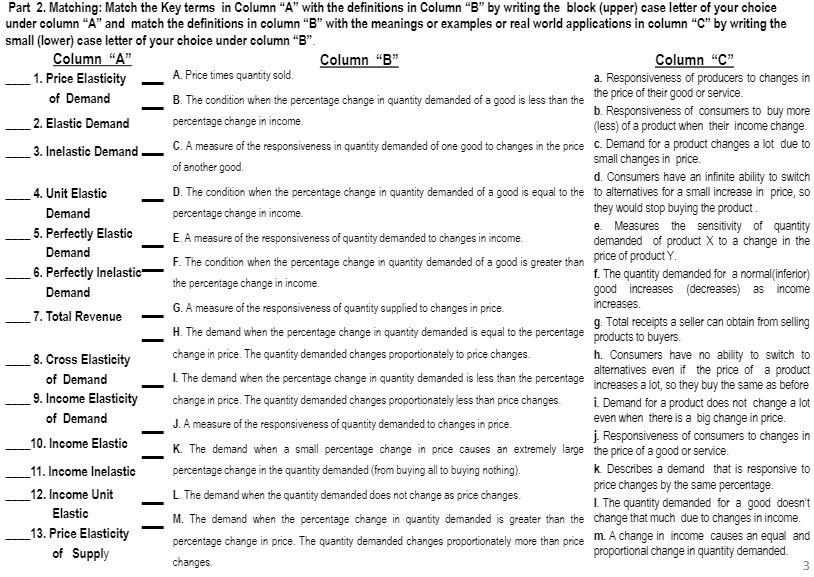
Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block (upper) case letter of your choice under column "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or real world applications in column "C" by writing the small (lower) case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" Column "B" Column "C" 1. Price Elasticity A. Price times quantity sold. a. Responsiveness of producers to changes in of Demand B. The condition when the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good is less than the the price of their good or service. b. Responsiveness of consumers to buy more 2. Elastic Demand percentage change in income. (less) of a product when their income change. 3. Inelastic Demand C. A measure of the responsiveness in quantity demanded of one good to changes in the price C. Demand for a product changes a lot due to of another good. small changes in price. d. Consumers have an infinite ability to switch 4. Unit Elastic D. The condition when the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good is equal to the to alternatives for a small increase in price, so Demand percentage change in income. they would stop buying the product 5. Perfectly Elastic e. Measures the sensitivity of quantity E. A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in income. demanded of product X to a change in the Demand F. The condition when the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good is greater than price of product Y. 6. Perfectly Inelastic- f. The quantity demanded for a normal(inferior) Demand the percentage change in income. good increases (decreases) as income G. A measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price. increases 7. Total Revenue g. Total receipts a seller can obtain from selling H. The demand when the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage products to buyers. 8. Cross Elasticity change in price. The quantity demanded changes proportionately to price changes. h. Consumers have no ability to switch to 1. The demand when the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage alternatives even if the price of a product of Demand increases a lot, so they buy the same as before 9. Income Elasticity change in price. The quantity demanded changes proportionately less than price changes. i. Demand for a product does not change a lot of Demand J. A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. even when there is a big change in price. 10. Income Elastic j. Responsiveness of consumers to changes in K. The demand when a small percentage change in price causes an extremely large the price of a good or service. 11. Income Inelastic percentage change in the quantity demanded (from buying all to buying nothing). k. Describes a demand that is responsive to price changes by the same percentage 12. Income Unit L. The demand when the quantity demanded does not change as price changes. I. The quantity demanded for a good doesn't Elastic M. The demand when the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the change that much due to changes in income. 13. Price Elasticity percentage change in price. The quantity demanded changes proportionately more than price . A Change in income causes an equal and of Supply proportional change in quantity demanded. changes. 3