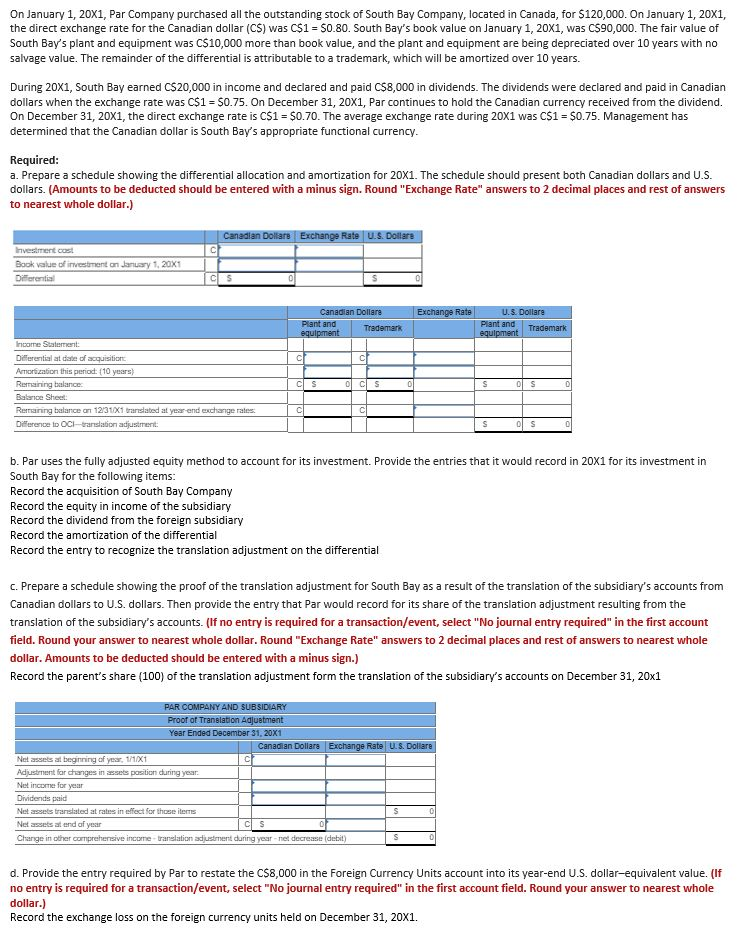
On January 1, 20x1, Par Company purchased all the outstanding stock of South Bay Company, located in Canada, for $120,000. On January 1, 20x1, the direct exchange rate for the Canadian dollar (CS) was C$1 = 50.80. South Bay's book value on January 1, 20x1, was C$90,000. The fair value of South Bay's plant and equipment was C$10,000 more than book value, and the plant and equipment are being depreciated over 10 years with no salvage value. The remainder of the differential is attributable to a trademark, which will be amortized over 10 years. During 20x1, South Bay earned CS20,000 in income and declared and paid C$8,000 in dividends. The dividends were declared and paid in Canadian dollars when the exchange rate was C$1 = $0.75. On December 31, 20x1, Par continues to hold the Canadian currency received from the dividend. On December 31, 20x1, the direct exchange rate is C$1 = $0.70. The average exchange rate during 20X1 was C$1 = $0.75. Management has determined that the Canadian dollar is South Bay's appropriate functional currency. Required: a. Prepare a schedule showing the differential allocation and amortization for 20X1. The schedule should present both Canadian dollars and U.S. dollars. (Amounts to be deducted should be entered with a minus sign. Round "Exchange Rate" answers to 2 decimal places and rest of answers to nearest whole dollar.) Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate U.S. Dollare Investment cost Book value of investment on January 1, 20X1 Differential CLS 0 S 0 Exchange Rate Canadian Dollars plant and Trademark equipment U.S. Dollare Plant and Trademark o c h Income Statement: Differential at date of acquisition Amortion this period: (10 years) Remaining balance Basice Sheet Remaining balance on 12/31x1 translated at yesrend exchange rates Difference to OCH-translation adjustment CSO CS 0 S 0 C C S 0S 0 b. Par uses the fully adjusted equity method to account for its investment. Provide the entries that it would record in 20x1 for its investment in South Bay for the following items: Record the acquisition of South Bay Company Record the equity in income of the subsidiary Record the dividend from the foreign subsidiary Record the amortization of the differential Record the entry to recognize the translation adjustment on the differential c. Prepare a schedule showing the proof of the translation adjustment for South Bay as a result of the translation of the subsidiary's accounts from Canadian dollars to U.S. dollars. Then provide the entry that Par would record for its share of the translation adjustment resulting from the translation of the subsidiary's accounts. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your answer to nearest whole dollar. Round "Exchange Rate" answers to 2 decimal places and rest of answers to nearest whole dollar. Amounts to be deducted should be entered with a minus sign.) Record the parent's share (100) of the translation adjustment form the translation of the subsidiary's accounts on December 31, 20x1 PAR COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARY Proof of Translation Adjustment Year Ended December 31, 20X1 Canadian Dollars Exchange Rate U.S. Dollare Net assets al beginning of year, 1/1/X1 Adjustment for changes in assets position during year. Net income for year Dividends paid Net assets translated at ratus in effect for those items Net assets at end of year Change in other comprehensive income-translation adjustment during year net decrease (debit) Ics d. Provide the entry required by Par to restate the C$8,000 in the Foreign Currency Units account into its year-end U.S. dollar-equivalent value. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required in the first account field. Round your answer to nearest whole dollar.) Record the exchange loss on the foreign currency units held on December 31, 20X1. On January 1, 20x1, Par Company purchased all the outstanding stock of South Bay Company, located in Canada, for $120,000. On January 1, 20x1, the direct exchange rate for the Canadian dollar (CS) was C$1 = 50.80. South Bay's book value on January 1, 20x1, was C$90,000. The fair value of South Bay's plant and equipment was C$10,000 more than book value, and the plant and equipment are being depreciated over 10 years with no salvage value. The remainder of the differential is attributable to a trademark, which will be amortized over 10 years. During 20x1, South Bay earned CS20,000 in income and declared and paid C$8,000 in dividends. The dividends were declared and paid in Canadian dollars when the exchange rate was C$1 = $0.75. On December 31, 20x1, Par continues to hold the Canadian currency received from the dividend. On December 31, 20x1, the direct exchange rate is C$1 = $0.70. The average exchange rate during 20X1 was C$1 = $0.75. Management has determined that the Canadian dollar is South Bay's appropriate functional currency. Required: a. Prepare a schedule showing the differential allocation and amortization for 20X1. The schedule should present both Canadian dollars and U.S. dollars. (Amounts to be deducted should be entered with a minus sign. Round "Exchange Rate" answers to 2 decimal places and rest of answers to nearest whole dollar.) Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate U.S. Dollare Investment cost Book value of investment on January 1, 20X1 Differential CLS 0 S 0 Exchange Rate Canadian Dollars plant and Trademark equipment U.S. Dollare Plant and Trademark o c h Income Statement: Differential at date of acquisition Amortion this period: (10 years) Remaining balance Basice Sheet Remaining balance on 12/31x1 translated at yesrend exchange rates Difference to OCH-translation adjustment CSO CS 0 S 0 C C S 0S 0 b. Par uses the fully adjusted equity method to account for its investment. Provide the entries that it would record in 20x1 for its investment in South Bay for the following items: Record the acquisition of South Bay Company Record the equity in income of the subsidiary Record the dividend from the foreign subsidiary Record the amortization of the differential Record the entry to recognize the translation adjustment on the differential c. Prepare a schedule showing the proof of the translation adjustment for South Bay as a result of the translation of the subsidiary's accounts from Canadian dollars to U.S. dollars. Then provide the entry that Par would record for its share of the translation adjustment resulting from the translation of the subsidiary's accounts. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your answer to nearest whole dollar. Round "Exchange Rate" answers to 2 decimal places and rest of answers to nearest whole dollar. Amounts to be deducted should be entered with a minus sign.) Record the parent's share (100) of the translation adjustment form the translation of the subsidiary's accounts on December 31, 20x1 PAR COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARY Proof of Translation Adjustment Year Ended December 31, 20X1 Canadian Dollars Exchange Rate U.S. Dollare Net assets al beginning of year, 1/1/X1 Adjustment for changes in assets position during year. Net income for year Dividends paid Net assets translated at ratus in effect for those items Net assets at end of year Change in other comprehensive income-translation adjustment during year net decrease (debit) Ics d. Provide the entry required by Par to restate the C$8,000 in the Foreign Currency Units account into its year-end U.S. dollar-equivalent value. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required in the first account field. Round your answer to nearest whole dollar.) Record the exchange loss on the foreign currency units held on December 31, 20X1







