Question
Part 1:1. Connect to the Rotary Motion Sensor. Select Linear Velocity (Large Pulley)..2. Configure the masses as they are in part one of the lab
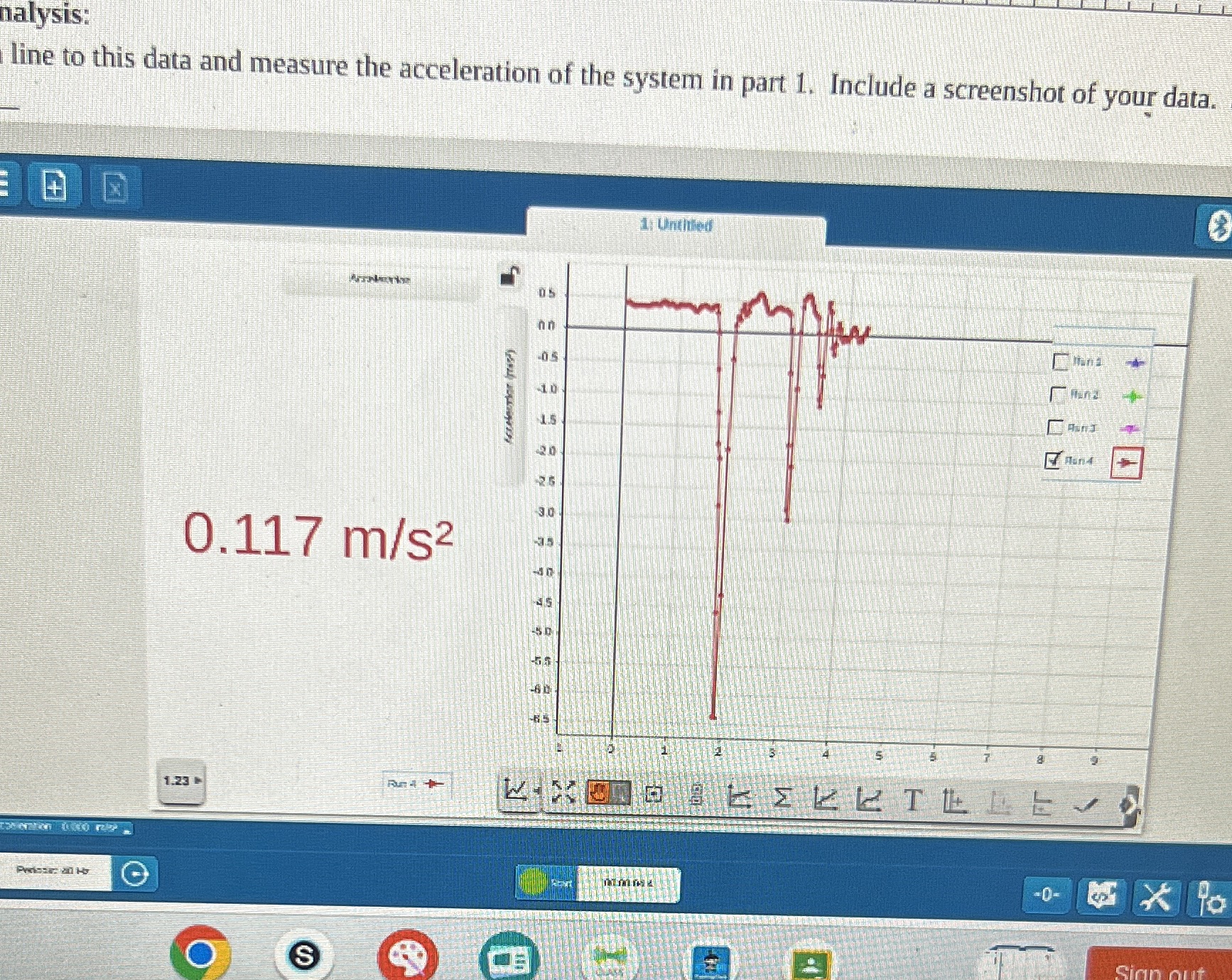
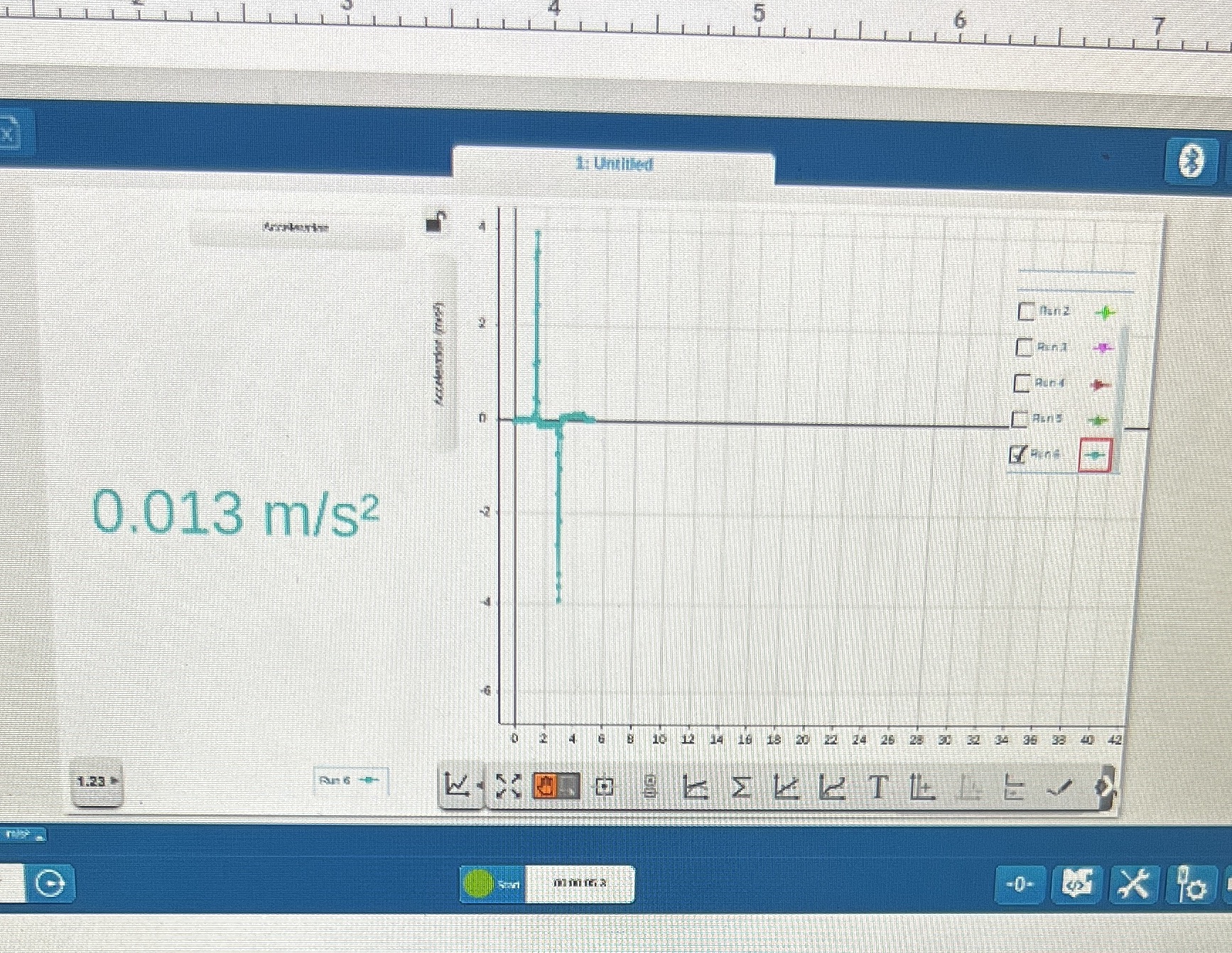
Part 1:1. Connect to the Rotary Motion Sensor. Select Linear Velocity (Large Pulley)..2. Configure the masses as they are in part one of the lab using m, = 100 grams andm, = 90 grams. Tip: The 90 g mass is made up of a 50 g mass and two 20 gmasses hooked together. When hooking the masses together be sure to keep the 50 g upright so that it stays attached to the string.3. Gently lower the 90 g mass by holding onto the bottom of the three masses hooked together. Keep the string vertical! Pulling the string to the side will cause the weights to swing as they go up (and possibly colliding with other objects).The 90 g mass does not need to be pulled all the way down to the table.4. Select the "Green Play" Arrow.5. Release the 90 g mass. You can stop collecting data when the masses stop moving.Part 2:1. Configure the weights so that there is an equal mass of 100 g on each side (you will have to remove the two 20 gmasses and replace them with a 50 g mass).2. Gently pull the two 50 g masses as far down as they will go. Let go (they should more or less stay in place.)3. Press the "Green Play" Arrow, to begin a new data collection. With one fluid motion, gently push the 100 g mass straight down with enough force to get it to the table. Do not use more force than is necessary, though, then what is needed for it to reach the table. Stop data collection when the masses come to rest.Data= 0.117 m/s^2and 0.013 m/s^2

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


