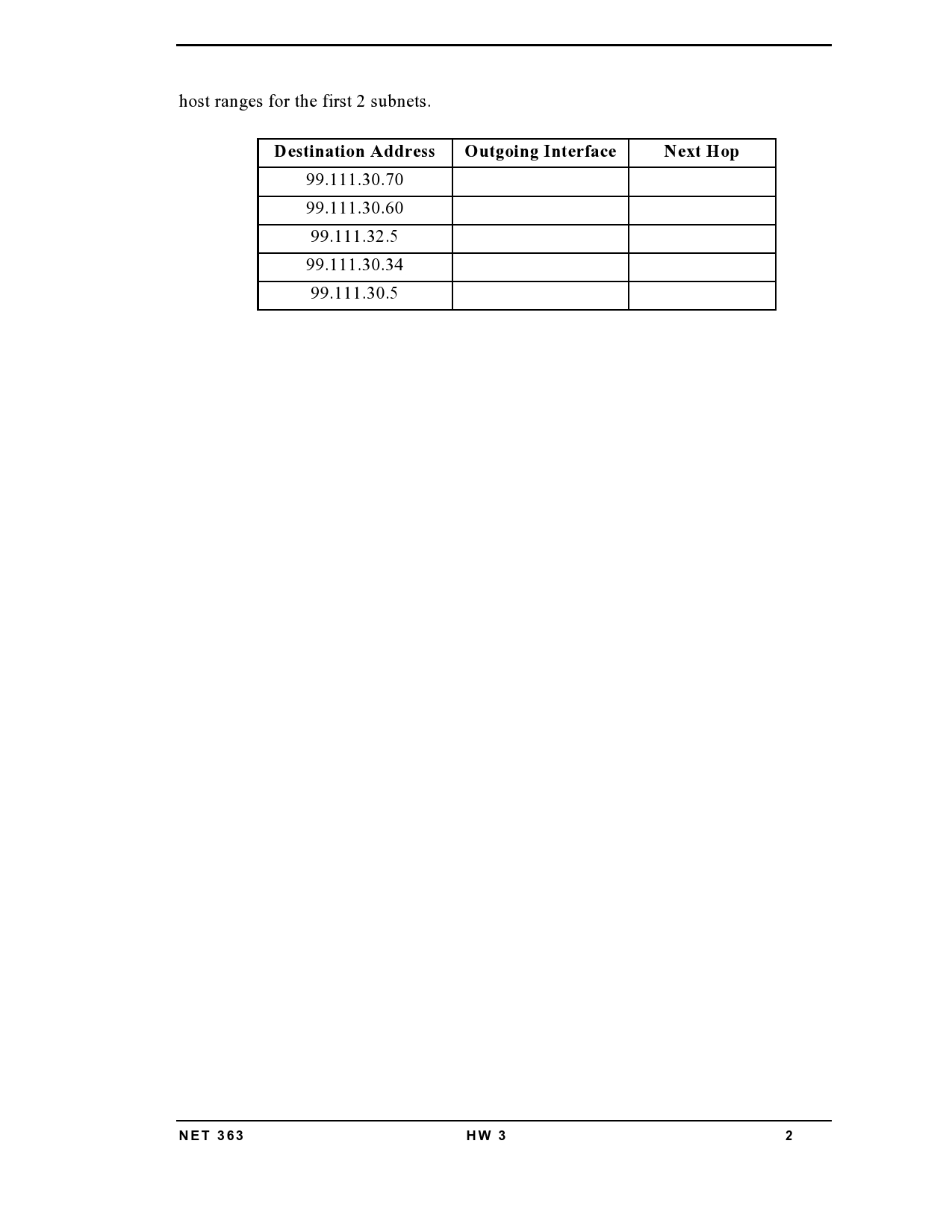
NET 363 Homework 3 Due Sunday, February 27, 2022, by 11:59 pm 50 points total 1. A DHCP Server allocates each IPv4 address with a lease time. a) (3 pts) What is the purpose of the lease time? b) (2 pts) What happens if an IPv4 client does not renew its IPv4 address before the lease time expires? (flip Os to 1s) 2. (5 pts) Write out the IPv6 address 2001:6A:112:2BB::69:C in binary. Your answer must contain 128-bit values - each bit value being '0' or '1'. 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 3. (5 pts) A workstation has a single Ethernet interface with MAC address 00:AB:99:51:C3:22. What is the IPv6 Link-Local Address for this interface, assuming the workstation uses the EUI-64 method to generate its Interface Identifier? 4. IPv6 does not use the ARP protocol. a) (3 pts) What protocol provides ARP functionality on an IPv6 network? 5. 6. b) (2 pts) What IPv6 Table serves the same purpose as the IPv4 ARP table for IPv6 hosts? When an IPv6 device with no pre-configured IPv6 address powers up, it can calculate a global 128-bit IPv6 address for itself using Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC), which combines two values: (a) a 64-bit IPv6 Prefix for the subnet (link) and (b) a 64-bit Interface ID (IID). a) (5 pts) How does the device learn the value of the IPv6 Prefix for its subnet? b) (5 pts) How does the device determine the value of its IID? Describe 2 ways. Describe two important differences between GLBP and HSRP. a) (3 pts) b) (2 pts) 7. (5 pts) In HSRP, what is the purpose of Interface Tracking? 8. (10 pts) Consider a router that has the following Routing Table contents. Destination Subnet Outgoing Interface Next Hop 99.111.30.32/27 Fa0/0 118.2.77.4 99.111.16.0/20 0.0.0.0/0 Fa0/1 59.16.1.1 Fa0/2 18.12.52.43 For each Destination Address, fill in the table below with Outgoing Interface and Next Hop. Show your work if you want a chance at partial credit, i.e., determine the valid IP NET 363 HW 3 1 host ranges for the first 2 subnets. Destination Address 99.111.30.70 99.111.30.60 99.111.32.5 99.111.30.34 99.111.30.5 NET 363 Outgoing Interface Next Hop HW 3 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


