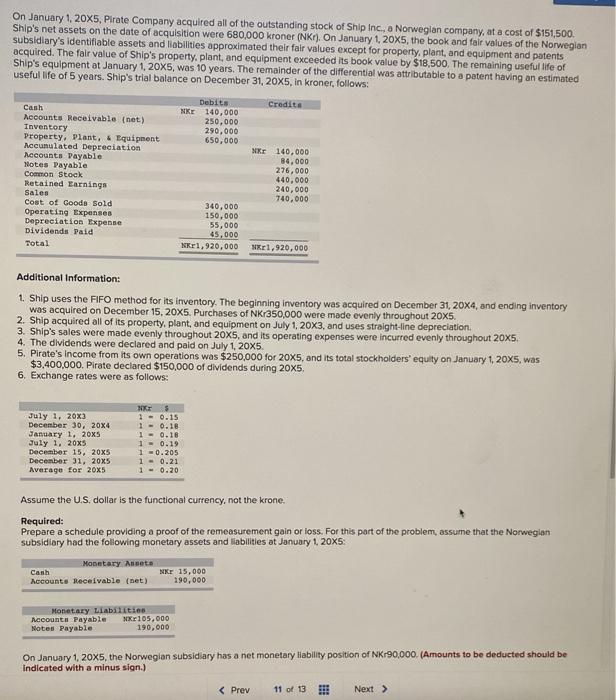
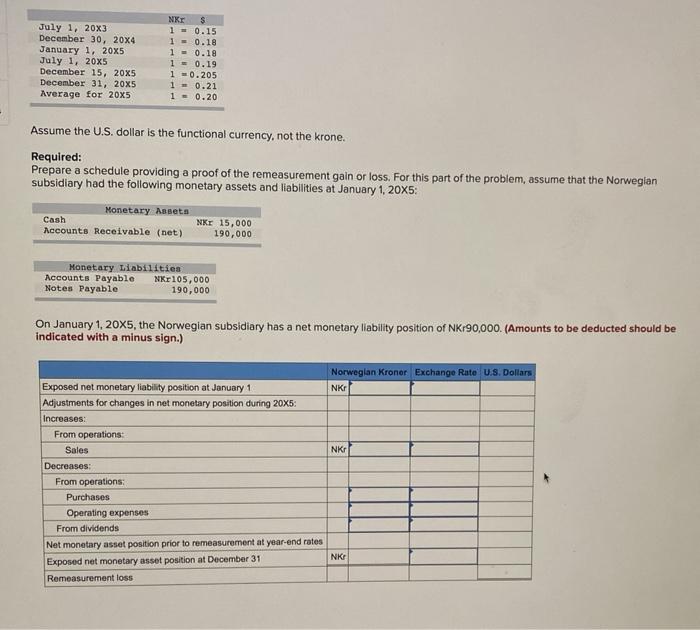
On January 1, 20X5, Pirate Company acquired all of the outstanding stock of Ship Inc., a Norwegian company, at a cost of $151,500 Ship's net assets on the date of acquisition were 680,000 kroner (NK). On January 1, 20X5, the book and fair values of the Norwegian subsidiary's identifiable assets and liabilities approximated their fair values except for property, plant, and equipment and patents acquired. The fair value of Ship's property, plant, and equipment exceeded its book value by $18,500. The remaining useful life of Ship's equipment at January 1, 20X5, was 10 years. The remainder of the differential was attributable to a patent having an estimated useful life of 5 years. Ship's trial balance on December 31, 20X5, in kroner, follows: Credit Debits MKE 140,000 250,000 290,000 650,000 Cash Accounts Receivable (net) Inventory Property, Plant, & Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Notes Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Sales Cost of Goods Sold Operating Expenses Depreciation Expense Dividends Paid Total NE 140,000 84,000 276,000 440,000 240,000 740,000 340,000 150,000 55,000 45,000 Nkr1, 920,000 1.920,000 Additional Information: 1. Ship uses the FIFO method for its inventory. The beginning inventory was acquired on December 31, 20X4, and ending inventory was acquired on December 15, 20X5. Purchases of NKr350,000 were made evenly throughout 20X5 2. Ship acquired all of its property, plant, and equipment on July 1, 20X3, and uses straight-line depreciation. 3. Ship's sales were made evenly throughout 20x5, and its operating expenses were incurred evenly throughout 20x5. 5. Pirate's income from its own operations was $250,000 for 20X5, and is total stockholders' equilty on January 1, 20x5, was $3,400,000. Pirate declared $150,000 of dividends during 20x5 6. Exchange rates were as follows: July 1, 20X3 December 30, 20X4 January 1, 2005 July 1, 2005 December 15, 20x5 December 31, 20X5 Average for 20X5 MORE 5 1 = 0.15 1 -0.18 1 = 0.18 1 - 0.19 1 -0.205 1 -0.21 1 -0.20 Assume the U.S. dollar is the functional currency, not the krone. Required: Prepare a schedule providing a proof of the remeasurement gain or loss. For this part of the problem, assume that the Norwegian subsidiary had the following monetary assets and liabilities at January 1, 20x5: Monetary Asset Canh NKE 15,000 Accounts Receivable (net) 190,000 Monetary Liabilities Accounts Payable Xr105,000 Notes Payable 190,000 On January 1, 20x5, the Norwegian subsidiary has a net monetary liability position of NK190,000. (Amounts to be deducted should be Indicated with a minus sign.) July 1, 20X3 December 30, 20X4 January 1, 20X5 July 1, 20x5 December 15, 2005 December 31, 20X5 Average for 20x5 NKE $ 10.15 10.18 10.18 1 = 0.19 1 0.205 1 0.21 1 = 0.20 Assume the U.S. dollar is the functional currency, not the krone. Required: Prepare a schedule providing a proof of the remeasurement gain or loss. For this part of the problem, assume that the Norwegian subsidiary had the following monetary assets and liabilities at January 1, 20x5: Monetary Annet Cash Accounts Receivable (net) Nkr 15,000 190,000 Monetary Liabilities Accounts Payable Nr 105,000 Notes Payable 190,000 On January 1, 20X5, the Norwegian subsidiary has a net monetary liability position of NK190,000. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign.) Norwegian Kroner Exchange Rate U.S. Dollars NKT NKT Exposed net monetary liability position at January 1 Adjustments for changes in net monetary position during 20x5: Increases: From operations Sales Decreases: From operations: Purchases Operating expenses From dividends Net monetary asset position prior to remeasurement at year-end rates Exposed net monetary asset position at December 31 Remeasurement loss NK On January 1, 20X5, Pirate Company acquired all of the outstanding stock of Ship Inc., a Norwegian company, at a cost of $151,500 Ship's net assets on the date of acquisition were 680,000 kroner (NK). On January 1, 20X5, the book and fair values of the Norwegian subsidiary's identifiable assets and liabilities approximated their fair values except for property, plant, and equipment and patents acquired. The fair value of Ship's property, plant, and equipment exceeded its book value by $18,500. The remaining useful life of Ship's equipment at January 1, 20X5, was 10 years. The remainder of the differential was attributable to a patent having an estimated useful life of 5 years. Ship's trial balance on December 31, 20X5, in kroner, follows: Credit Debits MKE 140,000 250,000 290,000 650,000 Cash Accounts Receivable (net) Inventory Property, Plant, & Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Notes Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Sales Cost of Goods Sold Operating Expenses Depreciation Expense Dividends Paid Total NE 140,000 84,000 276,000 440,000 240,000 740,000 340,000 150,000 55,000 45,000 Nkr1, 920,000 1.920,000 Additional Information: 1. Ship uses the FIFO method for its inventory. The beginning inventory was acquired on December 31, 20X4, and ending inventory was acquired on December 15, 20X5. Purchases of NKr350,000 were made evenly throughout 20X5 2. Ship acquired all of its property, plant, and equipment on July 1, 20X3, and uses straight-line depreciation. 3. Ship's sales were made evenly throughout 20x5, and its operating expenses were incurred evenly throughout 20x5. 5. Pirate's income from its own operations was $250,000 for 20X5, and is total stockholders' equilty on January 1, 20x5, was $3,400,000. Pirate declared $150,000 of dividends during 20x5 6. Exchange rates were as follows: July 1, 20X3 December 30, 20X4 January 1, 2005 July 1, 2005 December 15, 20x5 December 31, 20X5 Average for 20X5 MORE 5 1 = 0.15 1 -0.18 1 = 0.18 1 - 0.19 1 -0.205 1 -0.21 1 -0.20 Assume the U.S. dollar is the functional currency, not the krone. Required: Prepare a schedule providing a proof of the remeasurement gain or loss. For this part of the problem, assume that the Norwegian subsidiary had the following monetary assets and liabilities at January 1, 20x5: Monetary Asset Canh NKE 15,000 Accounts Receivable (net) 190,000 Monetary Liabilities Accounts Payable Xr105,000 Notes Payable 190,000 On January 1, 20x5, the Norwegian subsidiary has a net monetary liability position of NK190,000. (Amounts to be deducted should be Indicated with a minus sign.) July 1, 20X3 December 30, 20X4 January 1, 20X5 July 1, 20x5 December 15, 2005 December 31, 20X5 Average for 20x5 NKE $ 10.15 10.18 10.18 1 = 0.19 1 0.205 1 0.21 1 = 0.20 Assume the U.S. dollar is the functional currency, not the krone. Required: Prepare a schedule providing a proof of the remeasurement gain or loss. For this part of the problem, assume that the Norwegian subsidiary had the following monetary assets and liabilities at January 1, 20x5: Monetary Annet Cash Accounts Receivable (net) Nkr 15,000 190,000 Monetary Liabilities Accounts Payable Nr 105,000 Notes Payable 190,000 On January 1, 20X5, the Norwegian subsidiary has a net monetary liability position of NK190,000. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign.) Norwegian Kroner Exchange Rate U.S. Dollars NKT NKT Exposed net monetary liability position at January 1 Adjustments for changes in net monetary position during 20x5: Increases: From operations Sales Decreases: From operations: Purchases Operating expenses From dividends Net monetary asset position prior to remeasurement at year-end rates Exposed net monetary asset position at December 31 Remeasurement loss NK