Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read
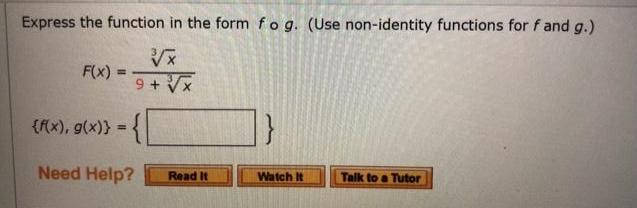
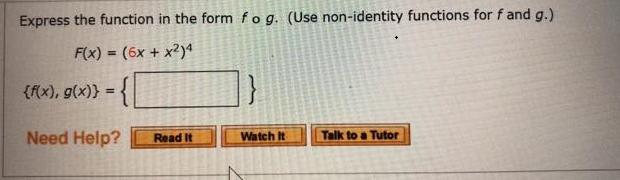
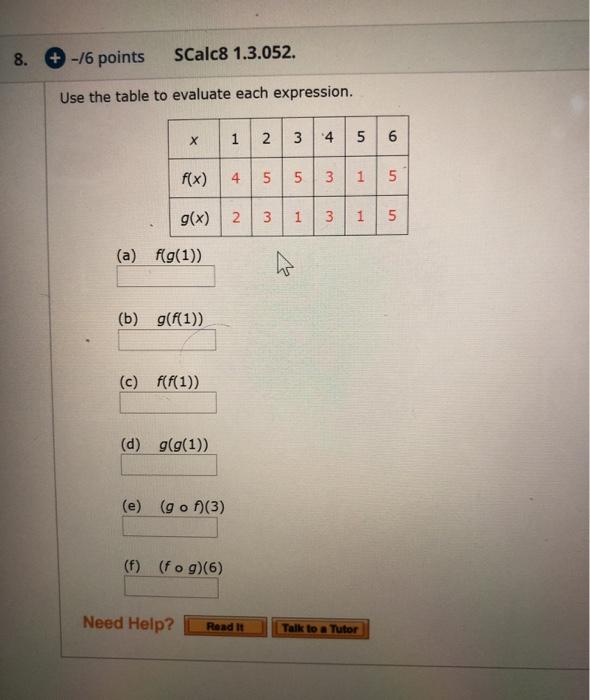
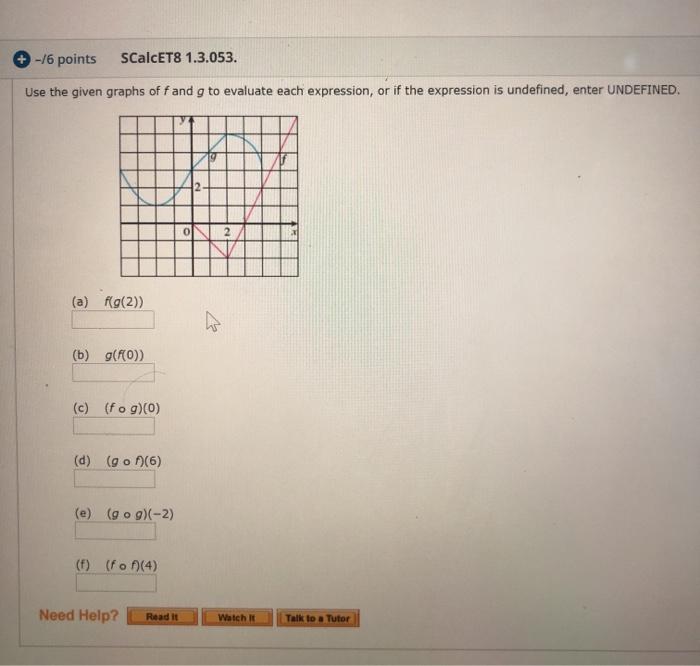
Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 3 4 4 5 5 Need Help? Read It 2 1 3 3 5 1 6 Talk to a Tutor 5 1 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 3 4 4 5 5 Need Help? Read It 2 1 3 3 5 1 1 Talk to a Tutor 6 5 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 3 4 4 5 5 Need Help? Read It 2 1 3 3 5 1 6 Talk to a Tutor 5 1 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 3 4 4 5 5 Need Help? Read It 2 1 3 3 5 1 6 Talk to a Tutor 5 1 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 3 4 4 5 5 Need Help? Read It 2 1 3 3 5 1 6 Talk to a Tutor 5 1 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fo g. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) x 9+x F(x) {f(x), g(x)} = Need Help? Read It Watch It Talk to a Tutor Express the function in the form fog. (Use non-identity functions for f and g.) F(x) = (6x + x2)4 {f(x), g(x)} = { Need Help? Read It B 7 Watch It Talk to a Tutor 8. + -/6 points SCalc8 1.3.052. Use the table to evaluate each expression. X f(x) g(x) 2 3 (a) f(g(1)) (b) g(f(1)) (c) f(f(1)) (d) g(g(1)) (e) (gof)(3) 1 2 (f) (fog)(6) 4 5 Need Help? Read It 3 4 5 3 2 1 3 5 1 1 Talk to a Tutor 6 5 5 + -/6 points SCalcET8 1.3.053. Use the given graphs of f and g to evaluate each expression, or if the expression is undefined, enter UNDEFINED. (a) f(g(2)) (b) g(f(0)) (c) (fog)(0) (d) (gof)(6) (e) (gog)(-2) (f) (fof)(4) Need Help? Read it 0 2- 2 Watch It Talk to a Tutor
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.45 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Question Q6 Q5 Q8 Q Use t...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


