On January 1, Year 9, P Corp. acquired 75% of S Corp. for $1,500,000. P uses the cost method to account for its investment

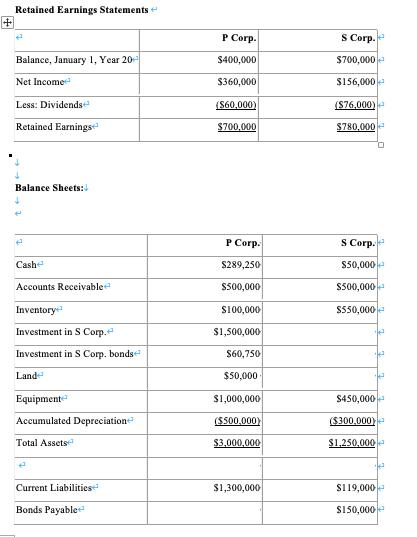
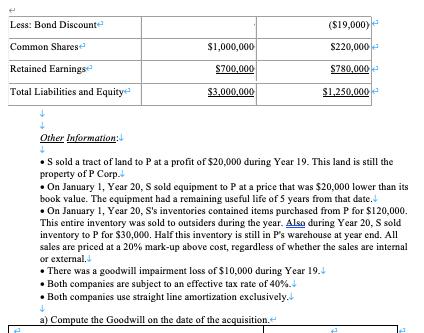

On January 1, Year 9, P Corp. acquired 75% of S Corp. for $1,500,000. P uses the cost method to account for its investment in S. On January 1, Year 9, S's retained earnings and common shares were $600,000 and $220,000, respectively. S's book values did not differ materially from its fair values on the date of acquisition with the following exceptions: Inventory had a fair value that was $50,000 higher than its book value. A patent (which had not previously been accounted for) was identified on the acquisition date with an estimated fair value of $20,000. The patent had an estimated useful life of 5 years. The Financial Statements of P Corp. and S Corp. for the year ended December 31, Year 20 are shown below: Income Statements! Sales Other Revenues Less: Expenses Cost of Goods Solde Depreciation Expense Other Expenses Income Tax Expense Net Income P Corp. $1,000,000 $600,000 $800,000 $40,000 $160,000 $240,000 $360,000 S Corp. $600,000 $240,000 $480,000 $20,000 $80,000 $104,000 $156,000 + Retained Earnings Statements + Balance, January 1, Year 20 Net Income Less: Dividends Retained Earnings Balance Sheets: Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Investment in S Corp. Investment in S Corp. bonds Land Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Total Assets 2 Current Liabilities Bonds Payable P Corp. $400,000 $360,000 ($60,000) $700,000 P Corp. $289,250 $500,000 $100,000 $1,500,000 $60,750 $50,000 $1,000,000 ($500,000) $3,000,000 $1,300,000 S Corp. $700,000 $156,000+ ($76,000) $780,000 S Corp. $50,000 $500,000 $550,000 $450,000 ($300,000) $1,250,000 $119,000 $150,000 Less: Bond Discounte Common Shares Retained Earnings Total Liabilities and Equity 4 Other Information: $1,000,000 $700,000 $3,000,000 ($19,000) $220,000 $780,000 $1,250,000 S sold a tract of land to P at a profit of $20,000 during Year 19. This land is still the property of P Corp. On January 1, Year 20, S sold equipment to P at a price that was $20,000 lower than its book value. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 5 years from that date. On January 1, Year 20, S's inventories contained items purchased from P for $120,000. This entire inventory was sold to outsiders during the year. Also during Year 20, S sold inventory to P for $30,000. Half this inventory is still in P's warehouse at year end. All sales are priced at a 20% mark-up above cost, regardless of whether the sales are internal or external. There was a goodwill impairment loss of $10,000 during Year 19. Both companies are subject to an effective tax rate of 40%. . Both companies use straight line amortization exclusively. 4 a) Compute the Goodwill on the date of the acquisition. Using the information from question 2, make the assumption you are preparing the consolidation worksheet for December 31, Year 20. Prepare the following journal entries. + H a) Eliminate S Corp's Shareholders' Equity and setup any goodwill and acquisition differential at the start of year 20. < b) Set up NCI at the start of year 20. < c) Record any amortization adjustment for year 20. < d) Record the entry related to profits in beginning inventory. < e) Record the entry to adjust beginning Retained Earnings from the cost method to the equity method. (
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a Eslimate Scorps shareholdeo Equity and goodwill and a...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


