Only answer if you are 100% sure(Just tell me the right choice)

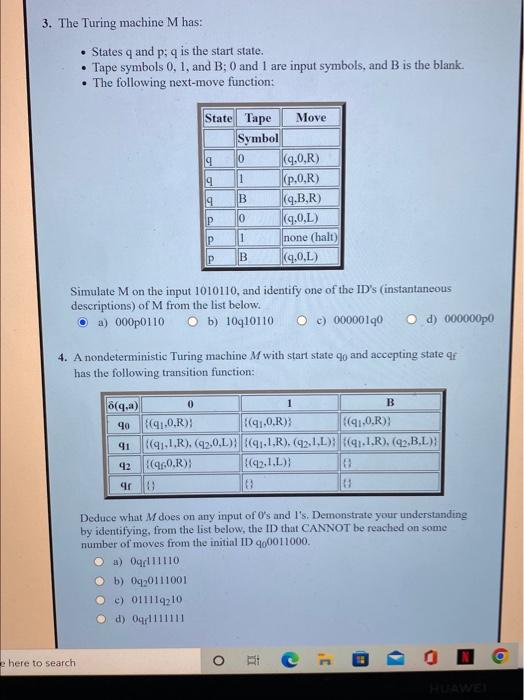
Suppose a problem P1 reduces to a problem P2. Which of the following statements can we conclude to be TRUE based on the above? a) If P2 is undecidable, then it must be that P1 is decidable. b) If P1 is undecidable, then it must be that P2 is decidable. c) If P1 is decidable, then it must be that P2 is decidable. d) If P2 is decidable, then it must be that P1 is decidable. Suppose there are three languages (i.e., problems), of which we know the following: 1. Ll is in P. 2. L2 is NP-complete. 3. L3 is not in NP. Suppose also that we do not know anything about the resolution of the "P vs. NP" question; for example, we do not know definitely whether P=NP. Classify each of the following languages as (a) Definitely in P, (b) Definitely in NP (but perhaps not in P and perhaps not NP-complete) (c) Definitely NP-complete (d) Definitely not in NP: - L1 [union] L2. - L1L2. - L2cL3, where c is a symbol not in the alphabet of L2 or L3 (i.e., the marked concatenation of L2 and L3, where there is a unique marker symbol between the strings from L2 and L3 ). - The complement of L3. Based on your analysis, pick the correct, definitely true statement from the list below. a) L2cL3 is definitely not in NP. b) The complement of L3 is definitely not NP-complete. c) L1L2 is definitely in P. d) L1L2 is definitely not in NP. 3. The Turing machine M has: - States q and p;q is the start state. - Tape symbols 0,1 , and B; 0 and 1 are input symbols, and B is the blank. - The following next-move function: Simulate M on the input 1010110 , and identify one of the ID's (instantaneous. deseriptions) of M from the list below. a) 000p0110 b) 10q10110 c) 000001q0 d) 000000p0 4. A nondeterministic Turing machine M with start state q0 and accepting state qf has the following transition function: Deduce what M does on any input of 0 's and l's. Demonstrate your understanding by identifying, from the list below, the ID that CANNOT be reached on some number of moves from the initial ID 900011000. a) 0qq111110 b) 0q20111001 c) 01111q210 d) 0qr1111111 5. The Turing machine M has: - States q and p;q is the start state. - Tape symbols 0,1 , and B; 0 and 1 are input symbols, and B is the blank. - The following next-move function: Your problem is to describe the property of an input string that makes M halt. Identify a string that makes M halt from the list below. a) 010110 b) 00100 c) 1001 d) 00001 6. In the following expressions, - represents negation of a variable. For example, x stands for "NOT x"), + represents logical OR, and juxtaposition represents logical AND (e.g., (x+y)(y+z) represents ( x OR y) AND (y OR z ). Identify the expression that is satisfiable, from the list below. a) (y+z)(z+x)(y)(x+y) b) (y+z)(y+z)(y)(z+x) c) (y+z)(z+x)(y)(x+y) d) (y)(y+z)(z+x)(x+y) or the purpose of this question, we assume that all languages are over input lphabet {0,1}. Also, we assume that a Turing machine can have any fixed iumber of tapes. Sometimes restricting what a Turing machine can do does not affect the class of languages that can be recognized ... the restricted Turing machines can still be designed to accept any recursively enumerable language. Other restrictions limit what languages the Turing machine can accept. For example, it might limit the languages to some subset of the recursive languages, which we know is smaller than the recursively enumerable languages. Here are some of the possible restrictions: 1. Limit the number of states the TM may have. 2. Limit the number of tape symbols the TM may have. 3. Limit the number of times any tape cell may change. 4. Limit the amount of tape the TM may use. 5. Limit the number of moves the TM may make. 6. Limit the way the tape heads may move. Consider the effect of limitations of these types, perhaps in pairs. Then, from the list below, identify the combination of restrictions that allows the restricted form of Turing machine to accept all recursively enumerable languages. a) Allow the TM to use only n2 tape cells when the input is of length n. b) Allow the TM to run for only 2n moves when the input is of length n. c) Allow only two input symbols, 0 and 1 , and one other tape symbol, B. d) Allow the TM to run for only n2 moves when the input is of length n