Question
On January 3, 2021, Jonah Inc. engaged an independent CPA to perform an audit for the year ended December 31, 2020. Jonah uses a perpetual
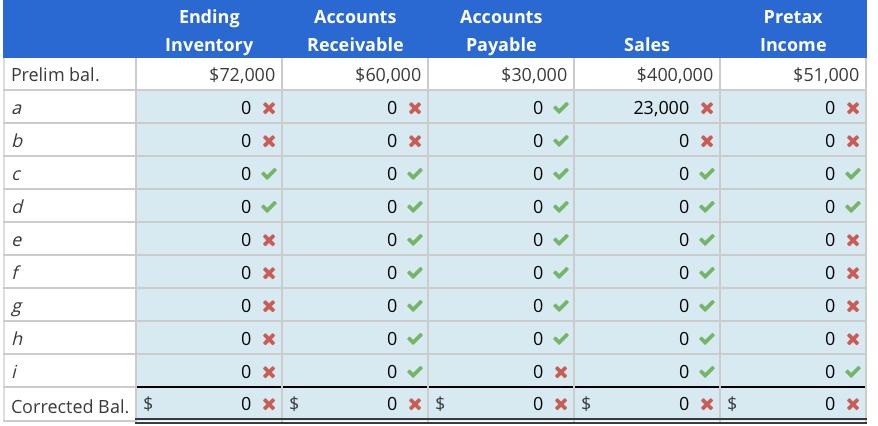
On January 3, 2021, Jonah Inc. engaged an independent CPA to perform an audit for the year ended December 31, 2020. Jonah uses a perpetual inventory system. The CPA did not observe the inventory count on December 31, 2020; as a result, a special examination was made of the inventory records. The financial statements prepared by the company (uncorrected) showed the following: ending inventory, $72,000; accounts receivable, $60,000; accounts payable, $30,000; sales, $400,000; and pretax income, $51,000.
The following items a through i were uncovered during the audit.
a. Merchandise that cost $18,000 was excluded from the physical inventory count, and the related sale for $23,000 was recorded. The goods had been segregated in the warehouse for shipment; however, control of the inventory had not passed to the customer.
b. Merchandise that cost $10,000 was out on consignment to Barr Company and was excluded from the ending inventory. The merchandise was recorded as a sale of $25,000 when shipped to Barr on December 2, 2020.
c. Merchandise costing $1,500 was received on December 28, 2020. but was excluded from the physical inventory count. The auditor located the source documents with the purchasing agent; they indicated, “On consignment from Baker Company.”
d. Merchandise costing $2,000 was received on January 8, 2021, and the related purchase invoice recorded January 9. The invoice showed the shipment was made on December 29, 2020, F.O.B. destination. The merchandise was excluded from inventory.
e. Merchandise that cost $11,000, was sold on December 31, 2020, for $16,000, shipped F.O.B. shipping point. The sale was recorded; however, the cost of the in-transit inventory was included in ending inventory.
f. Merchandise that cost $6,000 was excluded from ending inventory and not recorded as a sale for $7,500 on December 31, 2020. The goods had been specifically segregated. Control of the inventory will not pass to the customer until delivery.
g. Merchandise that cost $15,000 was included in ending inventory. The related purchase has not been recorded. The goods had been shipped by the vendor F.O.B. destination, and the invoice, but not the goods, was received on December 30, 2020.
h. Merchandise in transit that cost $7,000 was excluded from inventory because it was not yet received. The shipment from the vendor was F.O.B. shipping point. The purchase was recorded on December 29, 2020, when the invoice was received.
i. Merchandise that cost $8,000 was included in ending inventory because it was received. The merchandise had been rejected because of incorrect specifications and was being held for return to the vendor. The merchandise was recorded as a credit purchase on December 26, 2020.
Complete a row in the following table for each item a through i. Each item has one column for each of five financial statement amounts (unadjusted balances). Show the specific correction to each balance and the final corrected balance for each financial statement amount.
- Use a negative sign to show a decrease.
Ending Accounts Accounts Pretax Inventory Receivable Payable Sales Income Prelim bal. $72,000 $60,000 $30,000 $400,000 $51,000 0 x 23,000 x a 0 x f 0 x 0 x 0 x 0 x i 0 x Corrected Bal. $ 0 x $ 0 x $ 0 x $ 0 x $ 0 x of
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Solution Ending Accounts Accounts Pretax Sales Inventory Receivable ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


