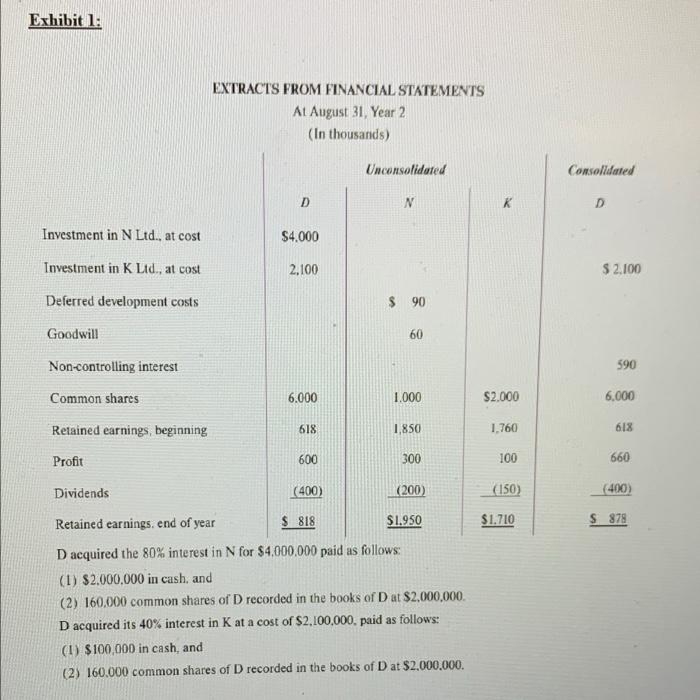
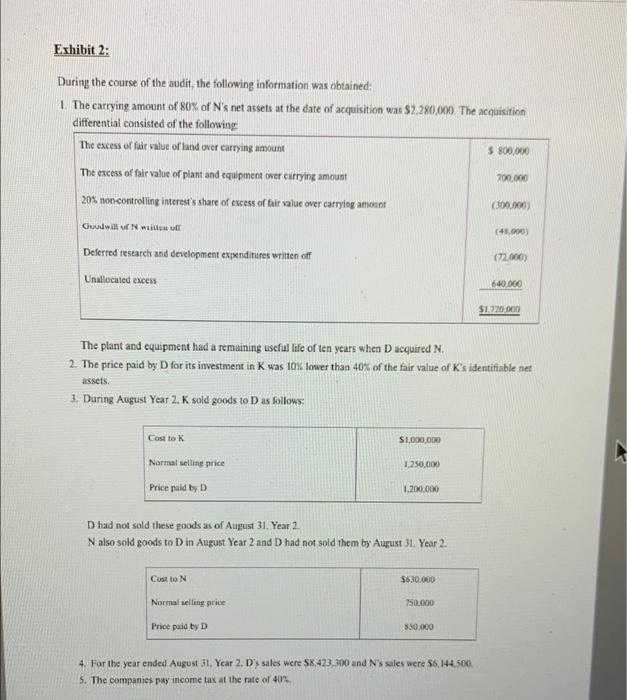
Part 2 In early September Year 1. your firm's audit client, D Ltd. (D) acquired in two separate transactions an 80% interest in N Ltd. (N) and a 40% interest in K Ltd. (K). All three companies are federally incorporated Canadian companies that follow IFRS and have August 31 year-ends. They all manufacture small appliances, but they do not compete with each other You are the senior on the audit of D. The partner has just received the preliminary consolidated financial statements from the controller of D along with unconsolidated statements for the three separate companies. Extracts from these statements are summarized in Exhibit 1. The partner suspects that the acquisition differential at the date of acquisition was not calculated correctly and asks you to recalculate the acquisition differential. Upon further review, the partner also suspects that there are other errors in the information provided and asks you to confirm the balance in Investment in Kon D's unconsolidated financial statements. As well as Goodwill, Non-controlling Interest on the Balance Sheet, and Consolidated Profit on D's consolidated financial statements I Pick one of the accounting errors that you uncovered in this file, and in your opinion state how you would explain this issue to the client including why it was incorrect. (Maximum: 300 words) Exhibit 1: Exhibit 1: EXTRACTS FROM FINANCIAL STATEMENTS At August 31, Year 2 (In thousands) Unconsolidated Consolidated D M K Investment in N Ltd., at cost $4.000 Investment in K Ltd., at cost 2.100 $ 2.100 Deferred development costs $ 90 Goodwill 60 Non-controlling interest 590 Common shares 6.000 1.000 $2.000 6.000 Retained earnings, beginning 618 1,850 1.760 618 Profit 600 300 100 660 Dividends (400) (200) (150) (400) $1.710 S 878 Retained earnings. end of year $ 818 $1.950 D acquired the 80% interest in N for $4,000,000 paid as follows: (1) $2,000,000 in cash, and (2) 160,000 common shares of D recorded in the books of D at $2,000,000 D acquired its 40% interest in K at a cost of $2,100,000. paid as follows: (1) $100,000 in cash, and (2) 160.000 common shares of D recorded in the books of D at $2.000.000. Exhibit 2: During the course of the audit, the following information was obtained: 1. The carrying amount of 80% of N's net assets at the date of acquisition was $2.280,000 The acquisition differential consisted of the following The excess of falt value of land over carrying amount $ 800.000 The excess of fair value of plant and equipment over carrying amount 20% non-controlling interest's share of excess of fair value over carrying amount (300.000) Gwill will (45.000) Deferred research and development expenditures written off (72.000) 700.000 Unallocated excess 640.000 $1,720.000 The plant and equipment had a remaining useful life of ten years when Dacquired N. 2. The price paid by D for its investment in Kwas 10% lower than 40% of the fair value of K's identifiable net assets 3. During August Year 2. K sold goods 10 Das follows: Cost to K SLOD0.000 Normal selling price 1,250,000 Price paid by D 1.200.000 Dhad not sold these poods as of August 31. Year 2 N also sold goods to D in August Year 2 and D had not sold them by August 31. Year 2. $530,000 Cost to N Normal selling price 750.000 Price paid by D 350.000 4. For the year ended August 31. Year 2. D's sales were $8,423.300 and N's sales were $8,144.500 5. The companies pay income tax at the rate of 40% Part 2 In early September Year 1. your firm's audit client, D Ltd. (D) acquired in two separate transactions an 80% interest in N Ltd. (N) and a 40% interest in K Ltd. (K). All three companies are federally incorporated Canadian companies that follow IFRS and have August 31 year-ends. They all manufacture small appliances, but they do not compete with each other You are the senior on the audit of D. The partner has just received the preliminary consolidated financial statements from the controller of D along with unconsolidated statements for the three separate companies. Extracts from these statements are summarized in Exhibit 1. The partner suspects that the acquisition differential at the date of acquisition was not calculated correctly and asks you to recalculate the acquisition differential. Upon further review, the partner also suspects that there are other errors in the information provided and asks you to confirm the balance in Investment in Kon D's unconsolidated financial statements. As well as Goodwill, Non-controlling Interest on the Balance Sheet, and Consolidated Profit on D's consolidated financial statements I Pick one of the accounting errors that you uncovered in this file, and in your opinion state how you would explain this issue to the client including why it was incorrect. (Maximum: 300 words) Exhibit 1: Exhibit 1: EXTRACTS FROM FINANCIAL STATEMENTS At August 31, Year 2 (In thousands) Unconsolidated Consolidated D M K Investment in N Ltd., at cost $4.000 Investment in K Ltd., at cost 2.100 $ 2.100 Deferred development costs $ 90 Goodwill 60 Non-controlling interest 590 Common shares 6.000 1.000 $2.000 6.000 Retained earnings, beginning 618 1,850 1.760 618 Profit 600 300 100 660 Dividends (400) (200) (150) (400) $1.710 S 878 Retained earnings. end of year $ 818 $1.950 D acquired the 80% interest in N for $4,000,000 paid as follows: (1) $2,000,000 in cash, and (2) 160,000 common shares of D recorded in the books of D at $2,000,000 D acquired its 40% interest in K at a cost of $2,100,000. paid as follows: (1) $100,000 in cash, and (2) 160.000 common shares of D recorded in the books of D at $2.000.000. Exhibit 2: During the course of the audit, the following information was obtained: 1. The carrying amount of 80% of N's net assets at the date of acquisition was $2.280,000 The acquisition differential consisted of the following The excess of falt value of land over carrying amount $ 800.000 The excess of fair value of plant and equipment over carrying amount 20% non-controlling interest's share of excess of fair value over carrying amount (300.000) Gwill will (45.000) Deferred research and development expenditures written off (72.000) 700.000 Unallocated excess 640.000 $1,720.000 The plant and equipment had a remaining useful life of ten years when Dacquired N. 2. The price paid by D for its investment in Kwas 10% lower than 40% of the fair value of K's identifiable net assets 3. During August Year 2. K sold goods 10 Das follows: Cost to K SLOD0.000 Normal selling price 1,250,000 Price paid by D 1.200.000 Dhad not sold these poods as of August 31. Year 2 N also sold goods to D in August Year 2 and D had not sold them by August 31. Year 2. $530,000 Cost to N Normal selling price 750.000 Price paid by D 350.000 4. For the year ended August 31. Year 2. D's sales were $8,423.300 and N's sales were $8,144.500 5. The companies pay income tax at the rate of 40%