Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
On 1 January 2020, Richer Ltd acquired 100 % of the ordinary voting shares of Rich Ltd, establishing Richer Ltd Group. The corporate income
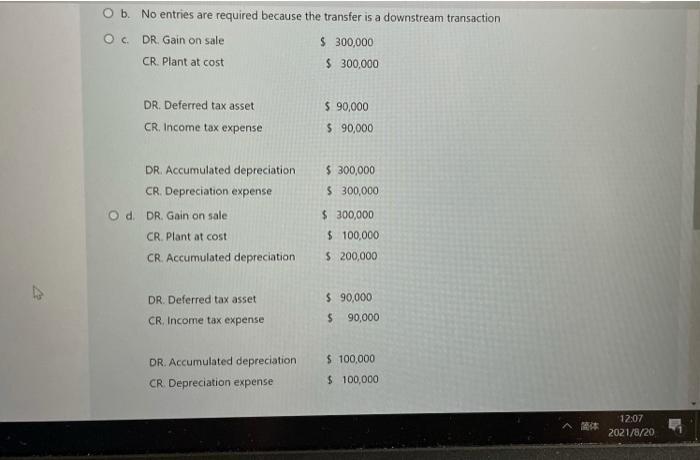
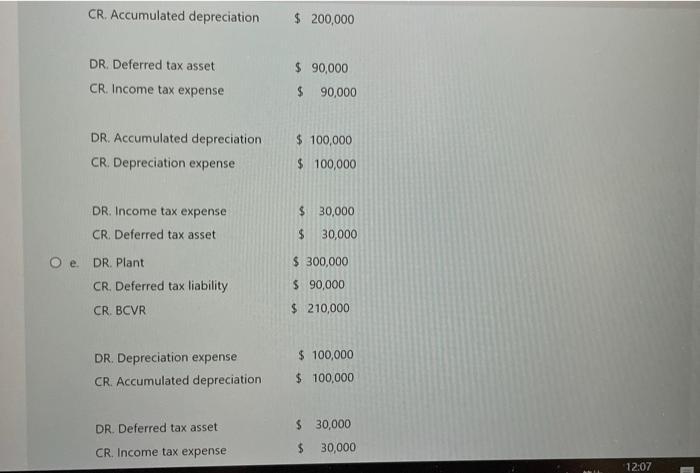
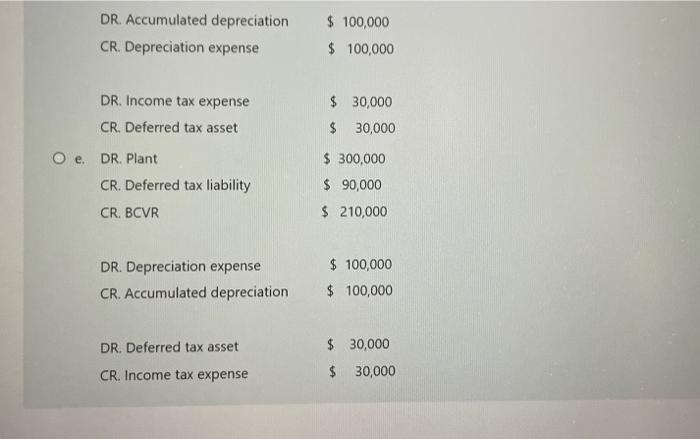
On 1 January 2020, Richer Ltd acquired 100 % of the ordinary voting shares of Rich Ltd, establishing Richer Ltd Group. The corporate income tax rate is 30%. Richer transferred plant to Rich on 1 January 2020 for $900,000. At the date, the plant had a carrying amount to Richer of $600,000 (cost $800,000 and accumulated depreciation $200,000) and the remaining useful life of the plant was three years. Richer did not change the pattern of use of the plant. The consolidation worksheet entries for the year to 31 December 2020 for the intragroup transfer of plant and excess depreciation on transferred plant are: DR. Plant $ 300,000 CR. Income tax expense $ 90,000 CR. Transfer from BCVR $ 210,000 O b. No entries are required because the transfer is a downstream transaction $ 300,000 $ 300,000 Oc. DR. Gain on sale CR. Plant at cost DR. Deferred tax asset $ 90,000 CR. Income tax expense $ 90,000 DR. Accumulated depreciation $ 300,000 12:07 2031/9no O b. No entries are required because the transfer is a downstream transaction O. DR. Gain on sale $ 300,000 CR. Plant at cost $ 300,000 DR. Deferred tax asset $ 90,000 CR. Income tax expense $ 90,000 DR. Accumulated depreciation $ 300,000 CR. Depreciation expense $ 300,000 O d. DR. Gain on sale $ 300,000 CR. Plant at cost $ 100,000 CR. Accumulated depreciation $ 200,000 DR. Deferred tax asset $ 90,000 CR, Income tax expense 90,000 DR. Accumulated depreciation $ 100,000 CR. Depreciation expense $ 100,000 12:07 2021/8/20 CR. Accumulated depreciation $ 200,000 DR. Deferred tax asset $ 90,000 CR. Income tax expense $ 90,000 DR. Accumulated depreciation $ 100,000 CR. Depreciation expense $ 100,000 DR. Income tax expense $ 30,000 CR. Deferred tax asset 30,000 O . DR. Plant $ 300,000 CR. Deferred tax liability S 90,000 CR. BCVR $ 210,000 DR. Depreciation expense $ 100,000 CR. Accumulated depreciation $ 100,000 $ 30,000 DR. Deferred tax asset $ 30,000 CR. Income tax expense 12:07 DR. Accumulated depreciation $ 100,000 $ 100,000 CR. Depreciation expense DR. Income tax expense $ 30,000 CR. Deferred tax asset $ 30,000 O e. DR. Plant $ 300,000 CR. Deferred tax liability $ 90,000 CR. BCVR $ 210,000 DR. Depreciation expense $ 100,000 CR. Accumulated depreciation $ 100,000 DR. Deferred tax asset $ 30,000 CR. Income tax expense $ 30,000
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.47 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Therefore ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started