Question
Part 1 Differences between two means (T-test) Differences in sleep and income by sex Group Statistics Sex N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Weight
Part 1 Differences between two means (T-test)
‘Differences in sleep and income by sex’ Group Statistics | |||||
Sex | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | |
Weight in pounds | Male | 170 | 168.12 | 24.210 | 1.857 |
Female | 136 | 129.51 | 18.429 | 1.580 | |
Average hours of sleep per night | Male | 170 | 7.653 | 1.5981 | .1226 |
Female | 136 | 8.281 | 1.8569 | .1592 | |
Household income | Male | 170 | 39403.24 | 19235.298 | 1475.280 |
Female | 136 | 41150.75 | 19850.689 | 1702.183 | |
Independent Samples Effect Sizes | |||||
Standardizera | Point Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
Lower | Upper | ||||
Weight in pounds | Cohen's d | 21.832 | 1.769 | 1.502 | 2.033 |
Hedges' correction | 21.886 | 1.764 | 1.498 | 2.028 | |
Glass's delta | 18.429 | 2.095 | 1.757 | 2.430 | |
Average hours of sleep per night | Cohen's d | 1.7178 | -.366 | -.593 | -.138 |
Hedges' correction | 1.7221 | -.365 | -.591 | -.138 | |
Glass's delta | 1.8569 | -.338 | -.567 | -.109 | |
Household income | Cohen's d | 19510.976 | -.090 | -.315 | .136 |
Hedges' correction | 19559.277 | -.089 | -.314 | .136 | |
Glass's delta | 19850.689 | -.088 | -.314 | .138 | |
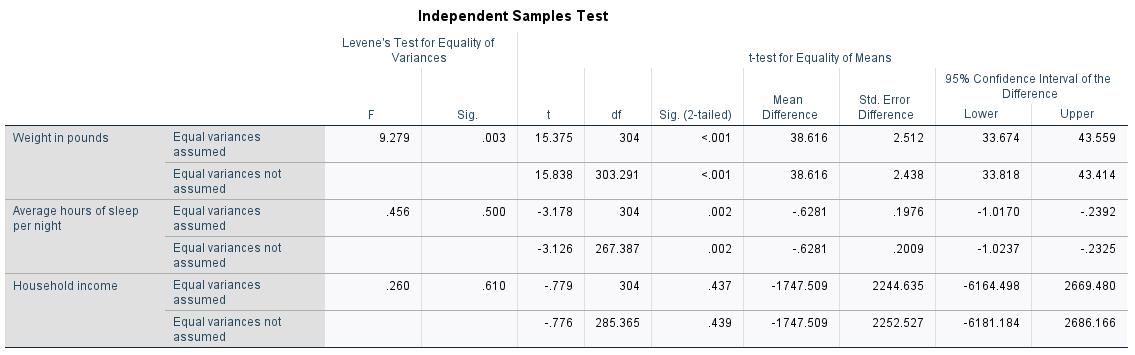
a. The denominator used in estimating the effect sizes. Cohen's d uses the pooled standard deviation. Hedges' correction uses the pooled standard deviation, plus a correction factor. Glass's delta uses the sample standard deviation of the control group. Part 1 Differences between two means Review your data output from your T-tests. 1. If we use t-tests to assess a significant difference between two means, why do we have consider the variance of the two group scores as part of this process? (1 mark) 2. Did you violate assumptions of variance with any of the t-tests? Explain. (2 marks) 3. What would be the statistical conclusion from the analyses for both sleep, income and weight? Ensure that in your conclusion you express your t-scores from your data (see Powerpoint and T-test Practice assignment for how to express t-values for such write-ups) (2 marks) 4. You ran three t-tests in this experiment. Why is this not advised? (1 mark) 5. Which type of t-test (dependent or independent) will always have less pooled variance associated with it? Why? (2 marks) 6. Why does the t-distribution use standard error instead of the standard deviation/z-scores? (2 marks)
| |||||
Weight in pounds Average hours of sleep per night Household income. Equal variances assumed Equal variances not assumed Equal variances assumed Equal variances not assumed. Equal variances assumed Equal variances not. assumed. Levene's Test for Equality of Variances Sig. F Independent Samples Test t df 304 15.375 15.838 303.291 -3.178 304 -3.126 267.387 -.779 304 -.776 285.365 9.279 .456 .260 .003 .500 .610 Sig. (2-tailed)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Part 1 Differences between two means Ttest Differences in sleep and income by sex Group Statistics Sex N Mean Std Deviation Std Error Mean Weight in p...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 1 attachment)
6295bc22df033_StatisticalConcept2.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


