Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Part 1: PRA Probability Calculations (70 points) Pump 'A' and Pump 'B' are pumps that perform the same function within the same system. Therefore,
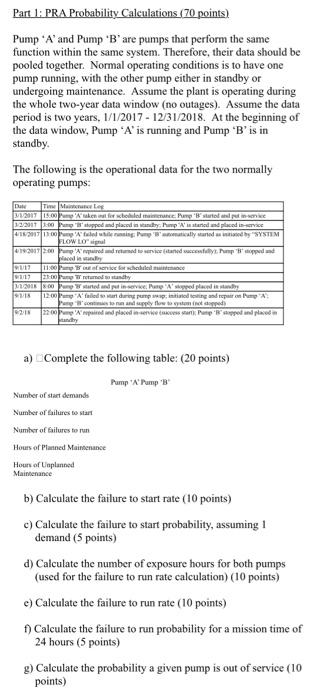
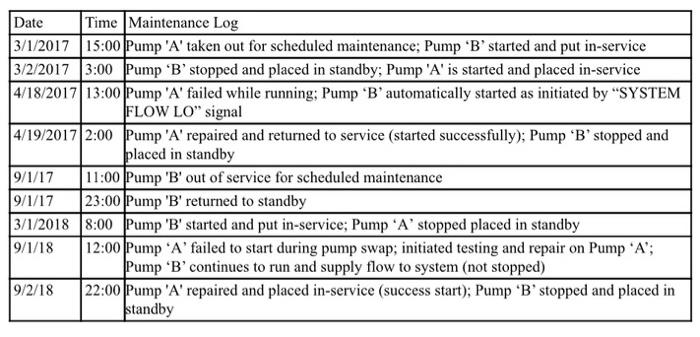
Part 1: PRA Probability Calculations (70 points) Pump 'A' and Pump 'B' are pumps that perform the same function within the same system. Therefore, their data should be pooled together. Normal operating conditions is to have one pump running, with the other pump either in standby or undergoing maintenance. Assume the plant is operating during the whole two-year data window (no outages). Assume the data period is two years, 1/1/2017- 12/31/2018. At the beginning of the data window, Pump 'A' is running and Pump 'B' is in standby. The following is the operational data for the two normally operating pumps: Date Time Maintenance Leg 3/1/2017 15:00 Pump A' taken out for scheduled maintenance Pump 'B' started and put in-service 32/2017 3:00 P' stopped and placed in standby Pump 'A' in started and placed in-service 4/16/2017 13:00 'A' failed while running Pump 'B'omatically started as initiated by "SYSTEM FLOW LO signal 4/19/2017 2:00 Pump A'repid and returned to service (stacy). Pump "B" stopped and placed in sedly 91/17 17 11:00Pmp out of service for scheduled t 23:00 Pump Wreturned to standby 31/2018 8:00 Pump started and put in-service, Pang 'A' stopped placed in standby 3/18 92/18 12:00 Pump A falled to start during pump; initiated testing and repair on Pump "A contesto nun and supply flow to system (not stopped 22:00 Pump 'A' repaired and placed in-service access start); Pamp 'B' stopped and placed in a) Complete the following table: (20 points) Pump 'A' Pump 'B' Number of start demands Number of failures to start Number of failures to run Hours of Planned Maintenance Hours of Unplanned Maintenance b) Calculate the failure to start rate (10 points) c) Calculate the failure to start probability, assuming I demand (5 points) d) Calculate the number of exposure hours for both pumps (used for the failure to run rate calculation) (10 points) e) Calculate the failure to run rate (10 points) f) Calculate the failure to run probability for a mission time of 24 hours (5 points) g) Calculate the probability a given pump is out of service (10 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


