- Out of sampling techniques found below, compare the techniques based on validity and efficiency. Choose the one that you would like to use to sample your population for your survey and justify why you chose it (hypothetical).
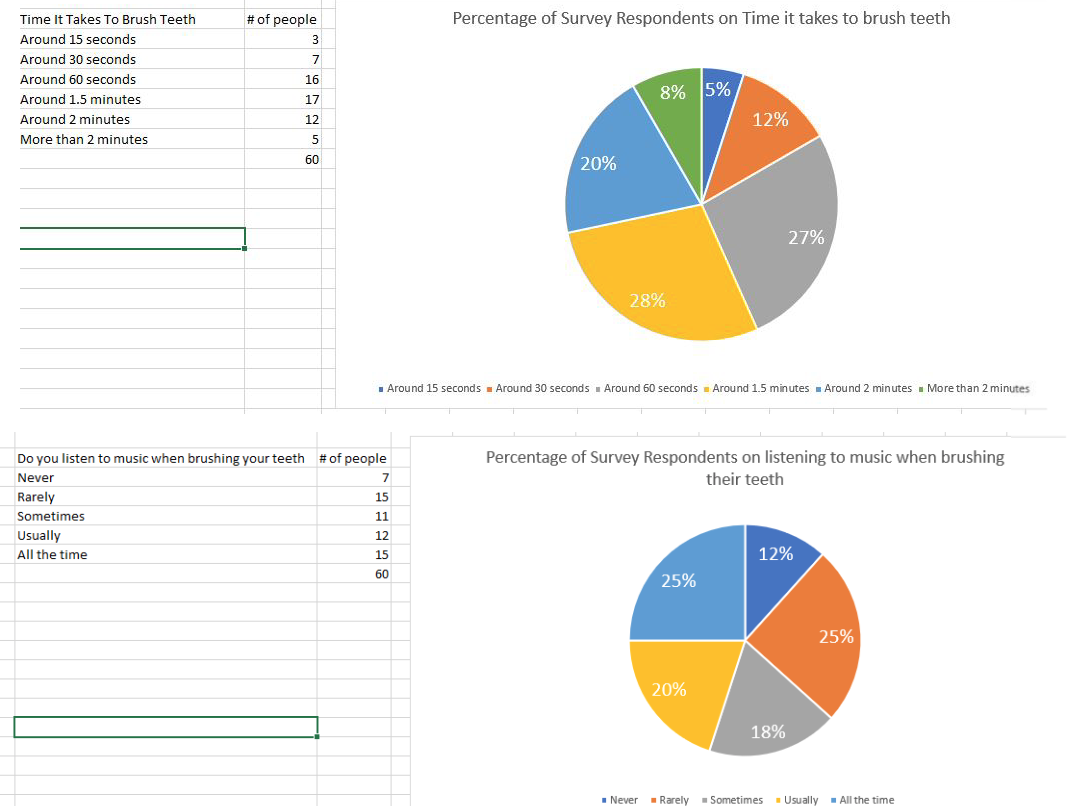
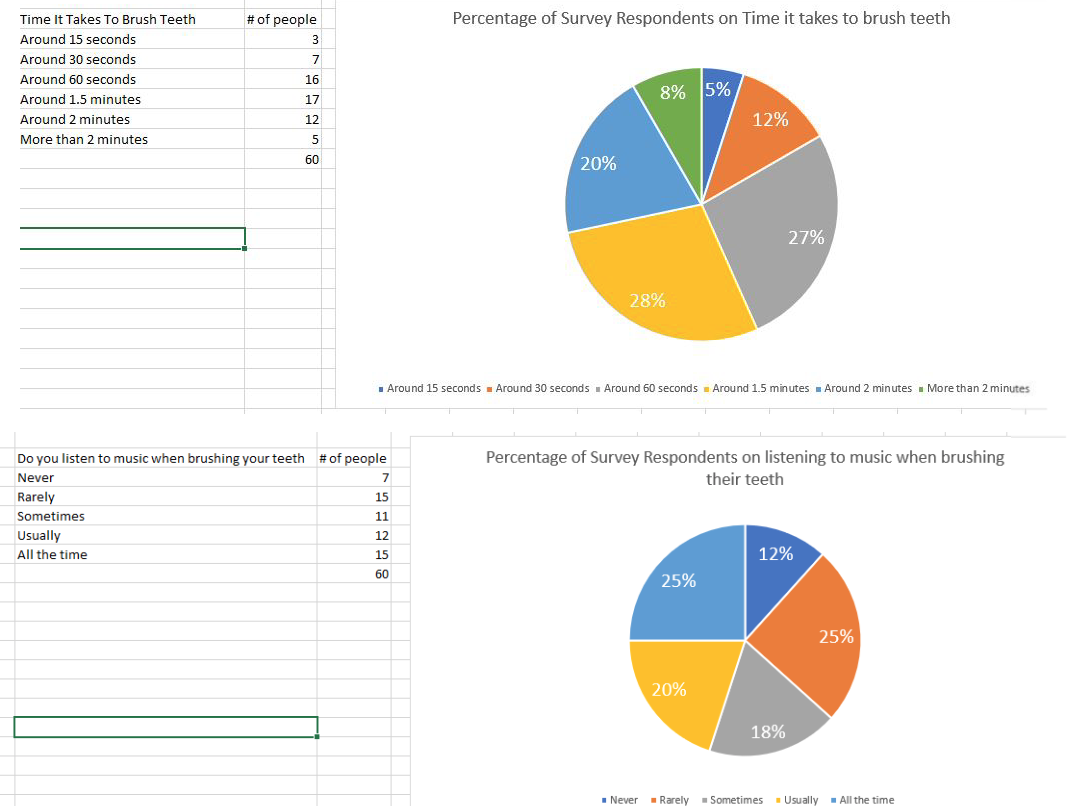
we asked 60 people on how long they brush their teeth; here is the survey result: TIME IT TAKES TO BRUSH TEETH 1. Around 15 seconds 2. Around 30 seconds 3. Around 60 seconds --- -16 4. Around 1.5 minutes ---- 17 5. Around 2 minutes ---- -12 6. More than 2 minutes -5 You listen to music when brushing your teeth 1. Never -7 2. Rarely ------ 15 3. Sometimes -- ----- -11 4. Usually 12 5. All the time 15Random Sampling Techniques Simple Random Sample: Asimple random sample is where a percentage of the population are randomly chosen. A technique to draw a random individual is used, such as a random number generator. Systematic Random Sample: The population is sampled from an ordered list which chooses individuals at regular intervals. For example, if the population has a size of 100, and you wanted to sample 20 of them, you would divide 100 by 20 which would give you twenty intervals of five. You would randomly select one of the first five people, and then take every fifth person next on the ordered list. Random Sampling from Groups Stratified Random Sample: The population is divided into groups based on certain The same percentage of each group is selected at random using the same technique as a simple random sample, but within each group. This would allow each group to be represented in the same proportion in the sample as they are in the population. For example, if you had 3 stratas, one with 50 people, one with 100 people, one with 200 people and you wanted 10%, you would take 5, 10 and 20 people from the groups respectively. Cluster Random Sample: The population is divided, usually geographically, into groups that generally have the same size. A certain number of groups are randomly chosen, and every individual in the chosen groups are chosen for the sample. Multi-Stage Random Sample: The population is divided into a hierarchy and a random sample is chosen at each level. For example, if you wanted to sample a city, you may randomly choose some subdivisions or buildings, and randomly choose some streets or floors, and randomly choose some addresses from each. Non-Random Sampling In non-random sampling, each member of the population does not have the same probability of being chosen. Voluntary Sample: A voluntary sample is where participants choose whether or not they will participate. Sometimes, the participants contact the researchers after being offered some kind of incentive. A common example of a voluntary sample is an online survey. Time It Takes To Brush Teeth # of people Percentage of Survey Respondents on Time it takes to brush teeth Around 15 seconds 3 Around 30 seconds 7 Around 60 seconds 16 8% 5% Around 1.5 minutes 17 Around 2 minutes 12 12% More than 2 minutes 5 60 20% 27% 28% Around 15 seconds . Around 30 seconds . Around 60 seconds . Around 1.5 minutes . Around 2 minutes . More than 2 minutes Do you listen to music when brushing your teeth # of people Percentage of Survey Respondents on listening to music when brushing Never 7 their teeth Rarely 15 Sometimes 11 Usually 12 All the time 15 12% 60 25% 25% 20% 18% Never Rarely Sometimes . Usually . All the time