Question
Objective of this Assignment: First Part: Develop an understanding of how to read and interpret financial statements. It is important to be able to understand
Objective of this Assignment:
- First Part: Develop an understanding of how to read and interpret financial statements. It is important to be able to understand and build financial statements these skills are essential to effective business planning. Interpret existing financial statements by building ratio analysis and interpretation abilities.
- Second Part: Based on supplied assumptions, create financial forecasting statements for your friends business idea (see Assignment 1 for background details).
Assignment Tasks:
Part A (7 marks)
Please find attached a multi-year Income Statement (Appendix A1) and multi-year Balance Sheet (Appendix A2) for Canadian Motorbikes. This company is a (fictional) motorcycle manufacturer that brought on a new CEO in 2012. You work for an investment company that is considering investing in the motorcycle company and, if the investment is made, whether or not to retain the CEO. You are part of a team that is evaluating the performance of the company. Your job is to calculate and interpret important financial ratios and to make comments to help make a decision on whether or not to invest. Appendix A3 contains financial ratio averages for all companies in the industry. This should be useful.
Please use the information in Appendices A1 to A3 to do the following:
- Calculate the Current Ratio, Debt Ratio, Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE). For the ROA and ROE, you should use the average total assets and the average total equity in your calculations. (The average is the total across two years divided by two). Calculate these values for each of 2011-2014. Interpret your calculations: what does this information mean? How is the company doing? (5 marks)
- Calculate ratios related to how quickly the company pays its trade debt and how quickly it collects from its customers. These are known as Accounts Payable (AP) Turnover and Accounts Receivable (AR) Turnover. The formula for AP Turnover is: cost of goods sold/average accounts payable. The formula for AR Turnover is: credit sales/average accounts receivable. [Note: For this assignment, you can use the Sales numbers that are given in the table for the Credit Sales numbers in the AR Turnover calculations.] Calculate the AP and AR Turnover for each of the years 2011 2014. Interpret your calculations: What does this information mean? How is the company doing? (2 marks)
Part B (18 marks) (Please review pages 346 to 361 of the course textbook)
It is now January 1st, 2021 and your friend has decided to start that new business. They have decided to: (1) provide equipment access and (2) offer training courses and (3) sell merchandise.
Part B1: Based on a number of assumptions your friend wants to forecast the first years Income Statement and Balance Sheet. Once again they call upon you to assist them in creating the forecasted statements. In this assignment you are to construct an Income Statement and Balance Sheet based on the assumptions your friend has provided to you. (6 marks)
- First year sales will total $100,000
- Gross margins will be 50%
- Operating margins will be 20%
- Accounts Receivable will be about 15% of sales
- Inventory will be 12% of sales
- Accounts Payable will be 5% of sales
- Accrued expenses payable will be 7% of sales
- The Bank will provide a loan of $50,000. The annual interest will be 4%, compounded annually. Interest-only payments are needed until the loan is due in 5 years, where a balloon payment for the full balance must be paid.
- The combined federal and provincial tax rates will be 30%
- Capital equipment purchases will be made at the start of the year. These will total $70,000. These will depreciate at 10% per year.
- Your friend wants ending cash to be $24,500, to have this amount on hand at year-end.
- Your friend will provide any other capital needed in the form of equity financing.
Part B2: It is January 1st, 2022. The previous year (2021) turned out very well for your friend the projections were quite close. You are now being asked to project out an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and a Cash Flow Statement for 2022 using the new assumptions outlined below. (8 marks)
- 2022 year sales will be 25% higher than the $100,000 realized in 2021
- Gross margins in 2022 will be 55%, 5% higher than the 50% realized in 2021
- Operating margins will be 22%, 2% higher than 20% realized in 2021
- Accounts Receivable will be 12% of sales, lower than the 15% seen in 2021
- Inventory will be 15% of sales, higher than the 12% seen in 2021
- Accounts Payable will be 4% of sales in 2022, lower than the 5% seen in 2021
- Accrued expenses payable will be 4% of sales in 2022, lower than the 7% seen in 2021
- The Bank will continue to be paid 4% interest on the $50,000 worth of loans
- The combined federal and provincial tax rates will be 30%
- No new capital purchases are made
- Closing cash is expected to remain at the same level predicted for and seen in 2021
- Depreciation of existing capital equipment continues at the same rate observed in 2021
Part B3: Comment on the performance of your friends company. How is the company doing? The friend is currently working at this business part-time.
- Should the friend quit the other job and work at this full-time?
- Should they do the opposite and exit the business?
- Or, should they stay the course and see how things unfold?
What other kinds of information might you want to know to answer these questions? (4 marks)
Supporting Details: Your assignment is to be submitted either in Microsoft WORD or Microsoft EXCEL format.
It should be submitted with the following guidelines:
- Include a cover page with the course code and course name, the assignment number, the title of your assignment, your name, the instructors name, and the date the assignment is created.
- Ensure that the first page of your assignment has the title at the top of the page and the sections of your report have headings and subheadings to chunk your paper into sections for each of the topics you are writing about.
- Font should be either Calibri or Arial, 11pt. Text should be double spaced but table may be single spaced.
- You must cite all of your sources of information using APA formatting.
- Create a separate reference page that lists all of your sources that you have cited in text. Sources include software used. Also, personal communications from a professional in the field count as a reference source. For citation and referencing examples, see https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
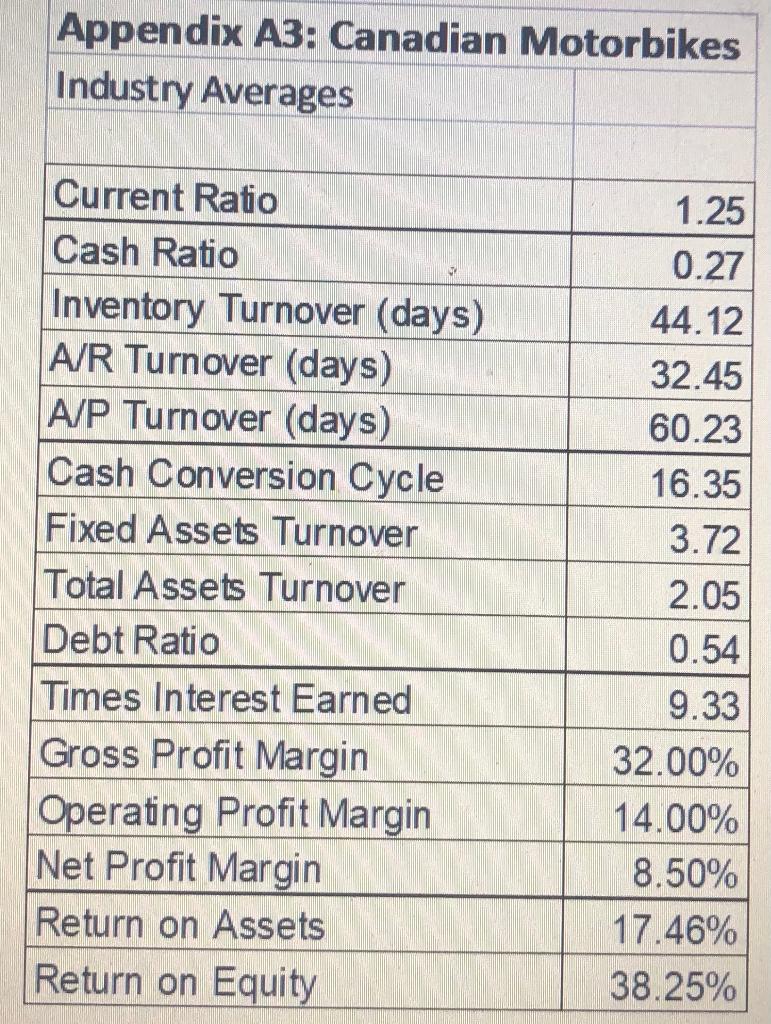
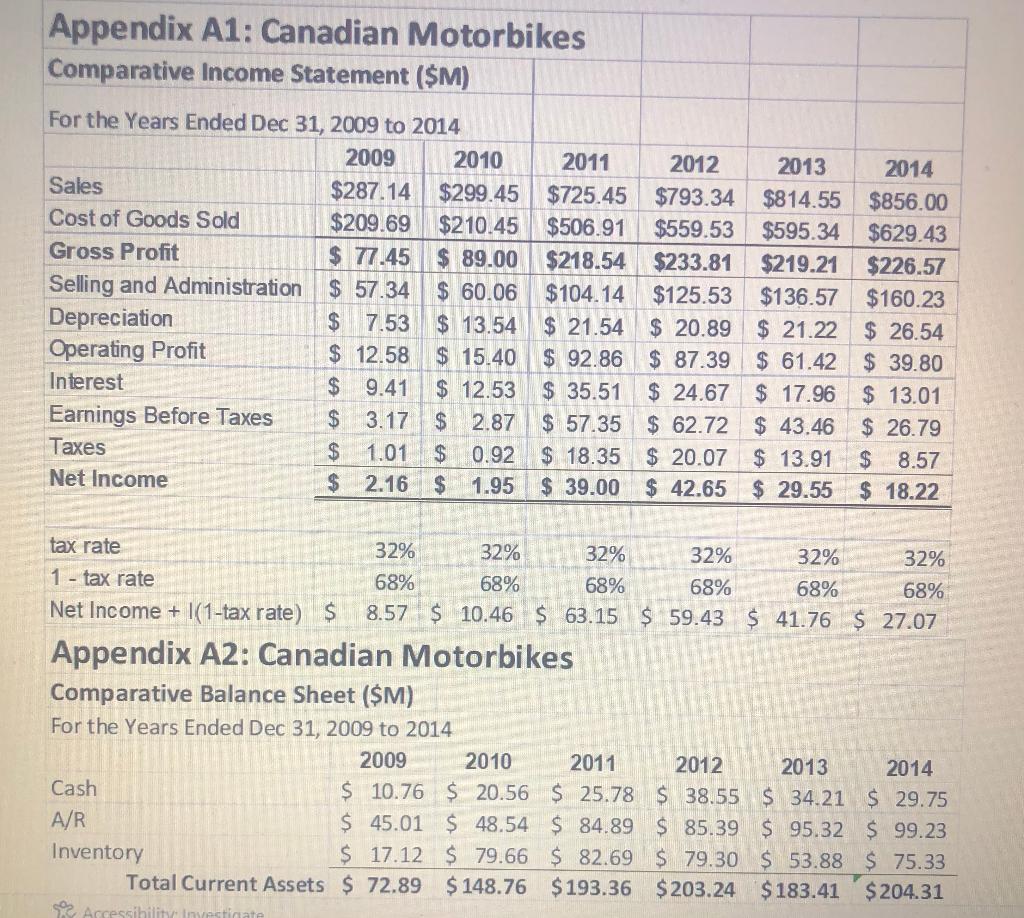
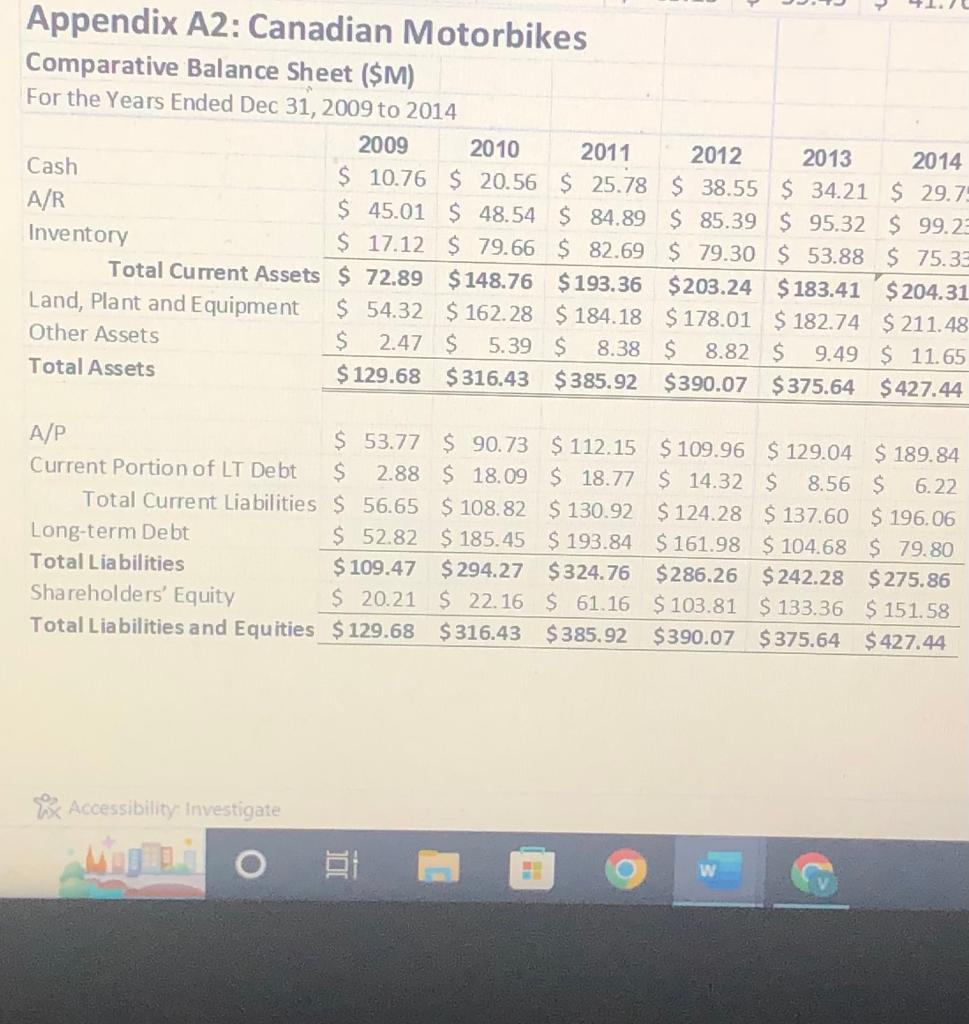
Appendix A3: Canadian Motorbikes Industry Averages Current Ratio Cash Ratio Inventory Turnover (days) A/R Turnover (days) A/P Turnover (days) Cash Conversion Cycle Fixed Assets Turnover Total Assets Turnover Debt Ratio Times Interest Earned Gross Profit Margin Operating Profit Margin Net Profit Margin Return on Assets Return on Equity 1.25 0.27 44.12 32.45 60.23 16.35 3.72 2.05 0.54 9.33 32.00% 14.00% 8.50% 17.46% 38.25% Appendix A1: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Income Statement ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2011 2012 2010 $287.14 $299.45 $209.69 $210.45 $725.45 $793.34 $506.91 $559.53 $77.45 $89.00 $219.21 $226.57 $218.54 $233.81 $125.53 $136.57 $20.89 $21.22 $26.54 $160.23 $ 57.34 $ 60.06 $104.14 $ 7.53 $13.54 $21.54 $ 92.86 $87.39 $61.42 $39.80 $35.51 $24.67 $17.96 $ 13.01 $57.35 $62.72 $43.46 $26.79 $18.35 $ 20.07 $13.91 $ 8.57 $29.55 $ 18.22 $ 12.58 $15.40 $9.41 $ 12.53 3.17 $ 2.87 1.01 $ 0.92 2.16 $ 1.95 $39.00 $42.65 Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling and Administration Depreciation Operating Profit Interest Earnings Before Taxes Taxes Net Income $ $ $ tax rate 32% 1 - tax rate 68% Net Income + 1(1-tax rate) $ 8.57 Cash A/R Inventory 32% 68% 32% 68% $10.46 $ 63.15 Total Current Assets $72.89 $148.76 $193.36 Accessibil 2013 2014 $814.55 $856.00 $595.34 $629.43 32% 68% 32% 32% 68% 68% $59.43 $ 41.76 $ 27.07 Appendix A2: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Balance Sheet ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 $ 10.76 $ 20.56 $ 25.78 $38.55 $ 34.21 $29.75 $45.01 $ 48.54 $84.89 $ 85.39 $ 95.32 $ 99.23 $ 17.12 $ 79.66 $ 82.69 $79.30 $53.88 $ 75.33 $203.24 $183.41 $204.31 Appendix A2: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Balance Sheet ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 $ 10.76 $ 20.56 $25.78 $38.55 $34.21 $29.75 $45.01 $ 48.54 $84.89 $85.39 $95.32 $ 99.23 $ 17.12 $ 79.66 $ 82.69 $ 79.30 $ 53.88 $ 75.33 $72.89 $148.76 $193.36 $203.24 $183.41 $204.31 $ 54.32 $ 162.28 $184.18 $178.01 $182.74 $211.48 $ 2.47 $ 5.39 $ 8.38 $ 8.82 $ 9.49 $ 11.65 $129.68 $316.43 $385.92 $390.07 $375.64 $427.44 Cash A/R Inventory Total Current Assets Land, Plant and Equipment Other Assets Total Assets A/P Current Portion of LT Debt Total Current Liabilities Long-term Debt Total Liabilities Shareholders' Equity Total Liabilities and Equities Accessibility Investigate 41.7 $ 53.77 $ 90.73 $ 2.88 $18.09 $ 56.65 $108.82 $ 52.82 $185.45 $109.47 $294.27 $20.21 $ 22.16 $129.68 $316.43 $112.15 $109.96 $129.04 $189.84 $18.77 $ 14.32 $ 8.56 $ 6.22 $130.92 $124.28 $ 137.60 $ 196.06 $161.98 $ 104.68 $ 79.80 $324.76 $286.26 $242.28 $275.86 $61.16 $103.81 $133.36 $ 151.58 $385.92 $390.07 $375.64 $427.44 $ 193.84 Appendix A3: Canadian Motorbikes Industry Averages Current Ratio Cash Ratio Inventory Turnover (days) A/R Turnover (days) A/P Turnover (days) Cash Conversion Cycle Fixed Assets Turnover Total Assets Turnover Debt Ratio Times Interest Earned Gross Profit Margin Operating Profit Margin Net Profit Margin Return on Assets Return on Equity 1.25 0.27 44.12 32.45 60.23 16.35 3.72 2.05 0.54 9.33 32.00% 14.00% 8.50% 17.46% 38.25% Appendix A1: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Income Statement ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2011 2012 2010 $287.14 $299.45 $209.69 $210.45 $725.45 $793.34 $506.91 $559.53 $77.45 $89.00 $219.21 $226.57 $218.54 $233.81 $125.53 $136.57 $20.89 $21.22 $26.54 $160.23 $ 57.34 $ 60.06 $104.14 $ 7.53 $13.54 $21.54 $ 92.86 $87.39 $61.42 $39.80 $35.51 $24.67 $17.96 $ 13.01 $57.35 $62.72 $43.46 $26.79 $18.35 $ 20.07 $13.91 $ 8.57 $29.55 $ 18.22 $ 12.58 $15.40 $9.41 $ 12.53 3.17 $ 2.87 1.01 $ 0.92 2.16 $ 1.95 $39.00 $42.65 Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling and Administration Depreciation Operating Profit Interest Earnings Before Taxes Taxes Net Income $ $ $ tax rate 32% 1 - tax rate 68% Net Income + 1(1-tax rate) $ 8.57 Cash A/R Inventory 32% 68% 32% 68% $10.46 $ 63.15 Total Current Assets $72.89 $148.76 $193.36 Accessibil 2013 2014 $814.55 $856.00 $595.34 $629.43 32% 68% 32% 32% 68% 68% $59.43 $ 41.76 $ 27.07 Appendix A2: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Balance Sheet ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 $ 10.76 $ 20.56 $ 25.78 $38.55 $ 34.21 $29.75 $45.01 $ 48.54 $84.89 $ 85.39 $ 95.32 $ 99.23 $ 17.12 $ 79.66 $ 82.69 $79.30 $53.88 $ 75.33 $203.24 $183.41 $204.31 Appendix A2: Canadian Motorbikes Comparative Balance Sheet ($M) For the Years Ended Dec 31, 2009 to 2014 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 $ 10.76 $ 20.56 $25.78 $38.55 $34.21 $29.75 $45.01 $ 48.54 $84.89 $85.39 $95.32 $ 99.23 $ 17.12 $ 79.66 $ 82.69 $ 79.30 $ 53.88 $ 75.33 $72.89 $148.76 $193.36 $203.24 $183.41 $204.31 $ 54.32 $ 162.28 $184.18 $178.01 $182.74 $211.48 $ 2.47 $ 5.39 $ 8.38 $ 8.82 $ 9.49 $ 11.65 $129.68 $316.43 $385.92 $390.07 $375.64 $427.44 Cash A/R Inventory Total Current Assets Land, Plant and Equipment Other Assets Total Assets A/P Current Portion of LT Debt Total Current Liabilities Long-term Debt Total Liabilities Shareholders' Equity Total Liabilities and Equities Accessibility Investigate 41.7 $ 53.77 $ 90.73 $ 2.88 $18.09 $ 56.65 $108.82 $ 52.82 $185.45 $109.47 $294.27 $20.21 $ 22.16 $129.68 $316.43 $112.15 $109.96 $129.04 $189.84 $18.77 $ 14.32 $ 8.56 $ 6.22 $130.92 $124.28 $ 137.60 $ 196.06 $161.98 $ 104.68 $ 79.80 $324.76 $286.26 $242.28 $275.86 $61.16 $103.81 $133.36 $ 151.58 $385.92 $390.07 $375.64 $427.44 $ 193.84
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


