Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
NOTE: SECOND TIME POSTING THIS QUESTION. PREVIOUS ANSWERS TO THIS QUESTION THAT EVEN OTHERS POSTED WERE FILLED WITH ERRORS AND MADE NO SENSE AT ALL.
NOTE: SECOND TIME POSTING THIS QUESTION. PREVIOUS ANSWERS TO THIS QUESTION THAT EVEN OTHERS POSTED WERE FILLED WITH ERRORS AND MADE NO SENSE AT ALL. (A LOT OF ERRORS/UNNECESSARY CODE SUCH "cout& #8203; `oaicite:", MADE ZERO SENSE).
COULD NOT TELL WHICH CODE IS FOR WHICH FILE NAMES. PLEASE LABEL ALL CODE ACCORDINGLY AS STATED IN THE INSTRUCTIONS. PLEASE AND THANK YOU.
C++ PROGRAMMING QUESTION. 3 FILES 1) testmaterials.cc 2) materials.cc 3) materials.h

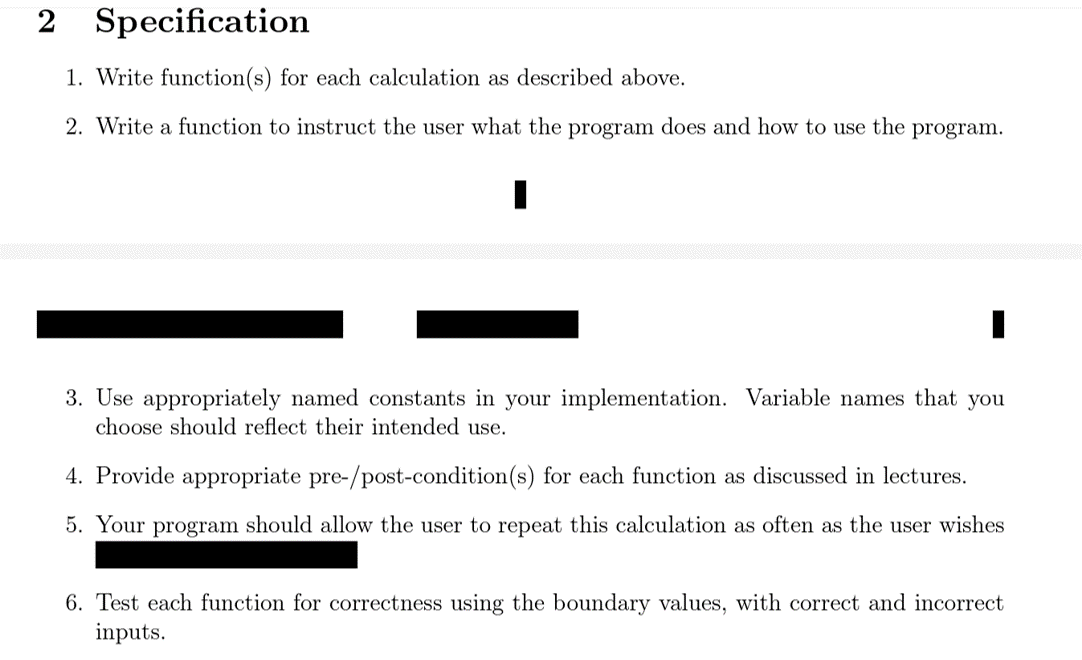

a warm-up exercise to designing programs using the top-down approach you are to write a C++ program to estimate the some of the materials required to renovate a rectangular room with a flat ceiling that is parallel the floor. The program asks for the room's length, width, height, the number of doorway ppenings and the number of windows, then computes the materials needed according to the tormulas: - Litres of paint = wall space (m2) divided by 6.5L/m2 then subtract 1L for every 4 windows or doors. (Note: If there is one door and two windows then do not subtract any litres but if there are three doors and three windows then subtract 1L.) - Boxes of flooring = floor space (m2) plus 0.05m2 per doorway divided by 1.8m2/ box. Adjust the number of boxes by adding an extra 1 box for every 10 boxes, round up. (Note: If the number of boxes required is 1 to 10 then the adjustment would add 1 box but if the number of boxes required is 21 to 30 then add 3 boxes.) - Trim in linear meters = the circumference of the room, plus 4 meters per door, plus 5 meters per window then add a cm for every three corners in the trim (round down) to account for the additional kerf. The trim includes the base board and the casing around each doorway and window. The room has four corners, each doorway has four corners and each window has four corners. 2 Specification 1. Write function(s) for each calculation as described above. 2. Write a function to instruct the user what the program does and how to use the program. 3. Use appropriately named constants in your implementation. Variable names that you choose should reflect their intended use. 4. Provide appropriate pre-/post-condition(s) for each function as discussed in lectures. 5. Your program should allow the user to repeat this calculation as often as the user wishes 6. Test each function for correctness using the boundary values, with correct and incorrect inputs. 1. Write the prototype declaration of each function in a file named 2. Write the implementation code for each function in a file named 3. Write the main program code in a file named
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


