Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
No there isnt a relation betwen A and B. public class Dog open TAB * The name of this dog Method comments must be written

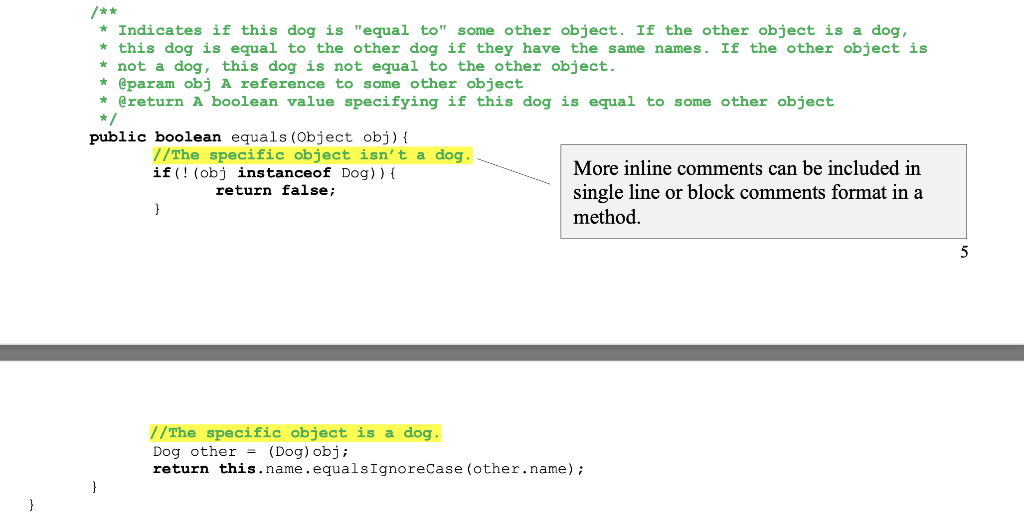




No there isnt a relation betwen A and B.
public class Dog open TAB * The name of this dog Method comments must be written in Javadoc for before the method header, the first word must be a capitalized verb in the third person. Use punctuat marks properly. private String name; TAB TAB * Constructs a newly created Dog object that represents a dog with an empty name. */ public Dog() { this(""); open { TAB A description of the method, comments on /** parameters if any, and comments on the return ty * Constructs a newly created Dog object wit if any are required. * @param name The name of this dog A Javadoc comment for a formal parameter consists of */ three parts: public Dog (String name) { - parameter tag, this.name = name; } - a name of the formal parameter in the design, (The name must be consistent in the comments and the /** header.) * Returns the name of this dog. - and a phrase explaining what this parameter specifies. * @return The name of this dog A Javadoc comment for return type consists of two par - return tag, public String getName() { - and a phrase explaining what this returned value specifie return this.name; } * Changes the name of this dog. * @param name The name of this dog */ public void setName (String name) { this.name = name; } /** * Returns a string representation of this dog. The returned string contains the type of this dog and the name of this dog. * @return A string representation of this dog */ public String toString() { return this.getClass().getSimpleName() ": " + this.name; + * Indicates if this dog is "equal to" some other object. If the other object is a dog, * this dog is equal to the other dog if they have the same names. If the other object is not a dog, this dog is not equal to the other object. * @param obj A reference to some other object * @return A boolean value specifying if this dog is equal to some other object */ public boolean equals (Object obj) { //The specific object isn't a dog. if (! (obj instanceof Dog) ) { More inline comments can be included in return false; single line or block comments format in a } method. 5 //The specific object is a dog. Dog other = (Dog) obj; return this.name.equals Ignorecase (other.name); Part IV: A. How to test a software design? There can be many classes in a software design. 1. First, create a UML class diagram containing the designs of all classes and the class relationships (For example, is-a, dependency or aggregation). 2. Next, test each class separately. Convert each class in the diagram into a Java program. When implementing each class, a driver is needed to test each method included in the class design. In the driver program, i. Use the constructors to create instances of the class(If a class is abstract, the members of the class will be tested in its subclasses.). For example, the following creates Dog objects. Create a default Dog object. Dog firstDog = new Dog(); Create a Dog object with a specific name. Die secondDog = new Dog ("Sky"); ii. Use object references to invoke the instance methods. If an instance method is a value-returning method, call this method where the returned value can be used. For example, method getName can be called to return a copy of firstDog's name. String first DogName; firstDogName = firstDog.getName(); You may print the value stored in firstDogName to verify. iii. If a method is a void method, invoke the method that simply performs a task. Use other method to verify the method had performed the task properly. For example, setName is a void method and changes the name of this dog. After this statement, the secondDog's name is changed to Blue. secondDog.setName ("Blue"); getName can be used to verify that setName had performed the task. iv. Repeat until all methods are tested. . And then, test the entire design by creating a driver program and a helper class of the driver program. i. Create a helper class. In the helper class, minimum three static methods should be included. public class Helper //method 1 public static void start() { This void method is decomposed. It creates an empty list. It calls the create method to add a list of objects to the list. And then, it calls the display method to display the list of objects. } //method 2 public static returnTypeOrvoid create (parameters if any) { This method creates a list of objects using data stored in text files. } 6 //method 3 public static returnTypeOrvoid display (parameters if any) { This method displays a list of objects. } } ii. Create a driver program. In main of the driver program, call method start to start the entire testing process. public class Driver public static void main(String[] args) { Helper.start(); } } B. Project description Project 1 Abstract Data Type(ADT) Bag An ADT Bag is composed of a list of grocery items and a set of operations on the list. You may think of a grocery bag as an instance of the ADT Bag. A grocery bag contains a list of groceries. There is a set of operations that operate on the list. For example, we can add an item, remove an item, count the number of items, check for a specific item, etc. In this project, you will design an ADT bag by following software development cycle including specification, design, implementation, test/debug, and documentation. . Specification/Analysis: The ADT Bag must contain the following operations: create an empty bag that can hold up to 100 items add an item to the end of the list of this bag- insert(item) remove the item at the end of this bag - removeLast() remove an item at a random index from this bag -removeRandom() get the index of the first occurrence of an item from this bag - get(a reference to an item) get a reference to an item at position index of this bag(get(index)), check how many items are there in this bag - size() check to see if this bag is empty - isEmpty() empty this bag - makeEmpty() . 0 0 . public class Dog open TAB * The name of this dog Method comments must be written in Javadoc for before the method header, the first word must be a capitalized verb in the third person. Use punctuat marks properly. private String name; TAB TAB * Constructs a newly created Dog object that represents a dog with an empty name. */ public Dog() { this(""); open { TAB A description of the method, comments on /** parameters if any, and comments on the return ty * Constructs a newly created Dog object wit if any are required. * @param name The name of this dog A Javadoc comment for a formal parameter consists of */ three parts: public Dog (String name) { - parameter tag, this.name = name; } - a name of the formal parameter in the design, (The name must be consistent in the comments and the /** header.) * Returns the name of this dog. - and a phrase explaining what this parameter specifies. * @return The name of this dog A Javadoc comment for return type consists of two par - return tag, public String getName() { - and a phrase explaining what this returned value specifie return this.name; } * Changes the name of this dog. * @param name The name of this dog */ public void setName (String name) { this.name = name; } /** * Returns a string representation of this dog. The returned string contains the type of this dog and the name of this dog. * @return A string representation of this dog */ public String toString() { return this.getClass().getSimpleName() ": " + this.name; + * Indicates if this dog is "equal to" some other object. If the other object is a dog, * this dog is equal to the other dog if they have the same names. If the other object is not a dog, this dog is not equal to the other object. * @param obj A reference to some other object * @return A boolean value specifying if this dog is equal to some other object */ public boolean equals (Object obj) { //The specific object isn't a dog. if (! (obj instanceof Dog) ) { More inline comments can be included in return false; single line or block comments format in a } method. 5 //The specific object is a dog. Dog other = (Dog) obj; return this.name.equals Ignorecase (other.name); Part IV: A. How to test a software design? There can be many classes in a software design. 1. First, create a UML class diagram containing the designs of all classes and the class relationships (For example, is-a, dependency or aggregation). 2. Next, test each class separately. Convert each class in the diagram into a Java program. When implementing each class, a driver is needed to test each method included in the class design. In the driver program, i. Use the constructors to create instances of the class(If a class is abstract, the members of the class will be tested in its subclasses.). For example, the following creates Dog objects. Create a default Dog object. Dog firstDog = new Dog(); Create a Dog object with a specific name. Die secondDog = new Dog ("Sky"); ii. Use object references to invoke the instance methods. If an instance method is a value-returning method, call this method where the returned value can be used. For example, method getName can be called to return a copy of firstDog's name. String first DogName; firstDogName = firstDog.getName(); You may print the value stored in firstDogName to verify. iii. If a method is a void method, invoke the method that simply performs a task. Use other method to verify the method had performed the task properly. For example, setName is a void method and changes the name of this dog. After this statement, the secondDog's name is changed to Blue. secondDog.setName ("Blue"); getName can be used to verify that setName had performed the task. iv. Repeat until all methods are tested. . And then, test the entire design by creating a driver program and a helper class of the driver program. i. Create a helper class. In the helper class, minimum three static methods should be included. public class Helper //method 1 public static void start() { This void method is decomposed. It creates an empty list. It calls the create method to add a list of objects to the list. And then, it calls the display method to display the list of objects. } //method 2 public static returnTypeOrvoid create (parameters if any) { This method creates a list of objects using data stored in text files. } 6 //method 3 public static returnTypeOrvoid display (parameters if any) { This method displays a list of objects. } } ii. Create a driver program. In main of the driver program, call method start to start the entire testing process. public class Driver public static void main(String[] args) { Helper.start(); } } B. Project description Project 1 Abstract Data Type(ADT) Bag An ADT Bag is composed of a list of grocery items and a set of operations on the list. You may think of a grocery bag as an instance of the ADT Bag. A grocery bag contains a list of groceries. There is a set of operations that operate on the list. For example, we can add an item, remove an item, count the number of items, check for a specific item, etc. In this project, you will design an ADT bag by following software development cycle including specification, design, implementation, test/debug, and documentation. . Specification/Analysis: The ADT Bag must contain the following operations: create an empty bag that can hold up to 100 items add an item to the end of the list of this bag- insert(item) remove the item at the end of this bag - removeLast() remove an item at a random index from this bag -removeRandom() get the index of the first occurrence of an item from this bag - get(a reference to an item) get a reference to an item at position index of this bag(get(index)), check how many items are there in this bag - size() check to see if this bag is empty - isEmpty() empty this bag - makeEmpty() . 0 0 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


