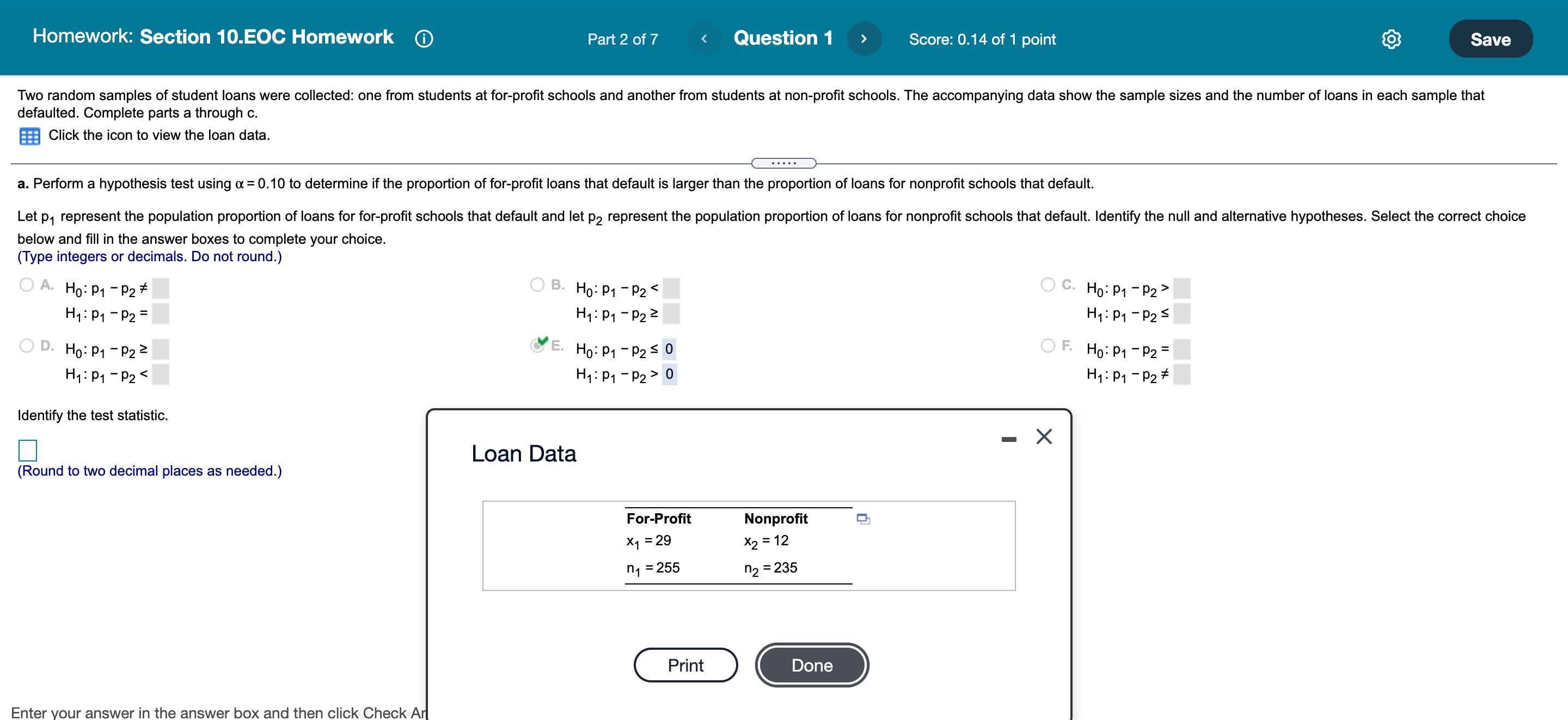
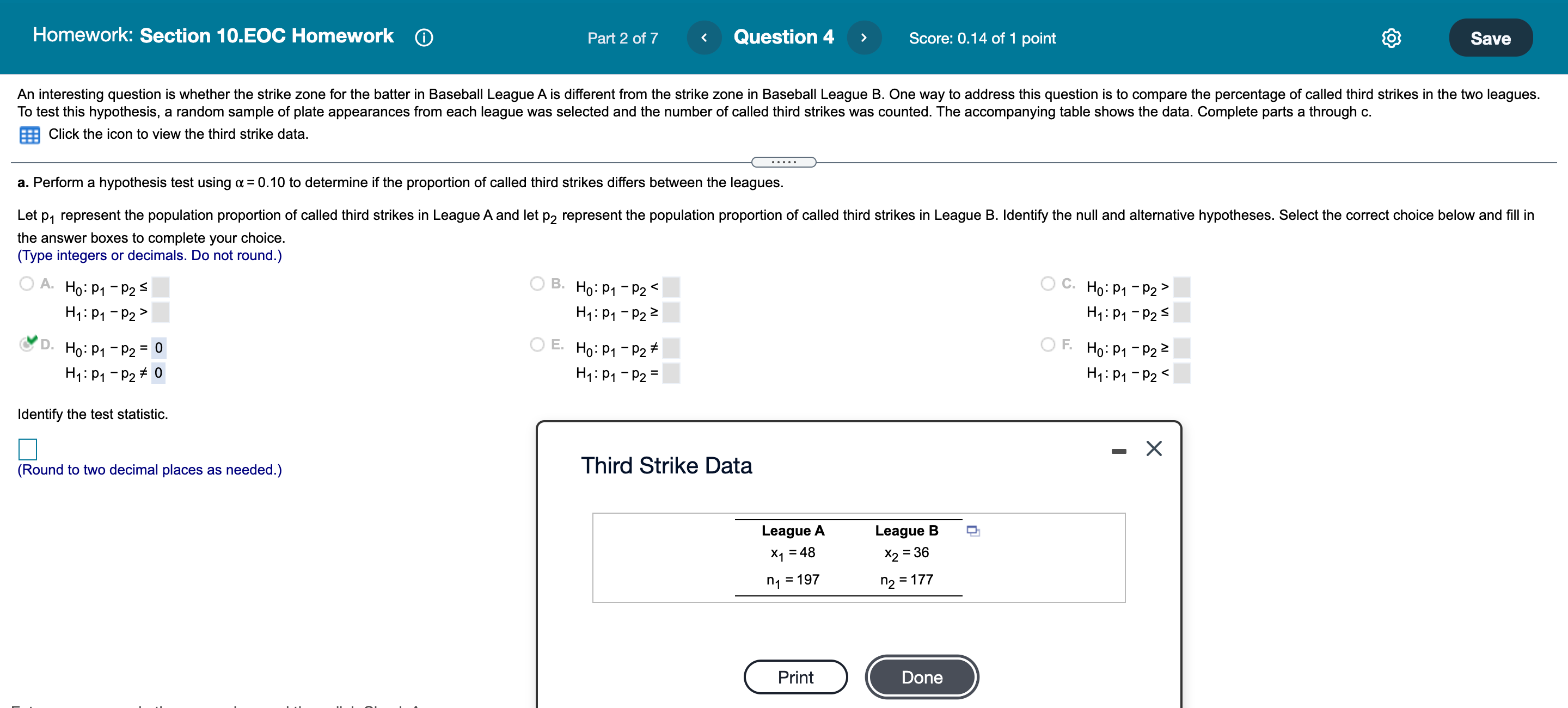
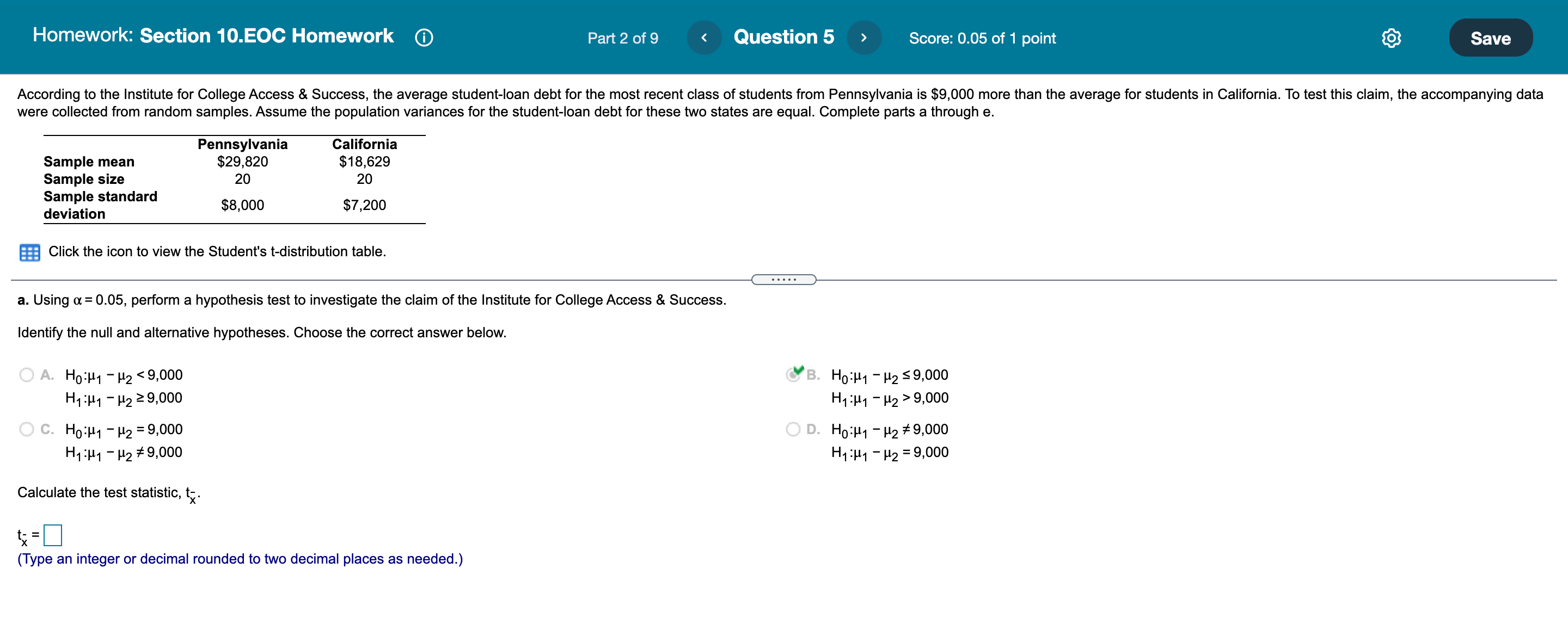
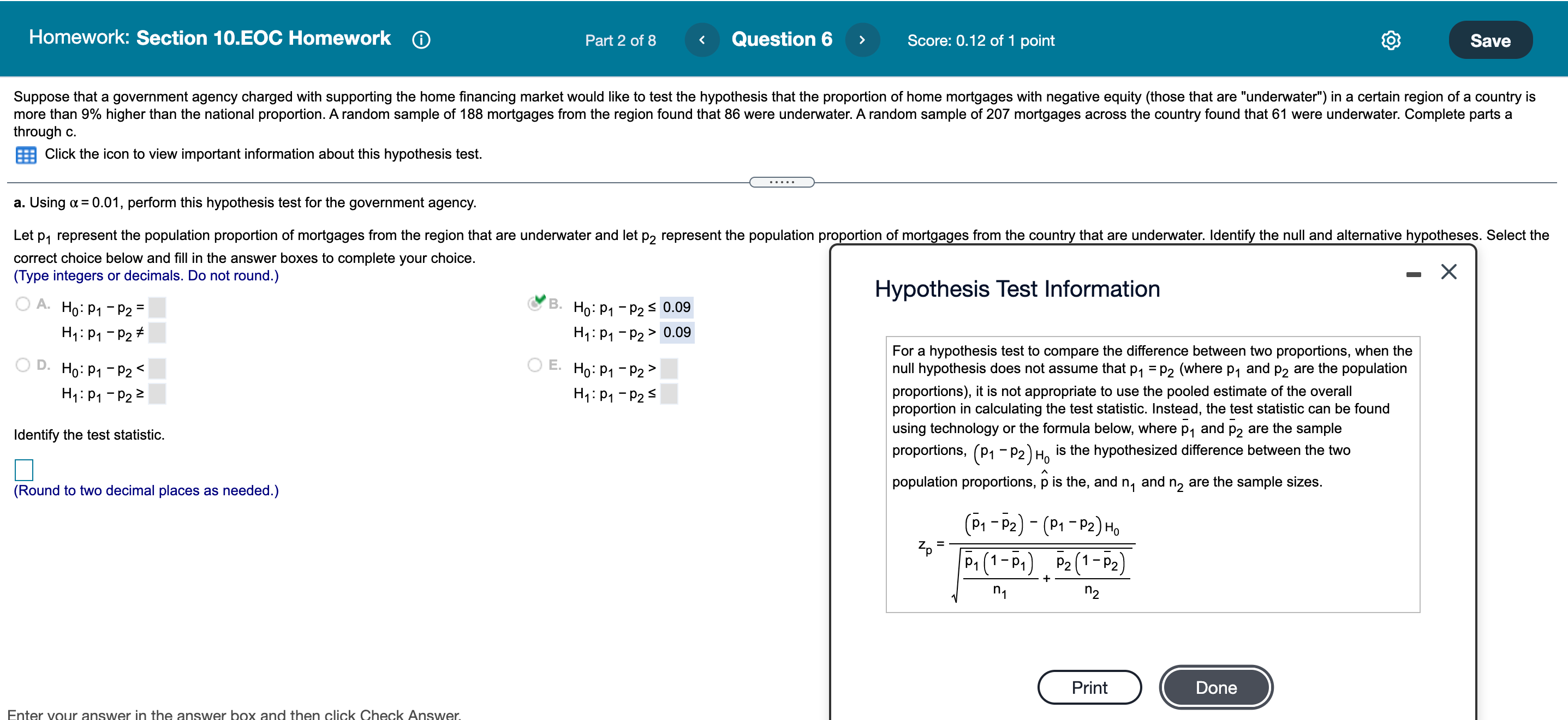
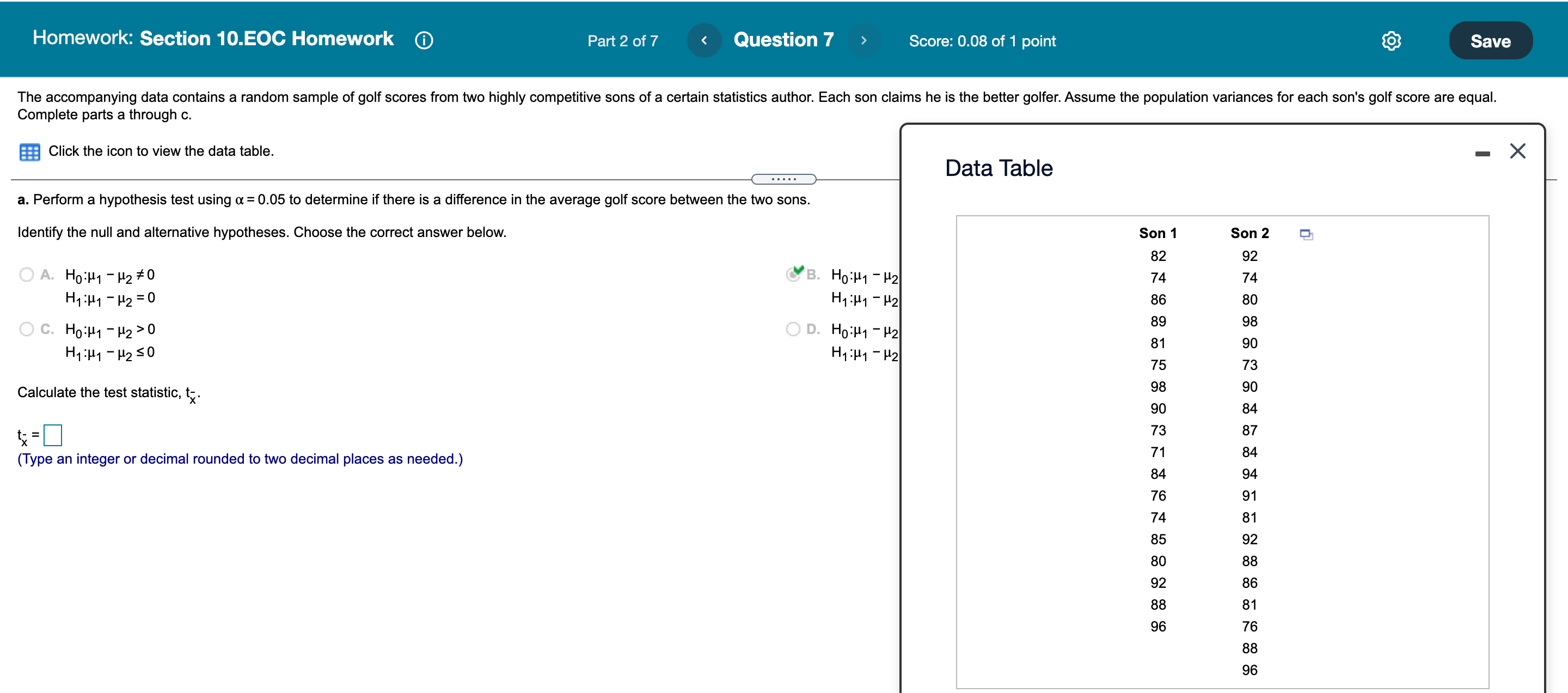
only do the blank ones
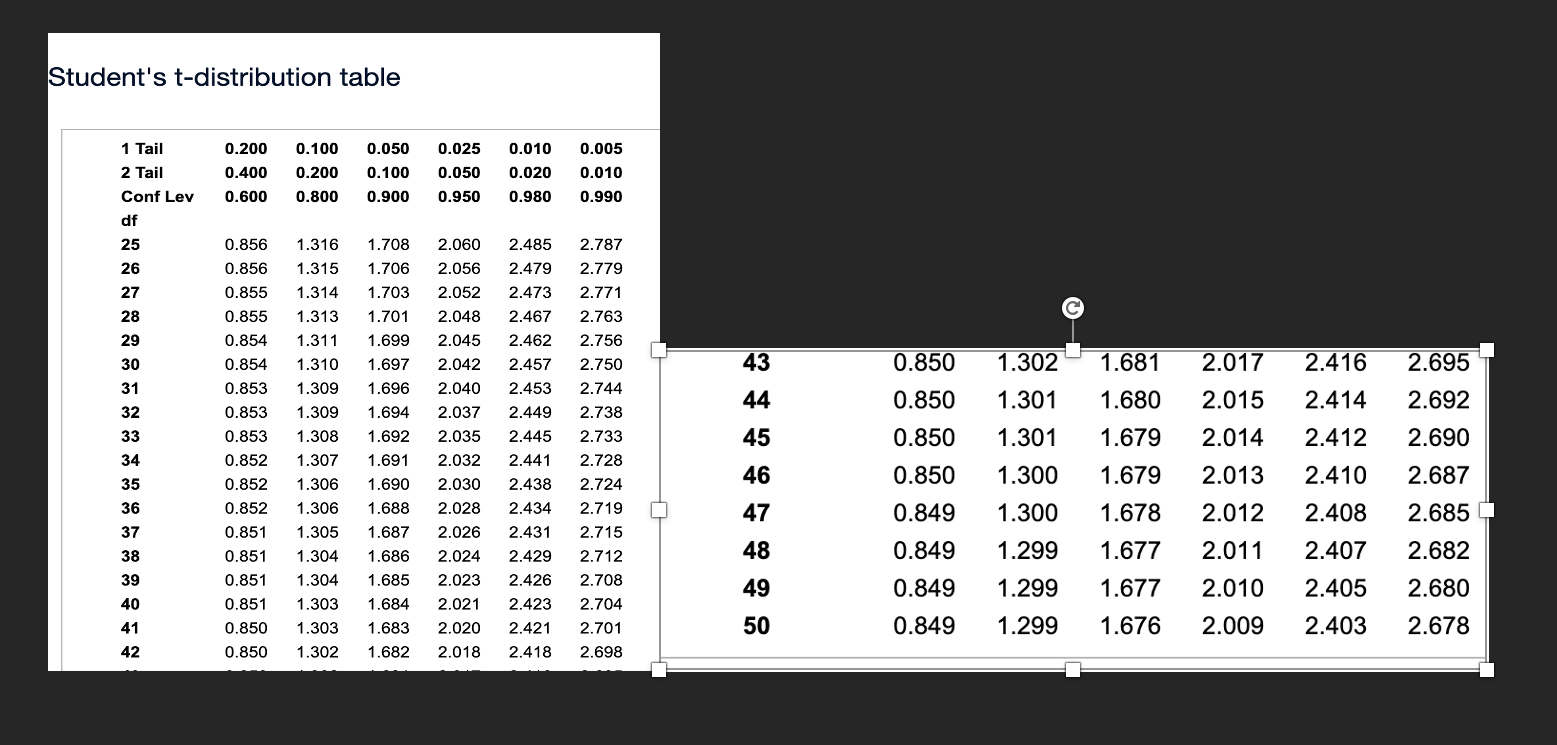
Student's t-distribution table 1 Tail 0.200 0.100 0.050 0.025 0.010 0.005 2 Tail 0.400 0.200 0.100 0.050 0.020 0.010 Conf Lev 0.600 0.800 0.900 0.950 0.980 0.990 df 25 0.856 1.316 1.708 2.060 2.485 2.787 26 0.856 1.315 1.706 2.056 2.479 2.779 27 0.855 1.314 1.703 2.052 2.473 2.771 28 0.855 1.313 1.701 2.048 2.467 2.763 C 29 0.854 1.311 1.699 2.045 2.462 2.756 30 0.854 1.310 1.697 2.042 2.457 2.750 43 0.850 1.302 1.681 2.017 2.416 2.695 31 0.853 1.309 1.696 2.040 2.453 2.744 32 0.853 1.309 1.694 2.037 2.449 2.738 44 0.850 1.301 1.680 2.015 2.414 2.692 33 0.853 1.308 1.692 2.035 2.445 2.733 45 0.850 1.301 1.679 2.014 2.412 2.690 34 0.852 1.307 1.691 2.032 2.441 2.728 35 0.852 1.306 1.690 2.030 2.438 2.724 46 0.850 1.300 1.679 2.013 2.410 2.687 36 0.852 1.306 1.688 2.028 2.434 2.719 47 0.849 37 1.300 1.678 2.012 2.408 2.685 0.851 1.305 1.687 2.026 2.431 2.715 38 0.851 1.304 1.686 2.024 2.429 2.712 48 0.849 1.299 1.677 2.011 2.407 2.682 39 0.851 1.304 1.685 2.023 2.426 2.708 49 40 0.849 0.851 1.299 1.303 1.684 2.021 1.677 2.423 2.704 2.010 2.405 2.680 41 0.850 1.303 1.683 2.020 2.421 2.701 50 0.849 1.299 1.676 2.009 2.403 2.678 42 0.850 1.302 1.682 2.018 2.418 2.698Homework: Section 10.EOC Homework O Part 2 of 7 Question 1 Score: 0.14 of 1 point KO Save Two random samples of student loans were collected: one from students at for-profit schools and another from students at non-profit schools. The accompanying data show the sample sizes and the number of loans in each sample that defaulted. Complete parts a through c. Click the icon to view the loan data. a. Perform a hypothesis test using a = 0.10 to determine if the proportion of for-profit loans that default is larger than the proportion of loans for nonprofit schools that default. Let p, represent the population proportion of loans for for-profit schools that default and let p2 represent the population proportion of loans for nonprofit schools that default. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) O A. Ho: P1 - P2* OB. Ho: P1 - P2 H1 : P1 - P2 = H1 : P1 - P2 2 H1 : P1 - P2 S OD. Ho: P1 - P2 2 ME. Ho: P1 - P2 5 0 OF. Ho: P1 - P2 = H1 : P1 - P2 0 H1 : P1 - P2# Identify the test statistic. - X Loan Data Round to two decimal places as needed.) For-Profit Nonprofit X1 = 29 X2 = 12 ng = 255 n2 = 235 Print Done Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check ArHomework: Section 10.EOC Homework Part 2 of 8 Question 2 Score: 0.07 of 1 point Save During the 2007-2008 decline in the housing market, it appeared that the average size of a newly constructed house fell. To investigate this trend, the square footages of a random sample of houses built in 2008 were compared to houses built in 2018. A random sample of 45 homes built in 2008 had a sample mean of 2,449.7 square feet and a sample standard deviation of 768.5 square feet. A random sample of 50 homes built in 2018 had a sample mean of 2,227.3 square feet and a sample standard deviation of 746.9 square feet. Assume that the population variances for the square footages of houses built in these two years are equal. Complete parts a through d. a. Using a = 0.05, perform a hypothesis test to determine if the average home constructed in 2008 was larger than a home built in 2018. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. HO:H1 - H2 So OB. HO:H1 - H2# 0 H1: 1 1 - H 2 > 0 H1: H1 - 12 = 0 O C. HO:H1 - H2 20 OD. HO:H1 - H2 = 0 H1: 1 1 - H2 50 H1:Hd # 50 Identify the test statistic, to. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.)Homework: Section 10.EOC Homework Part 2 of 7 Question 4 Score: 0.14 of 1 point Save An interesting question is whether the strike zone for the batter in Baseball League A is different from the strike zone in Baseball League B. One way to address this question is to compare the percentage of called third strikes in the two leagues. To test this hypothesis, a random sample of plate appearances from each league was selected and the number of called third strikes was counted. The accompanying table shows the data. Complete parts a through c. Click the icon to view the third strike data. a. Perform a hypothesis test using a = 0.10 to determine if the proportion of called third strikes differs between the leagues. Let p1 represent the population proportion of called third strikes in League A and let p2 represent the population proportion of called third strikes in League B. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) O A. Ho: P1 - P2 S OB. Ho: P1 - P2 H1 : P1 - P2 > H1 : P1 - P2 2 H1 : P1 - P2 s D. Ho: P1 - P2 = 0 OE. Ho: P1 - P2# OF. Ho: P1 - P2 2 H1 : P1 - P2 # 0 H1 : P1 - P2 = H1 : P1 - P2 9,000 O C. HO:H1 - H2 = 9,000 O D. HO:M1 - H2 #9,000 H1:141 - H2 # 9,000 H1:H1 - H2 = 9,000 Calculate the test statistic, to. 1 = 0 (Type an integer or decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.)Homework: Section 10.EOC Homework Part 2 of 8 0.09 For a hypothesis test to compare the difference between two proportions, when the OD. Ho: P1 - P2 null hypothesis does not assume that p, = P2 (where p, and p2 are the population H1 : P1 - P2 2 H1 : P1 - P2 s proportions), it is not appropriate to use the pooled estimate of the overall proportion in calculating the test statistic. Instead, the test statistic can be found Identify the test statistic. using technology or the formula below, where p, and p2 are the sample proportions, (P1 - P2 ) Ho is the hypothesized difference between the two 7 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) population proportions, p is the, and n, and n2 are the sample sizes. ( P1 - P2) - (P1 - P2 ) Ho Zo = P1 ( 1 - P 1 ) P2 ( 1 - P2 ) n2 Print DoneHomework: Section 10.EOC Homework (D Question 7 , Score: 0.08 of1 point The accompanying data contains a random sample of golf scores from two highly competitive sons of a certain statistics author. Each son claims he is the better golfer. Assume the population variances for each son's golf score are equal. Complete parts a through c. a Click the icon to view the data table, 3. Perform a hypothesis test using or = 0.05 to determine if there is a difference in the average golf score between the two sons. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. H0411 - p2 # 0 H14"1 ' P2 = 0 C. Hozp1-p2 >0 H1:p1 - #2 s 0 Calculate the test statistic, t; 0;: (Type an integer or decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.) Data Table