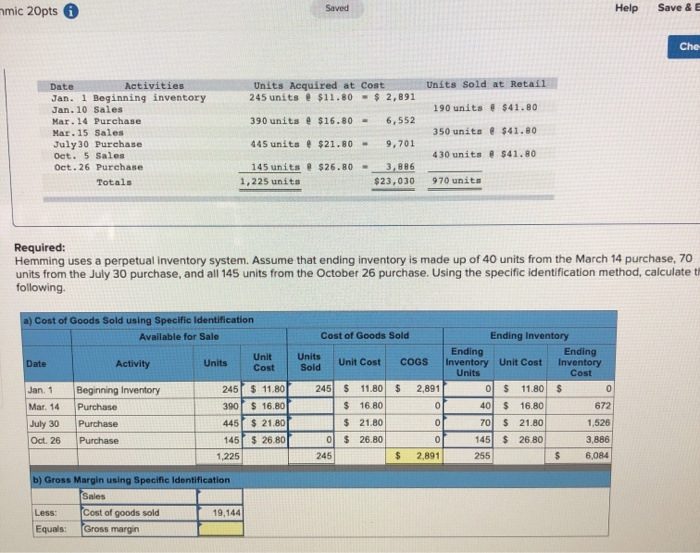
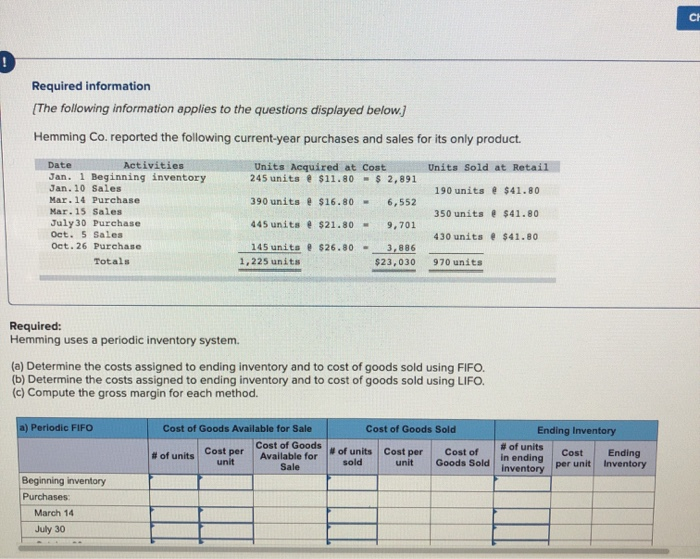
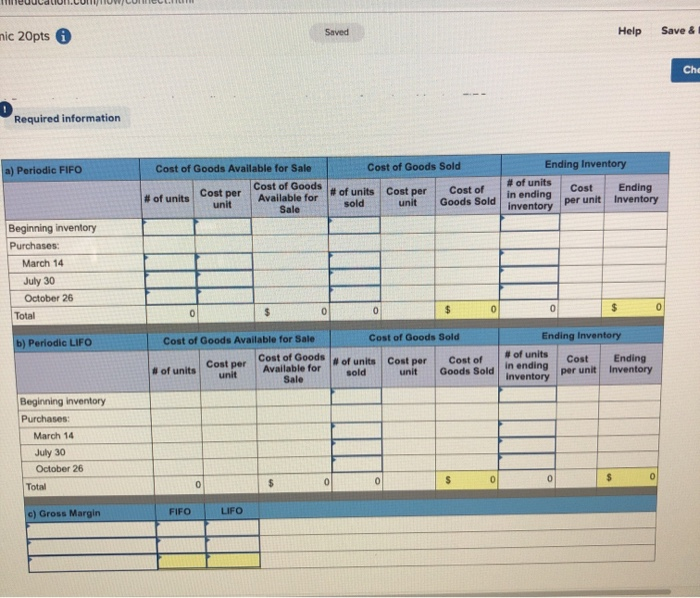
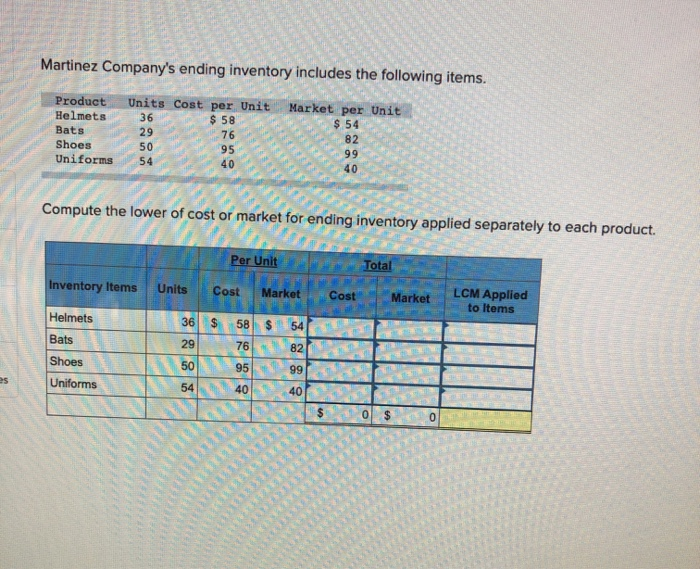
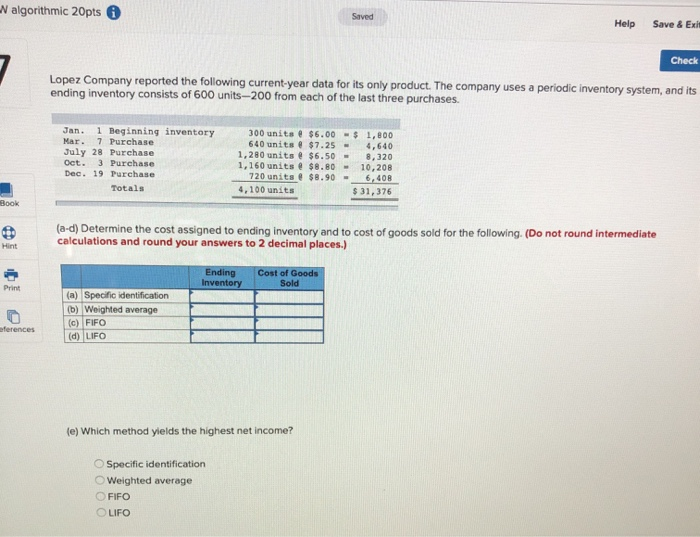
nmic 20pts 6 Saved Help Save & E Che Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 245 units $11.80 - $ 2,891 190 units $41.80 390 units @ $16.80 - 6,552 Date Activities Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Jan. 10 Sales Mar. 14 Purchase Mar. 15 Sales July 30 Purchase Oct. 5 Sales Oct. 26 Purchase Totals 350 units $41.80 445 units $21.80 - 9,701 430 units . $41.80 $26.80 - 145 units 1,225 units 3,886 $23,030 970 units Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. Assume that ending inventory is made up of 40 units from the March 14 purchase, 70 units from the July 30 purchase, and all 145 units from the October 26 purchase. Using the specific identification method, calculatet following a) Cost of Goods Sold using Specific Identification Available for Sale Date Activity Units Unit Cost Beginning Inventory Jan 1 Mar. 14 July 30 Oct 26 Purchase 245 390 445 Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Ending Units Ending Sold Unit Cost COGS Inventory Unit Cost Inventory Units Cost 245 $ 11.80 $ 2,891 o $ 11.80 $ $ 16.80 of 40 $ 16.80 672 $ 21.80 of 70 $ 21.80 1,526 0 $ 26.80 0 145 $ 26.80 245 $ 2,891 255 $ 11.80 $ 16.80 $ 21.80 Purchase Purchase 526 80 745 1.225 b) Gross Margin using Specific Identification Sales Cost of goods sold 19,144 Equals: Gross margin Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Hemming Co. reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Units Acquired at Cost 245 units $11.80 $ 2.891 Units Sold at Retail 190 units @ $41.80 390 units @ $16.80 = 6,552 Date Activities Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Jan. 10 Sales Mar. 14 Purchase Mar. 15 Sales July 30 Purchase Oct. 5 Sales Oct. 26 Purchase Totals 350 units $41.80 445 units @ $21.80 = 9,701 430 units $41.80 145 units @ $26.80 - 1,225 units 3,886 $23,030 970 units Required: Hemming uses a periodic inventory system. (a) Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO, (b) Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. (c) Compute the gross margin for each method. a) Periodic FIFO Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Available for unit Sale of units Cost per of units Cost per sold unit Ending Inventory of units Cost Ending in ending Inventory per unit inventory Cost of Goods Sold Beginning inventory Purchases March 14 July 30 nic 20pts Help Save & Ch Required information a) Periodic FIFO Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold of units Cost per Cost of sold unit Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost per # of units Ending Inventory # of units Cost Ending in ending per unit Inventory inventory unit Beginning inventory Purchases: March 14 July 30 October 26 Total 0 0 0 b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Cost per of units unit Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold of units Cost per unit Goods Sold Ending Inventory of units Cost Ending in ending Inventory per unit Inventory sold Beginning inventory Purchases March 14 July 30 October 26 Total 1 ol 0 c) Gross Margin FIFO L IFO Martinez Company's ending inventory includes the following items. Product Units Cost per Unit Market per Uni Helmets36 $ 58 $ 54 Bats 2976 82 Shoes 50 9 5 Uniforms 54 40 Compute the lower of cost or market for ending inventory applied separately to each product. T otal Market LCM Applied to Items Per Unit Units Cost Market 36 S 58 $ 54 29 76 822 N9599 544040 $ / / Inventory Items Helmets Bats Shoes Uniforms / / / 50 / / / / / / 0 $ O - / SA algorithmic 20pts Help Save & Exi Check Lopez Company reported the following current-year data for its only product. The company uses a periodic inventory system, and its ending inventory consists of 600 units-200 from each of the last three purchases. Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 7 Purchase July 28 Purchase Oct. 3 Purchase Dec. 19 Purchase Totals 300 units $6.00 640 units @ $7.25 - 1,280 units $6.50 = 1,160 units @ $8.80 720 units $8.90 4,100 units $ 1.800 4.640 8,320 1 0,208 6.408 $31.376 Book (a-d) Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold for the following. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold (a) Specific identification (b) Weighted average (c) FIFO (d) LIFO (e) Which method yields the highest net income? Specific identification Weighted average FIFO LIFO