Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Old MathJax webview Old MathJax webview Old MathJax webview need explanation on all updated updated updated transporter will always carry its maximum capacity of 10
Old MathJax webview
Old MathJax webview
Old MathJax webview
need explanation on all
updated
updated
updated
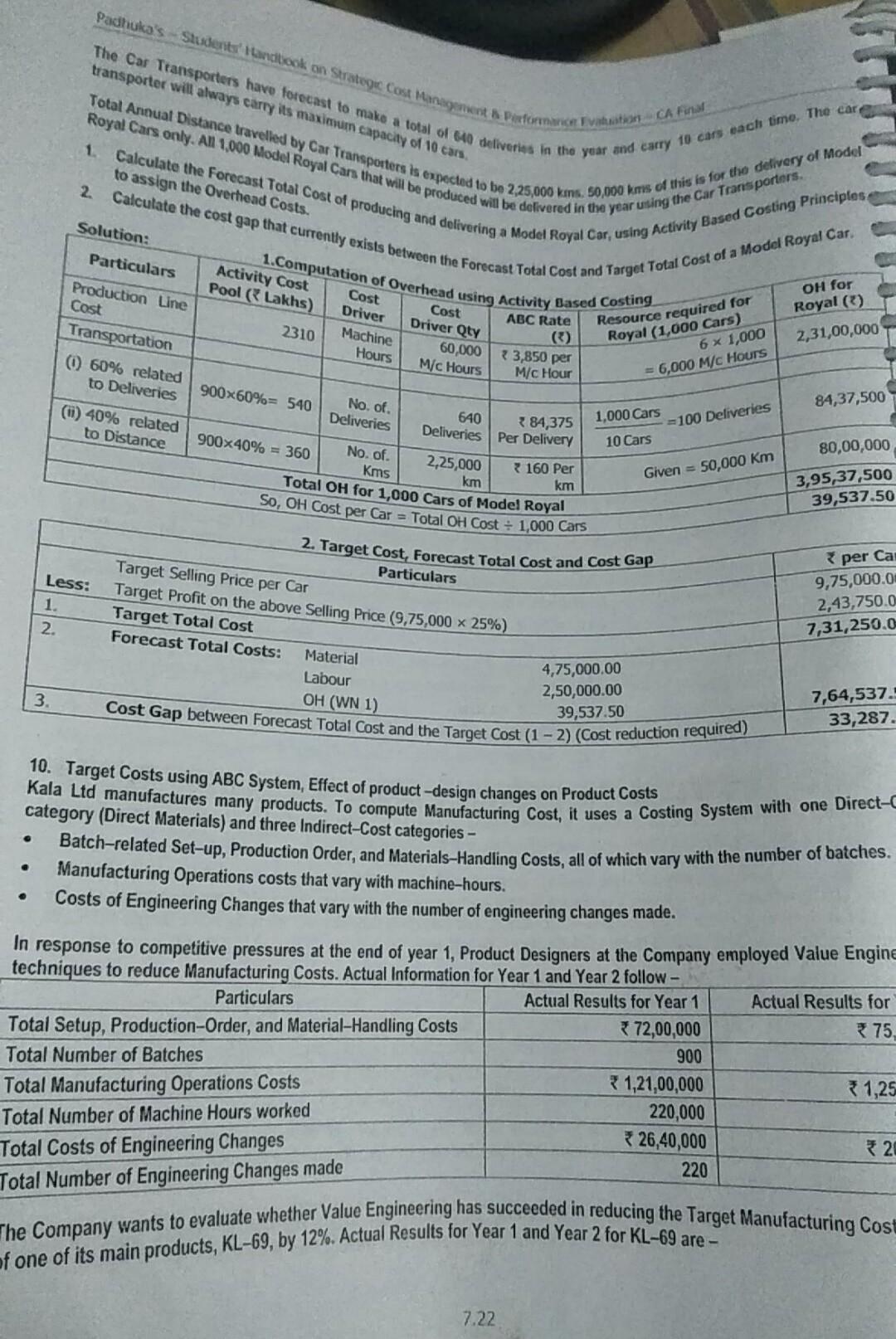
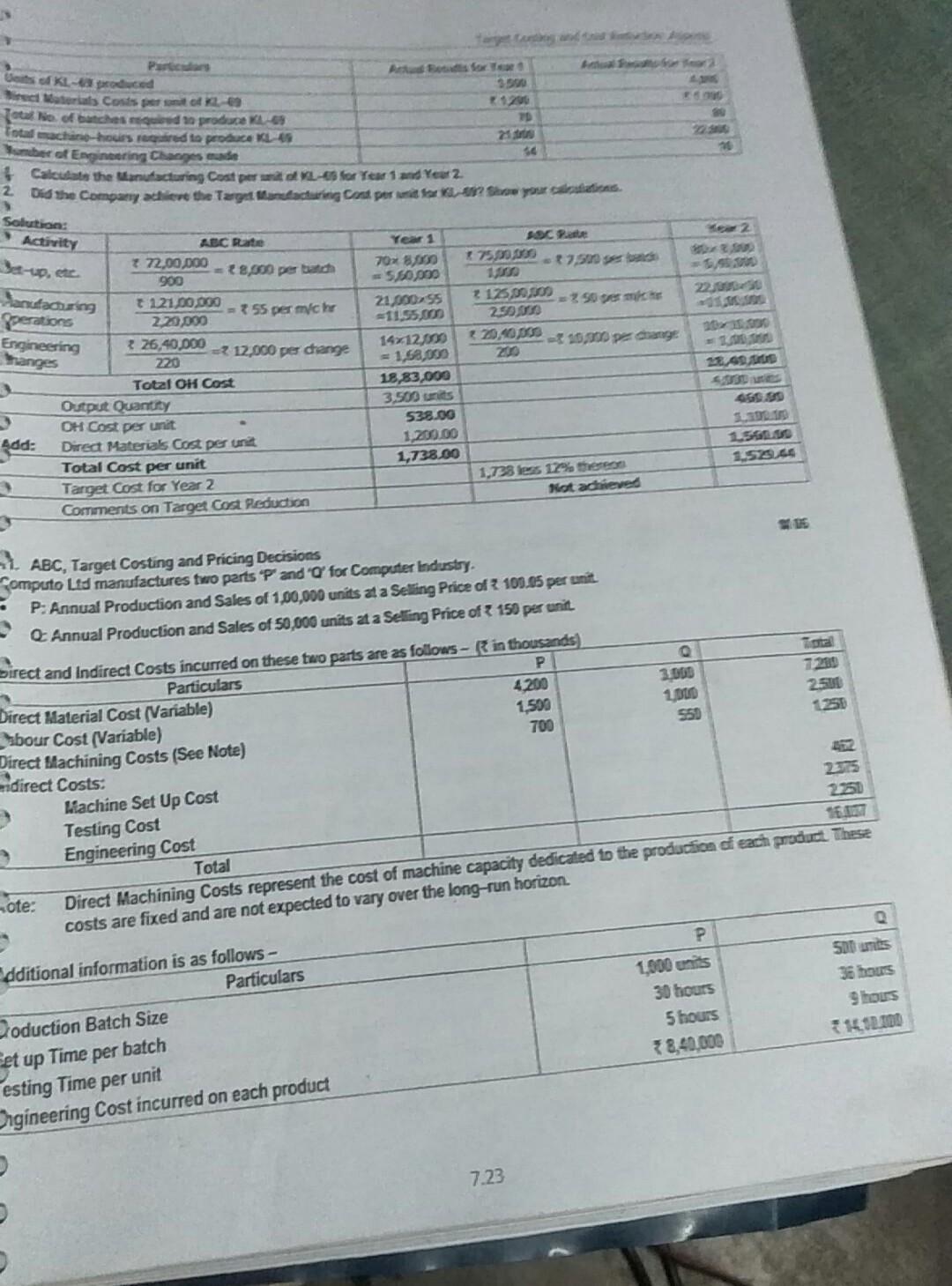
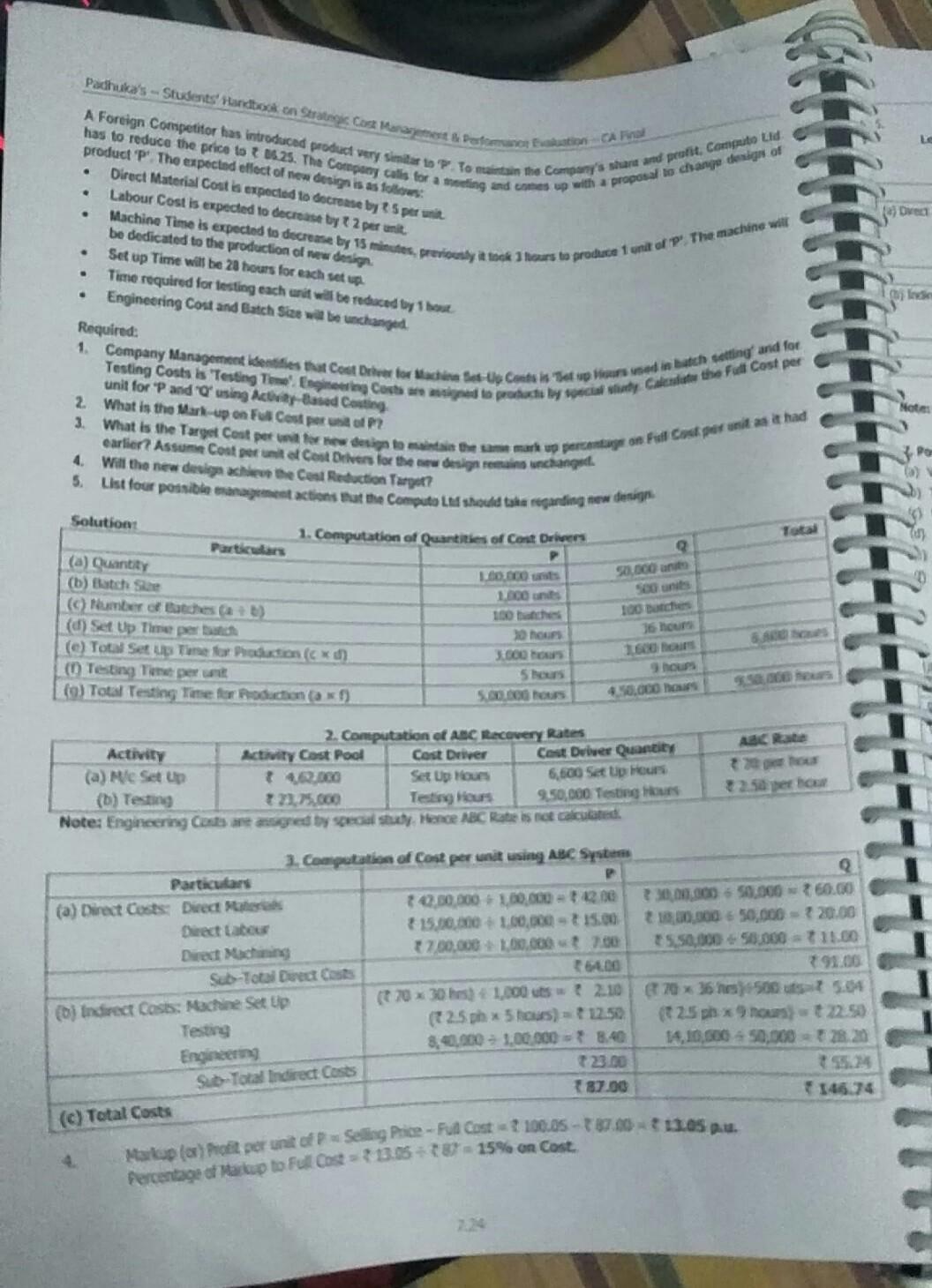
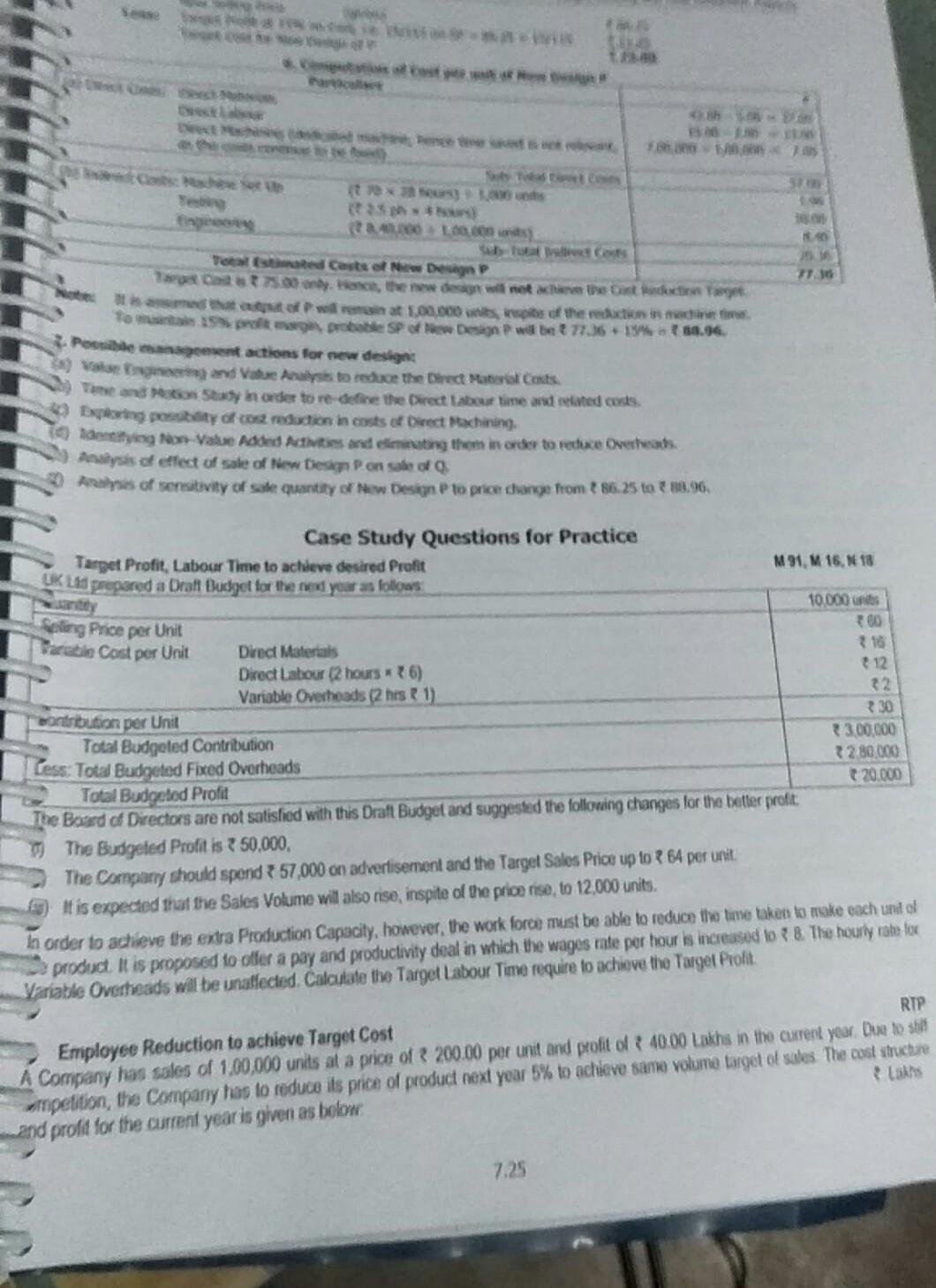
transporter will always carry its maximum capacity of 10 cars. 1 Padhuka's Students and took on Strategic Cost Management Performance on CAF The Car Transporters have fotocast to make a total of 640 deliveries in the year and carry 10 cars each time. The car Total Annual Distance travelled by Car Transporters is expected to be 2,25,000 kms. 50,000 kms of this is for the delivery of Model Royal Cars only. All 1,000 Model Royal Cans that will be produced will be delivered in the year using the Car Transporters. Calculate the Forecast Total Cost of producing and delivering a Model Royal Car, using Activity Based Costing Principles 2. Calculate the cost gap that currently exists between the Forecast Total Cost and Target Total Cost of a Model Royal Car 1.Computation of Overhead using Activity Based Costing ABC Rate () to assign the Overhead Costs. Solution: Particulars Activity Cost Pool (Lakhs) Cost Production Line Cost Transportation 0 60% related to Deliveries Cost Driver Machine Hours Driver Qty OH for Royal () 2,31,00,000 2310 60,000 M/c Hours 33,850 per Resource required for Royal (1,000 Cars) 6 x 1,000 = 6,000 M/C Hours M/c Hour 84,37,500 1,000 Cars 10 Cars =100 Deliveries 7160 Per km Given = 50,000 Km 80,00,000 3,95,37,500 39,537.50 900x60%= 540 No. of. 640 384,375 Deliveries Deliveries Per Delivery (1) 40% related to Distance 900x40% = 360 No. of. 2,25,000 Kms km Total OH for 1,000 Cars of Model Royal So, OH Cost per Car = Total OH Cost + 1,000 Cars 2. Target Cost, Forecast Total Cost and Cost Gap Particulars Target Selling Price per Car Target Profit on the above Selling Price (9,75,000 x 25%) 1. Target Total Cost 2. Forecast Total Costs: Material Labour OH (WN 1) 3. Less: per Ca 9,75,000.00 2,43,750.0 7,31,250.0 4,75,000.00 2,50,000.00 Cost Gap between Forecast Total Cost and the Target Cost (1-2) (Cost reduction required) 39,537.50 7,64,537. 33,287 . 10. Target Costs using ABC System, Effect of product-design changes on Product Costs Kala Ltd manufactures many products. To compute Manufacturing Cost, it uses a Costing System with one Direct- category (Direct Materials) and three Indirect-Cost categories - Batch-related Set-up, Production Order, and Materials-Handling Costs, all of which vary with the number of batches. Manufacturing Operations costs that vary with machine-hours. Costs of Engineering Changes that vary with the number of engineering changes made. In response to competitive pressures at the end of year 1, Product Designers at the Company employed Value Engine techniques to reduce Manufacturing Costs. Actual Information for Year 1 and Year 2 follow- Particulars Actual Results for Year 1 Actual Results for Total Setup, Production-Order, and Material Handling Costs 72,00,000 75 Total Number of Batches 900 Total Manufacturing Operations Costs 1,21,00,000 31,25 Total Number of Machine Hours worked 220,000 Total Costs of Engineering Changes 326,40,000 * 2 220 Total Number of Engineering Changes made The Company wants to evaluate whether Value Engineering has succeeded in reducing the Target Manufacturing Cost of one of its main products, KL-69, by 12%. Actual Results for Year 1 and Year 2 for KL-69 arare 7.22 Activity Janutacuring Gets of KL cod Sind orals Costs per totes otal lie of banches do produce - Totalchan hours tored to produce KL 4 Humber of Engineering Changes made Calculate the Manufacturing Cost per una L-ES for Year 1 and Year 2 ? Did the Company achieve the Target Marutacturing and per una sera Stow your dreams. Solution: ABC Rate Year 1 SCP 2 72,00.000 70 8,000 75.900 7,5 = 8,500 per batch 900 50.00 + 121,00.000 21.00095 z 125,99,000 350 sem = 755 per mich fperations 2.20,000 239930 3 26,40.000 = 12,000 pes change 14712.000 10,000 per change 220 =1,58,000 Total OH Cost 18,83,000 Output Quantity 3.500 units OH Cost per unit 538.00 1,200.00 Add: Direct Materials cos pesurit Total Cost per unit 1,738.00 Target Cost for Year 2 Comments on Target Cost Reduction Engineering Thanges 1.528.45 1,738 les 12% teren Not achieved 22. ABC, Target Costing and Pricing Decisions Computo Lid manufactures two parts P and 'a for Computer Industry. P. Annual Production and Sales of 1,00,000 units at a Selling Price of 100.05 personit Annual Production and Sales of 50,000 units at a Selling Price of 150 per unit Direct and Indirect Costs incurred on these two parts are as follows - in thousands) Particulars O Direct Material Cost (Variable) 4200 3.000 7200 abour Cost (Variable) 1,500 1,000 2.501 Direct Machining Costs (See Note) 700 direct Costs: Machine Set Up Cost 225 Testing Cost Engineering Cost Total ote: Direct Machining Costs represent the cost of machine capacity dedicated to the production of each product. These costs are fixed and are not expected to vary over the long-run horizon. P. 1,000 units 30 hours 5 hours 38,40.000 500 units 35 hours 9 hous 1.1.100 dditional information is as follows - Particulars Zoduction Batch Size set up Time per batch esting Time per unit Ongineering Cost incurred on each product 7.23 Pachuka's - Students' Handbook on Strategic Cast Marne Doston on CAP has to reduce the price to 1425. The Company calls for a meeting and come up with a proposal to change den of A Foreign Competitor has introduced product very similar to to main the Company's share and profit, Computo Lid product p The expected effect of new design is as follows: Direct Material Cost is expected to decrease by per unit Labour Cost is expected to decrease by 2 per unit . De Machine Time is expected to decrease by 15 minutes, previously it took hours to produce 1 unit of P' The machine will be dedicated to the production of new design Set up Time will be 20 hours for each set up Time required for testing each unit will be reduced by 1 hout Engineering Cost and Batch Sise be unchanged. Required: . unit for P and 'Q' using Act Based Costing 2. What is the Mark up on Fucos por of P2 Notes Pa 1. Company Management identifies that Cool Det for din Uy Co is used in Batch setting and for Testing Costs is Testing Engineering Costs and to protectie lo speciality Calendar the fil Cost per 3. What is the Target Cost pere design in the markup pre on Full Conta a had earlier? Assume Cont per unitat Cost Drivers for the sew design remains unchanged. 4. Will the new desigpache the Cost Reduction Target? 5. List four possible management actions at the Computo Liat should take regarding new derpu Solution 1. Computation of Quantities of Cont Drivers Parts (a) Quantity 100 000 (b) Batch Se 1.000 units Member of Butches) (d) Set Up Time perba hours (c) Total Set up Time for production 3600 hours ( Testing Time per 5 hours (0) Total Testing Time for Roduction (a) 5.000 hours Total P Q 50.000 un 500 units 100 Dances 36 hours 1600 9 hours 4.50.000 hours As Son 2. Computation of ABC Recovery Rates Activity Activity Cast Pool Cost Driver Cast Diver Quantity (a) Me Set Up Set Up Hous 6,000 Set Up Hours (b) Testing Testing Hours 950,000 Testing Hours Note: Engineering Costs are gred by special study. Hence ABC Rate is not calculated 25 perc 2. Computation of Cost per unit using ABC Systems Particulars P (a) Direct Costs: Direct Me 10.30.000 100.000 30.000.000 - 50.000 60.00 Direct Labour 15.00.000 1.00.000 - 15.00 19.00.000 50,000 - 20.00 Direct Machining 17.00.000 100.000 700 5.50.000 - 50.000 - 11.00 Sub-Total Diet Costs 6400 191.00 (0) Indirect costs: Machine Setup (720 x 30 hes) 1.000 uts? 2.10 670 x 36 hes) 500 uts5.04 Testing (2.5 ph 5 hours) = 12.50 25 px 9 mont22.50 Engineering 8,40.000 - 100.000 - 8.40 14,10.000 - 50.000 - 2020 Sub-Total Indirect costs 23.00 87.00 (c) Total Costs 146.74 Markup (a) Poft per unit of Selang Pace - Full Costa 100.05-187.00 - 13. Percentage of a cup to Full cost = 13.08 - 15% on Cost. Se SIN (1000 Teste Caste of New Design 13.00. Here, the desen met een set We met at 10.000 units pite of the reduction in einem To 15 pro me probleSpor How Desan w bet77.36 19% = 10.96 3. Po management actions for new designs enging and Value Analysis to reduce the Direct Costs Time and to stay in order to redefine the Direct Labour time and related costs Exploring poety of cos reduction in costs of ect Machining Identifying to Value Added Activities and citing them in order to reduce Overheads Analysis of effect of sale of New Design Pon sale of Analysis of sensitivity of Sale quantity of New Design P to price change from 66.25 to 88.96. Case Study Questions for Practice Target Profit, Labour Time to achieve desired Profit M 91, M 16. N18 UK Lad grupared a Draft Buckzet for the next year as follows ty 10.000 Selling Price per Unit Vale Cost per Unit Direct Materials 316 Direct Labour (2 hours *6) 12 Variable Overheads (2 hrs ? 1) 32 ontribution per Unit 330 Total Budgeted Contribution 300.000 Dess: Total Budgeted Fixed Overheads 1280.000 Total Budgeted Profit 20.000 The Board of Directors are not satisfied with this Draft Budget and suggested the following changes for the better profit The Budgeted Profit is 750.000, The Company should spend 57,000 on advertisement and the Target Sales Price up to 3 64 per unit. It is expected that the Sales Volume will also rise inspite of the price rise to 12,000 units. In order to achieve the extra Production Capacity, however, the work force must be able to reduce the time takes to make each und of product. It is proposed to offer a pay and productivity deal in which the wages rate per hour is increased to 38. The hourly rate for Variable Overheads will be unaffected. Calculate the Target Labour Time require to achieve the Target Profit RTP Employee Reduction to achieve Target Cost A Company has sales of 1,00,000 units at a price of 200.00 per unit and profit of 40.00 Lakhs in the current your Dee to shit Lakhs ompetition, the Company has to reduce its price of product next year 5% to achieve same volume target of sales. The cost structure and profit for the current year is given as below 7.25 transporter will always carry its maximum capacity of 10 cars. 1 Padhuka's Students and took on Strategic Cost Management Performance on CAF The Car Transporters have fotocast to make a total of 640 deliveries in the year and carry 10 cars each time. The car Total Annual Distance travelled by Car Transporters is expected to be 2,25,000 kms. 50,000 kms of this is for the delivery of Model Royal Cars only. All 1,000 Model Royal Cans that will be produced will be delivered in the year using the Car Transporters. Calculate the Forecast Total Cost of producing and delivering a Model Royal Car, using Activity Based Costing Principles 2. Calculate the cost gap that currently exists between the Forecast Total Cost and Target Total Cost of a Model Royal Car 1.Computation of Overhead using Activity Based Costing ABC Rate () to assign the Overhead Costs. Solution: Particulars Activity Cost Pool (Lakhs) Cost Production Line Cost Transportation 0 60% related to Deliveries Cost Driver Machine Hours Driver Qty OH for Royal () 2,31,00,000 2310 60,000 M/c Hours 33,850 per Resource required for Royal (1,000 Cars) 6 x 1,000 = 6,000 M/C Hours M/c Hour 84,37,500 1,000 Cars 10 Cars =100 Deliveries 7160 Per km Given = 50,000 Km 80,00,000 3,95,37,500 39,537.50 900x60%= 540 No. of. 640 384,375 Deliveries Deliveries Per Delivery (1) 40% related to Distance 900x40% = 360 No. of. 2,25,000 Kms km Total OH for 1,000 Cars of Model Royal So, OH Cost per Car = Total OH Cost + 1,000 Cars 2. Target Cost, Forecast Total Cost and Cost Gap Particulars Target Selling Price per Car Target Profit on the above Selling Price (9,75,000 x 25%) 1. Target Total Cost 2. Forecast Total Costs: Material Labour OH (WN 1) 3. Less: per Ca 9,75,000.00 2,43,750.0 7,31,250.0 4,75,000.00 2,50,000.00 Cost Gap between Forecast Total Cost and the Target Cost (1-2) (Cost reduction required) 39,537.50 7,64,537. 33,287 . 10. Target Costs using ABC System, Effect of product-design changes on Product Costs Kala Ltd manufactures many products. To compute Manufacturing Cost, it uses a Costing System with one Direct- category (Direct Materials) and three Indirect-Cost categories - Batch-related Set-up, Production Order, and Materials-Handling Costs, all of which vary with the number of batches. Manufacturing Operations costs that vary with machine-hours. Costs of Engineering Changes that vary with the number of engineering changes made. In response to competitive pressures at the end of year 1, Product Designers at the Company employed Value Engine techniques to reduce Manufacturing Costs. Actual Information for Year 1 and Year 2 follow- Particulars Actual Results for Year 1 Actual Results for Total Setup, Production-Order, and Material Handling Costs 72,00,000 75 Total Number of Batches 900 Total Manufacturing Operations Costs 1,21,00,000 31,25 Total Number of Machine Hours worked 220,000 Total Costs of Engineering Changes 326,40,000 * 2 220 Total Number of Engineering Changes made The Company wants to evaluate whether Value Engineering has succeeded in reducing the Target Manufacturing Cost of one of its main products, KL-69, by 12%. Actual Results for Year 1 and Year 2 for KL-69 arare 7.22 Activity Janutacuring Gets of KL cod Sind orals Costs per totes otal lie of banches do produce - Totalchan hours tored to produce KL 4 Humber of Engineering Changes made Calculate the Manufacturing Cost per una L-ES for Year 1 and Year 2 ? Did the Company achieve the Target Marutacturing and per una sera Stow your dreams. Solution: ABC Rate Year 1 SCP 2 72,00.000 70 8,000 75.900 7,5 = 8,500 per batch 900 50.00 + 121,00.000 21.00095 z 125,99,000 350 sem = 755 per mich fperations 2.20,000 239930 3 26,40.000 = 12,000 pes change 14712.000 10,000 per change 220 =1,58,000 Total OH Cost 18,83,000 Output Quantity 3.500 units OH Cost per unit 538.00 1,200.00 Add: Direct Materials cos pesurit Total Cost per unit 1,738.00 Target Cost for Year 2 Comments on Target Cost Reduction Engineering Thanges 1.528.45 1,738 les 12% teren Not achieved 22. ABC, Target Costing and Pricing Decisions Computo Lid manufactures two parts P and 'a for Computer Industry. P. Annual Production and Sales of 1,00,000 units at a Selling Price of 100.05 personit Annual Production and Sales of 50,000 units at a Selling Price of 150 per unit Direct and Indirect Costs incurred on these two parts are as follows - in thousands) Particulars O Direct Material Cost (Variable) 4200 3.000 7200 abour Cost (Variable) 1,500 1,000 2.501 Direct Machining Costs (See Note) 700 direct Costs: Machine Set Up Cost 225 Testing Cost Engineering Cost Total ote: Direct Machining Costs represent the cost of machine capacity dedicated to the production of each product. These costs are fixed and are not expected to vary over the long-run horizon. P. 1,000 units 30 hours 5 hours 38,40.000 500 units 35 hours 9 hous 1.1.100 dditional information is as follows - Particulars Zoduction Batch Size set up Time per batch esting Time per unit Ongineering Cost incurred on each product 7.23 Pachuka's - Students' Handbook on Strategic Cast Marne Doston on CAP has to reduce the price to 1425. The Company calls for a meeting and come up with a proposal to change den of A Foreign Competitor has introduced product very similar to to main the Company's share and profit, Computo Lid product p The expected effect of new design is as follows: Direct Material Cost is expected to decrease by per unit Labour Cost is expected to decrease by 2 per unit . De Machine Time is expected to decrease by 15 minutes, previously it took hours to produce 1 unit of P' The machine will be dedicated to the production of new design Set up Time will be 20 hours for each set up Time required for testing each unit will be reduced by 1 hout Engineering Cost and Batch Sise be unchanged. Required: . unit for P and 'Q' using Act Based Costing 2. What is the Mark up on Fucos por of P2 Notes Pa 1. Company Management identifies that Cool Det for din Uy Co is used in Batch setting and for Testing Costs is Testing Engineering Costs and to protectie lo speciality Calendar the fil Cost per 3. What is the Target Cost pere design in the markup pre on Full Conta a had earlier? Assume Cont per unitat Cost Drivers for the sew design remains unchanged. 4. Will the new desigpache the Cost Reduction Target? 5. List four possible management actions at the Computo Liat should take regarding new derpu Solution 1. Computation of Quantities of Cont Drivers Parts (a) Quantity 100 000 (b) Batch Se 1.000 units Member of Butches) (d) Set Up Time perba hours (c) Total Set up Time for production 3600 hours ( Testing Time per 5 hours (0) Total Testing Time for Roduction (a) 5.000 hours Total P Q 50.000 un 500 units 100 Dances 36 hours 1600 9 hours 4.50.000 hours As Son 2. Computation of ABC Recovery Rates Activity Activity Cast Pool Cost Driver Cast Diver Quantity (a) Me Set Up Set Up Hous 6,000 Set Up Hours (b) Testing Testing Hours 950,000 Testing Hours Note: Engineering Costs are gred by special study. Hence ABC Rate is not calculated 25 perc 2. Computation of Cost per unit using ABC Systems Particulars P (a) Direct Costs: Direct Me 10.30.000 100.000 30.000.000 - 50.000 60.00 Direct Labour 15.00.000 1.00.000 - 15.00 19.00.000 50,000 - 20.00 Direct Machining 17.00.000 100.000 700 5.50.000 - 50.000 - 11.00 Sub-Total Diet Costs 6400 191.00 (0) Indirect costs: Machine Setup (720 x 30 hes) 1.000 uts? 2.10 670 x 36 hes) 500 uts5.04 Testing (2.5 ph 5 hours) = 12.50 25 px 9 mont22.50 Engineering 8,40.000 - 100.000 - 8.40 14,10.000 - 50.000 - 2020 Sub-Total Indirect costs 23.00 87.00 (c) Total Costs 146.74 Markup (a) Poft per unit of Selang Pace - Full Costa 100.05-187.00 - 13. Percentage of a cup to Full cost = 13.08 - 15% on Cost. Se SIN (1000 Teste Caste of New Design 13.00. Here, the desen met een set We met at 10.000 units pite of the reduction in einem To 15 pro me probleSpor How Desan w bet77.36 19% = 10.96 3. Po management actions for new designs enging and Value Analysis to reduce the Direct Costs Time and to stay in order to redefine the Direct Labour time and related costs Exploring poety of cos reduction in costs of ect Machining Identifying to Value Added Activities and citing them in order to reduce Overheads Analysis of effect of sale of New Design Pon sale of Analysis of sensitivity of Sale quantity of New Design P to price change from 66.25 to 88.96. Case Study Questions for Practice Target Profit, Labour Time to achieve desired Profit M 91, M 16. N18 UK Lad grupared a Draft Buckzet for the next year as follows ty 10.000 Selling Price per Unit Vale Cost per Unit Direct Materials 316 Direct Labour (2 hours *6) 12 Variable Overheads (2 hrs ? 1) 32 ontribution per Unit 330 Total Budgeted Contribution 300.000 Dess: Total Budgeted Fixed Overheads 1280.000 Total Budgeted Profit 20.000 The Board of Directors are not satisfied with this Draft Budget and suggested the following changes for the better profit The Budgeted Profit is 750.000, The Company should spend 57,000 on advertisement and the Target Sales Price up to 3 64 per unit. It is expected that the Sales Volume will also rise inspite of the price rise to 12,000 units. In order to achieve the extra Production Capacity, however, the work force must be able to reduce the time takes to make each und of product. It is proposed to offer a pay and productivity deal in which the wages rate per hour is increased to 38. The hourly rate for Variable Overheads will be unaffected. Calculate the Target Labour Time require to achieve the Target Profit RTP Employee Reduction to achieve Target Cost A Company has sales of 1,00,000 units at a price of 200.00 per unit and profit of 40.00 Lakhs in the current your Dee to shit Lakhs ompetition, the Company has to reduce its price of product next year 5% to achieve same volume target of sales. The cost structure and profit for the current year is given as below 7.25Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


