Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
On an essentially frictionless, horizontal ice rink, a skater moving at 6.0 m/s encounters a rough patch that reduces her speed by 41% due
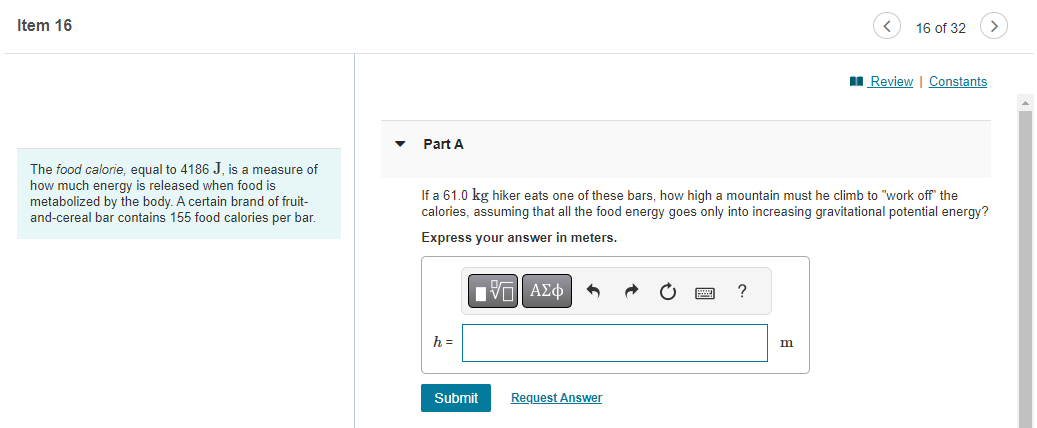
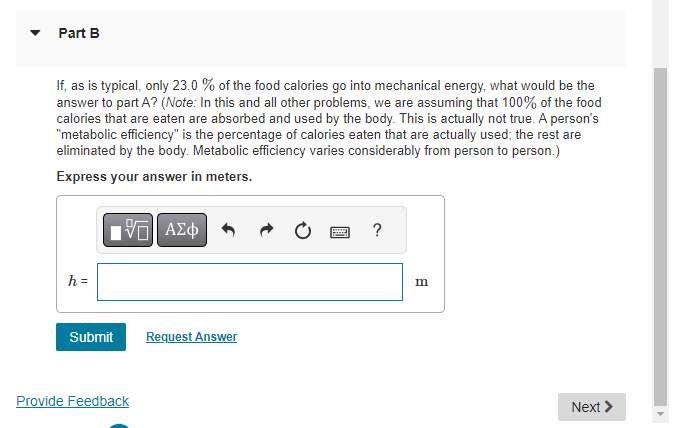
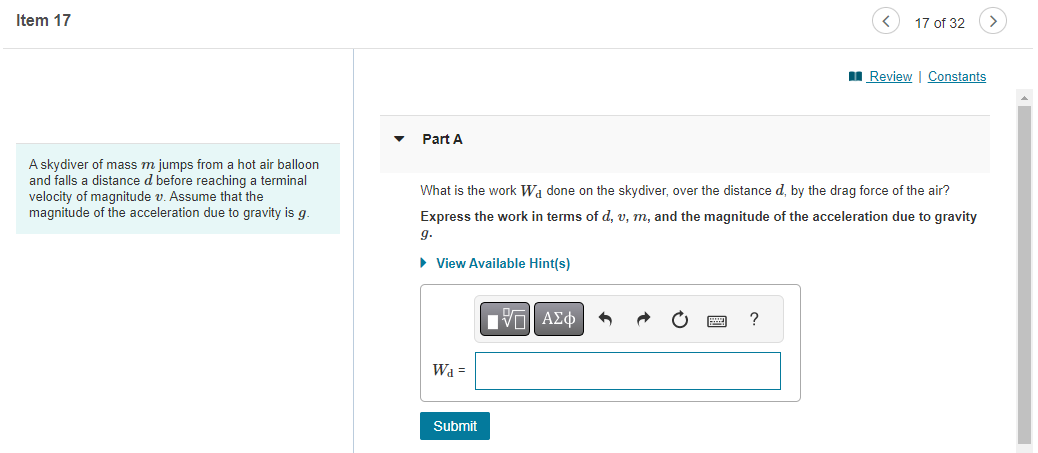
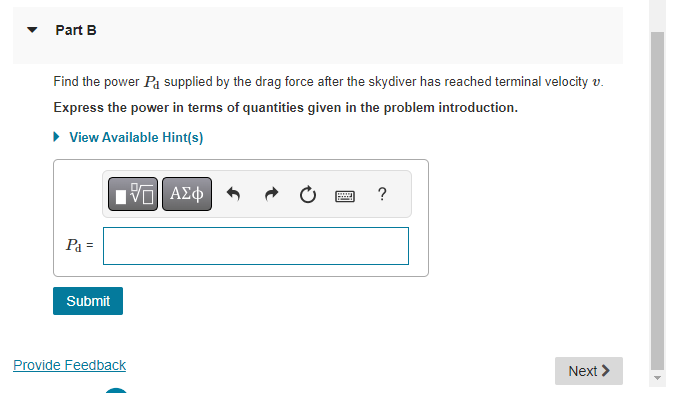
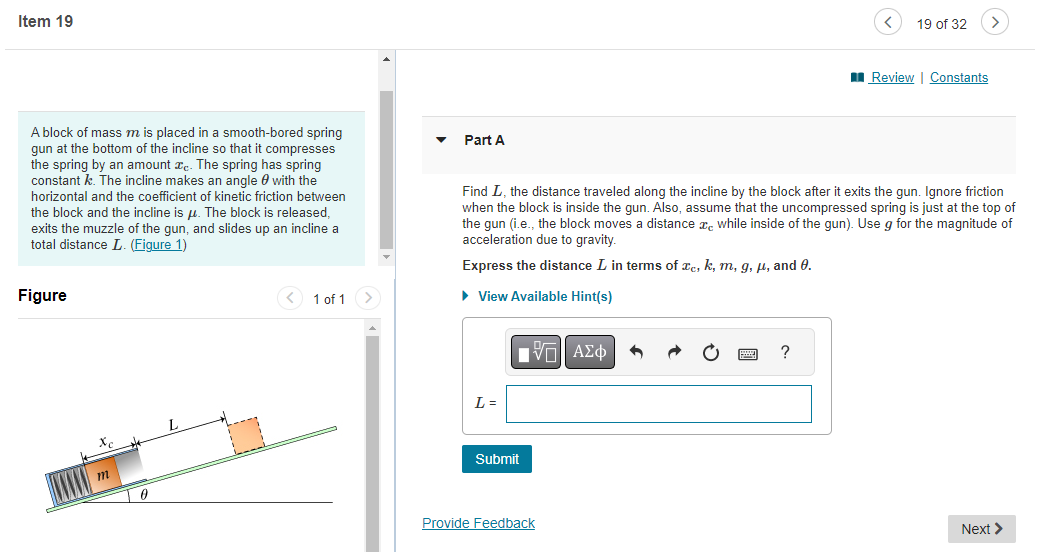
On an essentially frictionless, horizontal ice rink, a skater moving at 6.0 m/s encounters a rough patch that reduces her speed by 41% due to a friction force that is 29% of her weight. Part A Use the work-energy theorem to find the length of this rough patch. Express your answer in meters. ? S= m Item 12 Part A A spring of force constant 275.0 N/m and unstretched length 0.300 m is stretched by two forces, pulling in opposite directions at opposite ends of the spring, that increase to 18.0 N. How long will the spring now be? Express your answer in meters. 1 = Submit Request Answer ? m 12 of 32 > Review | Constants Part B How much work was required to stretch it that distance? Express your answer in joules. W = Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? J Next > Item 13 13 of 32 Review | Constants You weigh 530 N. Your bathroom scale contains a light but very stiff ideal spring. When you stand at rest on the scale, the spring is compressed 1.80 cm. Your 180 N dog then gently jumps into your arms. Part A How much work is done by the spring as the two of you are brought to rest by friction? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? W = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next > Item 16 > 16 of 32 > Review | Constants The food calorie, equal to 4186 J, is a measure of how much energy is released when food is metabolized by the body. A certain brand of fruit- and-cereal bar contains 155 food calories per bar. Part A If a 61.0 kg hiker eats one of these bars, how high a mountain must he climb to "work off" the calories, assuming that all the food energy goes only into increasing gravitational potential energy? Express your answer in meters. h= Submit Request Answer ? m Part B If, as is typical, only 23.0 % of the food calories go into mechanical energy, what would be the answer to part A? (Note: In this and all other problems, we are assuming that 100% of the food calories that are eaten are absorbed and used by the body. This is actually not true. A person's "metabolic efficiency" is the percentage of calories eaten that are actually used; the rest are eliminated by the body. Metabolic efficiency varies considerably from person to person.) Express your answer in meters. h = ? m Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next > Item 17 < 17 of 32 > Review | Constants A skydiver of mass m jumps from a hot air balloon and falls a distance d before reaching a terminal velocity of magnitude v. Assume that the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is g. Part A What is the work Wa done on the skydiver, over the distance d, by the drag force of the air? Express the work in terms of d, v, m, and the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity 9. View Available Hint(s) ? Wa= Submit Part B Find the power Pa supplied by the drag force after the skydiver has reached terminal velocity v. Express the power in terms of quantities given in the problem introduction. View Available Hint(s) Pa= Submit Provide Feedback Next > Item 18 < 18 of 32 Review | Constants A 3.00 kg block on a horizontal floor is attached to a horizontal spring that is initially compressed 0.0360 m. The spring has force constant 890 N/m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0.350. The block and spring are released from rest and the block slides along the floor. Part A What is the speed of the block when it has moved a distance of 0.0120 m from its initial position? (At this point the spring is compressed 0.0240 m.) Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? v= Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next > Item 19 19 of 32 > Review | Constants A block of mass m is placed in a smooth-bored spring gun at the bottom of the incline so that it compresses the spring by an amount c. The spring has spring constant k. The incline makes an angle with the horizontal and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is . The block is released, exits the muzzle of the gun, and slides up an incline a total distance L. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A Find L, the distance traveled along the incline by the block after it exits the gun. Ignore friction when the block is inside the gun. Also, assume that the uncompressed spring is just at the top of the gun (i.e., the block moves a distance while inside of the gun). Use g for the magnitude of acceleration due to gravity. Express the distance L in terms of xc, k, m, g, , and 0. View Available Hint(s) x m 0 L = Submit Provide Feedback ? Next > Item 20 20 of 32 Review | Constants In a "worst-case" design scenario, a 2000 kg elevator with broken cables is falling at 4.00 m/s when it first contacts a cushioning spring at the bottom of the shaft. The spring is supposed to stop the elevator, compressing 2.00 m as it does so. Spring coefficient is 10.6 kN/m. During the motion a safety clamp applies a constant 17000-N frictional force to the elevator. Part A What is the speed of the elevator after it has moved downward 1.00 m from the point where it first contacts a spring? Express your answer in meters per second. ? v= Submit Request Answer m/s Part B When the elevator is 1.00 m below point where it first contacts a spring, what is its acceleration? Express your answer in meters per square second. a = Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? m/s Next >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


