Question
Overview:You will need to run yarn along the inside of a shoebox to represent two initial vectors. Then, after a series of calculations, you will
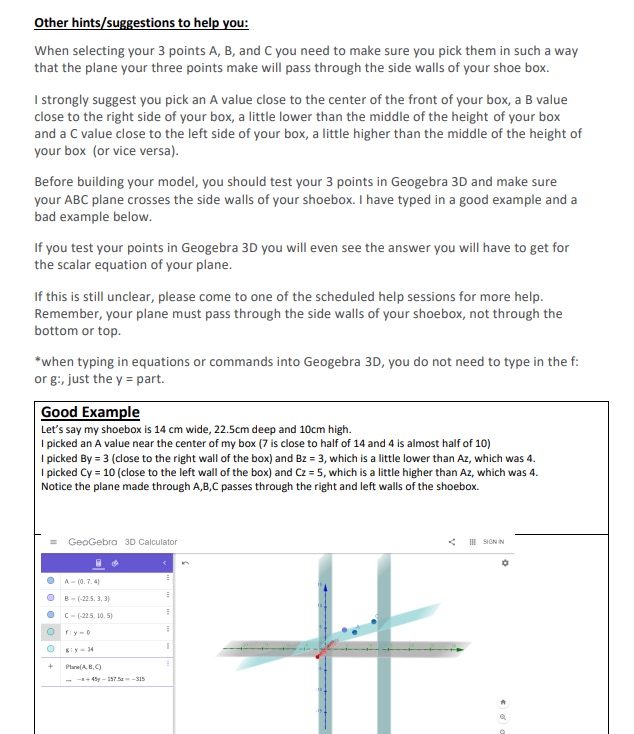
Overview:You will need to run yarn along the inside of a shoebox to represent two initial vectors. Then, after a series of calculations, you will run a third vector that crosses the two vectors you originally taped. If your calculations are correct, the third vector you make should cross the other two vectors at two intersection points.*All measurements are in centimeters, rounded to 1 decimal place.Example of a correct answer: Point A(0,7,5)Point B (-27.2,6,4)Point C(-27.2,12,6)Equation of the Plane: 4x+54.4y+-163.2z+435.2=0Point D(-10,0,2.42)larrI chose x=-10 and y=0 because they are on the left of the shoebox and solved for zPoint E(-20,157.18)larr I chose x=-20 and y=15 because they are on the right of the shoebox and solved for zIMPORTANT NOTE: For this year's project, the x value you choose for points D and E must be exactly half the xvalue of your shoebox. In my case that would have been -13.6Point Flarr is the intersection of the line formed by DE and ABPoint Glarr is the intersection of the line formed by DE and ACOther hints/suggestions to help you:When selecting your 3 points A,B, and C you need to make sure you pick them in such a waythat the plane your three points make will pass through the side walls of your shoe box.I strongly suggest you pick an A value close to the center of the front of your box, a B valueclose to the right side of your box, a little lower than the middle of the height of your boxand a C value close to the left side of your box, a little higher than the middle of the height ofyour box (or vice versa).Before building your model, you should test your 3 points in Geogebra 3D and make sureyour ABC plane crosses the side walls of your shoebox. I have typed in a good example and abad example below.If you test your points in Geogebra 3D you will even see the answer you will have to get forthe scalar equation of your plane.Remember, your plane must pass through the side walls of your shoebox, not through thebottom or top.*when typing in equations or commands into Geogebra 3D, you do not need to type in the f :or g:, just the y= part.Good ExampleLet's say my shoebox is 14 cm wide, 22.5 cm deep and 10 cm high.I picked an A value near the center of my box ( 7 is close to half of 14 and 4 is almost half of 10)I picked By=3 (close to the right wall of the box) and Bz=3, which is a little lower than Az , which was 4 .I picked Cy=10 (close to the left wall of the box) and Cz=5, which is a little higher than AZ, which was 4 .Notice the plane made through A,B,C passes through the right and left walls of the shoebox.Bad ExampleLet's say my shoebox is 14 cm wide, 22.5 cm deep and 10 cm high.I picked an A value a little more off center of my box ( 8 is off from the middle, but 4 wasn't to bad)I picked By=5 (more to the centre than the right wall of the box) and Bz=3, which is a little lower than Az , whichwas 4.I picked Cy=8 (more to the centre than the left wall of the box) and Cz=5, which is a little higher than Az , which wasNotice the plane made through A,B,C passes through the floor of the shoebox and not the side wall of the shoebox.Following this: use a new hight, width and depth, as well as new A,B,C coordinates to get a new answer that follows the criteria
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


