Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
part a b c answer is right here please help with part (d) (e) it will be good if the answer are typed thanks Question

part a b c answer is right here
please help with part (d) (e)
it will be good if the answer are typed
thanks
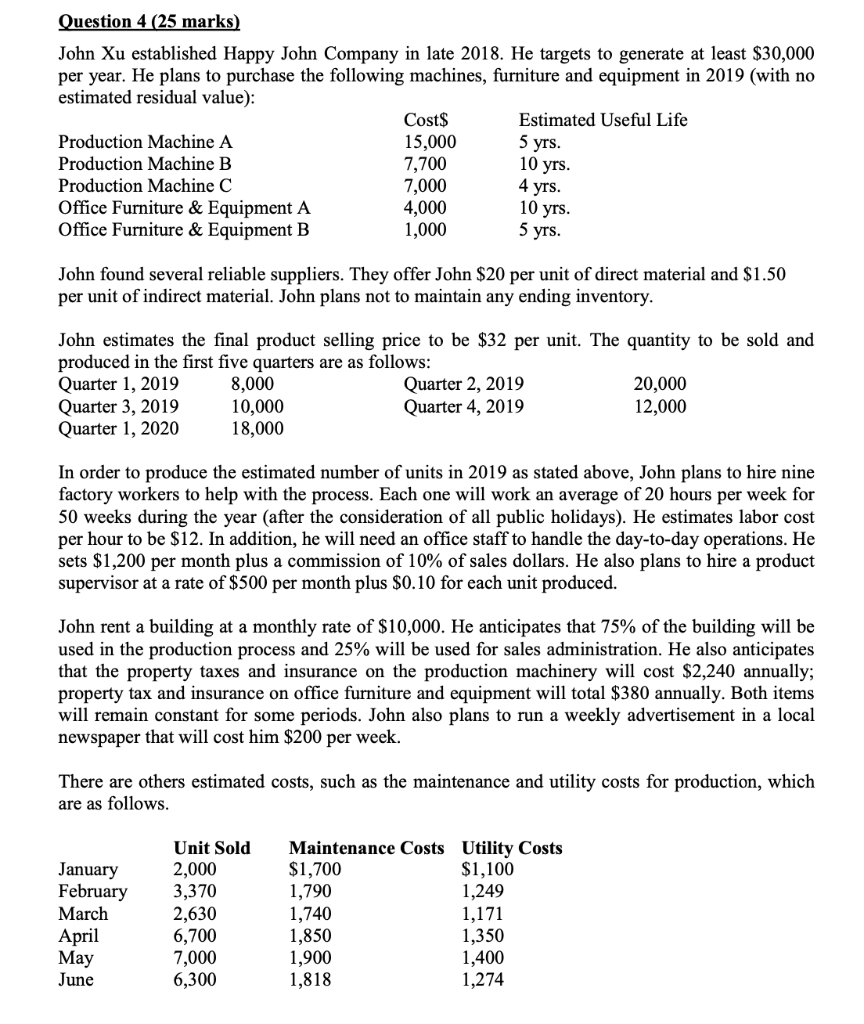
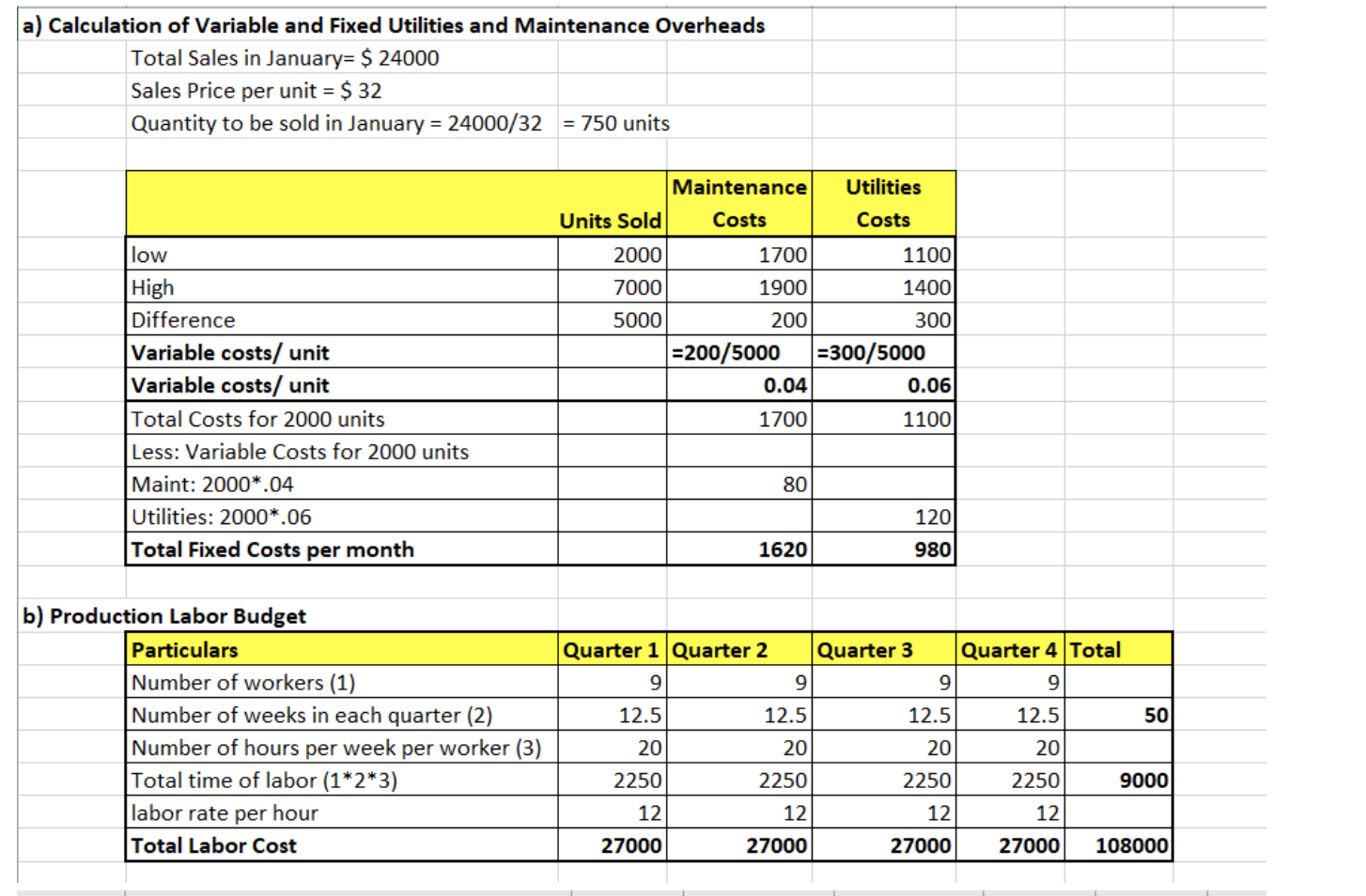
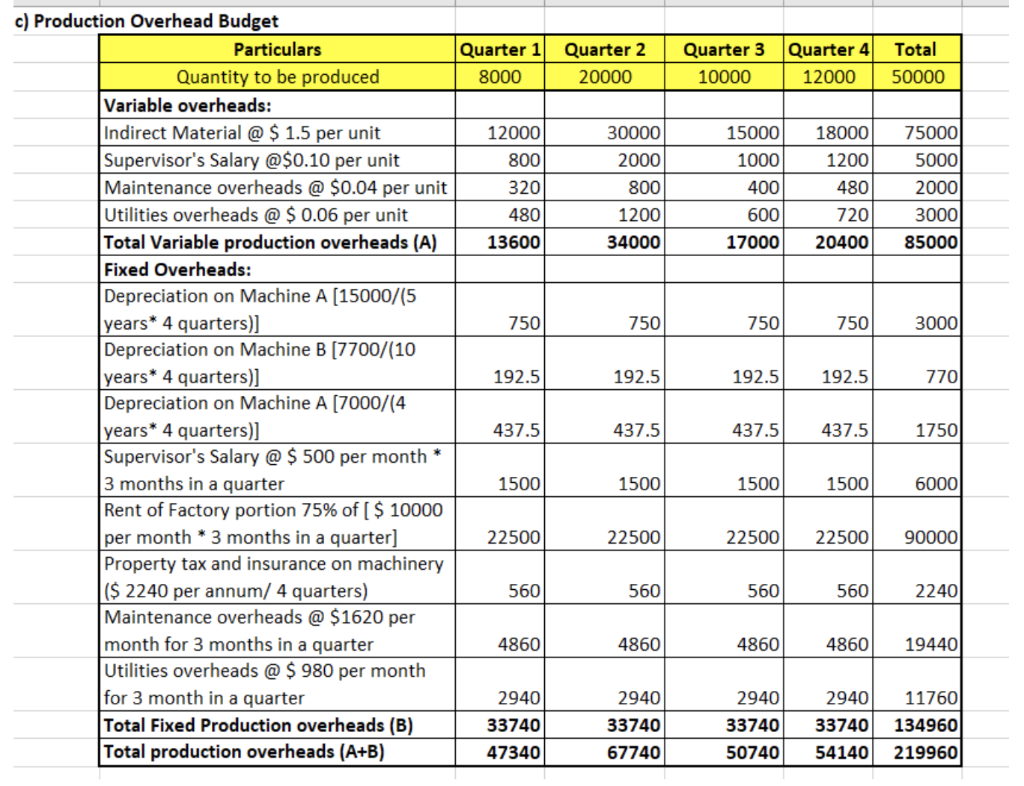
Question 4 (25 marks) John Xu established Happy John Company in late 2018. He targets to generate at least $30,000 per year. He plans to purchase the following machines, furniture and equipment in 2019 (with no estimated residual value): Cost$ Estimated Useful Life Production Machine A 15,000 5 yrs. Production Machine B 7,700 10 yrs. Production Machine C 7,000 4 yrs. Office Furniture & Equipment A 4,000 10 yrs. Office Furniture & Equipment B 1,000 5 yrs. John found several reliable suppliers. They offer John $20 per unit of direct material and $1.50 per unit of indirect material. John plans not to maintain any ending inventory. John estimates the final product selling price to be $32 per unit. The quantity to be sold and produced in the first five quarters are as follows: Quarter 1, 2019 8,000 Quarter 2, 2019 20,000 Quarter 3, 2019 10,000 Quarter 4, 2019 12,000 Quarter 1, 2020 18,000 In order to produce the estimated number of units in 2019 as stated above, John plans to hire nine factory workers to help with the process. Each one will work an average of 20 hours per week for 50 weeks during the year after the consideration of all public holidays). He estimates labor cost per hour to be $12. In addition, he will need an office staff to handle the day-to-day operations. He sets $1,200 per month plus a commission of 10% of sales dollars. He also plans to hire a product supervisor at a rate of $500 per month plus $0.10 for each unit produced. John rent a building at a monthly rate of $10,000. He anticipates that 75% of the building will be used in the production process and 25% will be used for sales administration. He also anticipates that the property taxes and insurance on the production machinery will cost $2,240 annually; property tax and insurance on office furniture and equipment will total $380 annually. Both items will remain constant for some periods. John also plans to run a weekly advertisement in a local newspaper that will cost him $200 per week. There are others estimated costs, such as the maintenance and utility costs for production, which are as follows. January February March April May June Unit Sold 2,000 3,370 2,630 6,700 7,000 6,300 Maintenance Costs Utility Costs $1,700 $1,100 1,790 1,249 1,740 1,171 1,850 1,350 1,900 1,400 1,818 1,274 Question 4 (Continue) Required: (a) If the company has sales of $24,000 during January of the first year of business, determine the amount of the total variable and total fixed costs associated with utilities and maintenance using the high-low method for each. Round unit variable costs to two decimal places where necessary. (2 marks) (b) Prepare a production labor budget for the year end December 31, 2019. Please present your budget on quarterly basis. (3 marks) (c) Prepare a production overhead budget for the year end December 31, 2019. John expects variable costs to fluctuate with the units produced. Please present your budget in quarterly basis and show your formula for the first quarter. (6 marks) (d) Using the information contained in the question and the previous budgets, calculate the total estimated fixed costs and the contribution margin per unit for the year end December 31, 2019. Please show your formulas and workings. Round unit variable costs and unit contribution margin to two decimal places where necessary. (6 marks) (e) John heard from his friends that the price of his product direct materials might be doubled or tripled in the coming year. John is very optimistic with his business and expects the sales will grow more than 200% in the future. He would like to maintain high level of direct materials inventory. What are the potential problems for this decision? How would you evaluate the reasonableness of the 200% future growth? (8 marks) a) Calculation of Variable and Fixed Utilities and Maintenance Overheads Total Sales in January=$ 24000 Sales Price per unit = $ 32 Quantity to be sold in January = 24000/32 = 750 units Utilities Costs 1100 1400 Maintenance Units Sold Costs 2000 1700 7000 1900 5000 200 =200/5000 0.04 1700 low High Difference Variable costs/ unit Variable costs/ unit Total Costs for 2000 units Less: Variable Costs for 2000 units Maint: 2000*.04 Utilities: 2000*.06 Total Fixed Costs per month 300 =300/5000 0.06 1100 80 120 1620 980 Old 9 50 b) Production Labor Budget Particulars Number of workers (1) Number of weeks in each quarter (2) Number of hours per week per worker (3) Total time of labor (1*2*3) labor rate per hour Total Labor Cost Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Total 9 9 9 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 20 20 20 20 2250 2250 2250 2250 9000 12 12 27000 27000 27000 27000 108000 12 12 Quarter 1] Quarter 2 8000 20000 Quarter 3 10000 Quarter 4 12000 Total 50000 12000 8001 30000 2000 800 320 480 13600 15000 1000 400 600 17000 18000 1200 4801 720 20400 75000 5000 2000 3000 85000 1200 34000 750 750 750 750 3000 c) Production Overhead Budget Particulars Quantity to be produced Variable overheads: Indirect Material @ $ 1.5 per unit Supervisor's Salary @$0.10 per unit Maintenance overheads @ $0.04 per unit Utilities overheads @ $ 0.06 per unit Total Variable production overheads (A) Fixed Overheads: Depreciation on Machine A (15000/(5 years* 4 quarters)] Depreciation on Machine B (7700/(10 years* 4 quarters)] Depreciation on Machine A (7000/(4 years* 4 quarters)] Supervisor's Salary @ $ 500 per month * 3 months in a quarter Rent of Factory portion 75% of [ $ 10000 per month * 3 months in a quarter] Property tax and insurance on machinery ($ 2240 per annum/ 4 quarters) Maintenance overheads @ $1620 per month for 3 months in a quarter Utilities overheads @ $ 980 per month for 3 month in a quarter Total Fixed Production overheads (B) Total production overheads (A+B) 192.5 192.5 192.5 192.5 437.5 437.5 437.5 437.5 1750 1500 1500 1500 1500 22500 22500 22500 22500 90000 560 560 560 560 2240 4860 4860 48604860 19440 2940 33740 473401 2940 33740 67740 2940 2940 11760 3374033740134960 50740 54140 219960 Question 4 (25 marks) John Xu established Happy John Company in late 2018. He targets to generate at least $30,000 per year. He plans to purchase the following machines, furniture and equipment in 2019 (with no estimated residual value): Cost$ Estimated Useful Life Production Machine A 15,000 5 yrs. Production Machine B 7,700 10 yrs. Production Machine C 7,000 4 yrs. Office Furniture & Equipment A 4,000 10 yrs. Office Furniture & Equipment B 1,000 5 yrs. John found several reliable suppliers. They offer John $20 per unit of direct material and $1.50 per unit of indirect material. John plans not to maintain any ending inventory. John estimates the final product selling price to be $32 per unit. The quantity to be sold and produced in the first five quarters are as follows: Quarter 1, 2019 8,000 Quarter 2, 2019 20,000 Quarter 3, 2019 10,000 Quarter 4, 2019 12,000 Quarter 1, 2020 18,000 In order to produce the estimated number of units in 2019 as stated above, John plans to hire nine factory workers to help with the process. Each one will work an average of 20 hours per week for 50 weeks during the year after the consideration of all public holidays). He estimates labor cost per hour to be $12. In addition, he will need an office staff to handle the day-to-day operations. He sets $1,200 per month plus a commission of 10% of sales dollars. He also plans to hire a product supervisor at a rate of $500 per month plus $0.10 for each unit produced. John rent a building at a monthly rate of $10,000. He anticipates that 75% of the building will be used in the production process and 25% will be used for sales administration. He also anticipates that the property taxes and insurance on the production machinery will cost $2,240 annually; property tax and insurance on office furniture and equipment will total $380 annually. Both items will remain constant for some periods. John also plans to run a weekly advertisement in a local newspaper that will cost him $200 per week. There are others estimated costs, such as the maintenance and utility costs for production, which are as follows. January February March April May June Unit Sold 2,000 3,370 2,630 6,700 7,000 6,300 Maintenance Costs Utility Costs $1,700 $1,100 1,790 1,249 1,740 1,171 1,850 1,350 1,900 1,400 1,818 1,274 Question 4 (Continue) Required: (a) If the company has sales of $24,000 during January of the first year of business, determine the amount of the total variable and total fixed costs associated with utilities and maintenance using the high-low method for each. Round unit variable costs to two decimal places where necessary. (2 marks) (b) Prepare a production labor budget for the year end December 31, 2019. Please present your budget on quarterly basis. (3 marks) (c) Prepare a production overhead budget for the year end December 31, 2019. John expects variable costs to fluctuate with the units produced. Please present your budget in quarterly basis and show your formula for the first quarter. (6 marks) (d) Using the information contained in the question and the previous budgets, calculate the total estimated fixed costs and the contribution margin per unit for the year end December 31, 2019. Please show your formulas and workings. Round unit variable costs and unit contribution margin to two decimal places where necessary. (6 marks) (e) John heard from his friends that the price of his product direct materials might be doubled or tripled in the coming year. John is very optimistic with his business and expects the sales will grow more than 200% in the future. He would like to maintain high level of direct materials inventory. What are the potential problems for this decision? How would you evaluate the reasonableness of the 200% future growth? (8 marks) a) Calculation of Variable and Fixed Utilities and Maintenance Overheads Total Sales in January=$ 24000 Sales Price per unit = $ 32 Quantity to be sold in January = 24000/32 = 750 units Utilities Costs 1100 1400 Maintenance Units Sold Costs 2000 1700 7000 1900 5000 200 =200/5000 0.04 1700 low High Difference Variable costs/ unit Variable costs/ unit Total Costs for 2000 units Less: Variable Costs for 2000 units Maint: 2000*.04 Utilities: 2000*.06 Total Fixed Costs per month 300 =300/5000 0.06 1100 80 120 1620 980 Old 9 50 b) Production Labor Budget Particulars Number of workers (1) Number of weeks in each quarter (2) Number of hours per week per worker (3) Total time of labor (1*2*3) labor rate per hour Total Labor Cost Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Total 9 9 9 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 20 20 20 20 2250 2250 2250 2250 9000 12 12 27000 27000 27000 27000 108000 12 12 Quarter 1] Quarter 2 8000 20000 Quarter 3 10000 Quarter 4 12000 Total 50000 12000 8001 30000 2000 800 320 480 13600 15000 1000 400 600 17000 18000 1200 4801 720 20400 75000 5000 2000 3000 85000 1200 34000 750 750 750 750 3000 c) Production Overhead Budget Particulars Quantity to be produced Variable overheads: Indirect Material @ $ 1.5 per unit Supervisor's Salary @$0.10 per unit Maintenance overheads @ $0.04 per unit Utilities overheads @ $ 0.06 per unit Total Variable production overheads (A) Fixed Overheads: Depreciation on Machine A (15000/(5 years* 4 quarters)] Depreciation on Machine B (7700/(10 years* 4 quarters)] Depreciation on Machine A (7000/(4 years* 4 quarters)] Supervisor's Salary @ $ 500 per month * 3 months in a quarter Rent of Factory portion 75% of [ $ 10000 per month * 3 months in a quarter] Property tax and insurance on machinery ($ 2240 per annum/ 4 quarters) Maintenance overheads @ $1620 per month for 3 months in a quarter Utilities overheads @ $ 980 per month for 3 month in a quarter Total Fixed Production overheads (B) Total production overheads (A+B) 192.5 192.5 192.5 192.5 437.5 437.5 437.5 437.5 1750 1500 1500 1500 1500 22500 22500 22500 22500 90000 560 560 560 560 2240 4860 4860 48604860 19440 2940 33740 473401 2940 33740 67740 2940 2940 11760 3374033740134960 50740 54140 219960Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


