Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Part A: Hypothesis Testing for Mode of Inheritance Section 1 a) Attach your data set to your report so that we know which cross
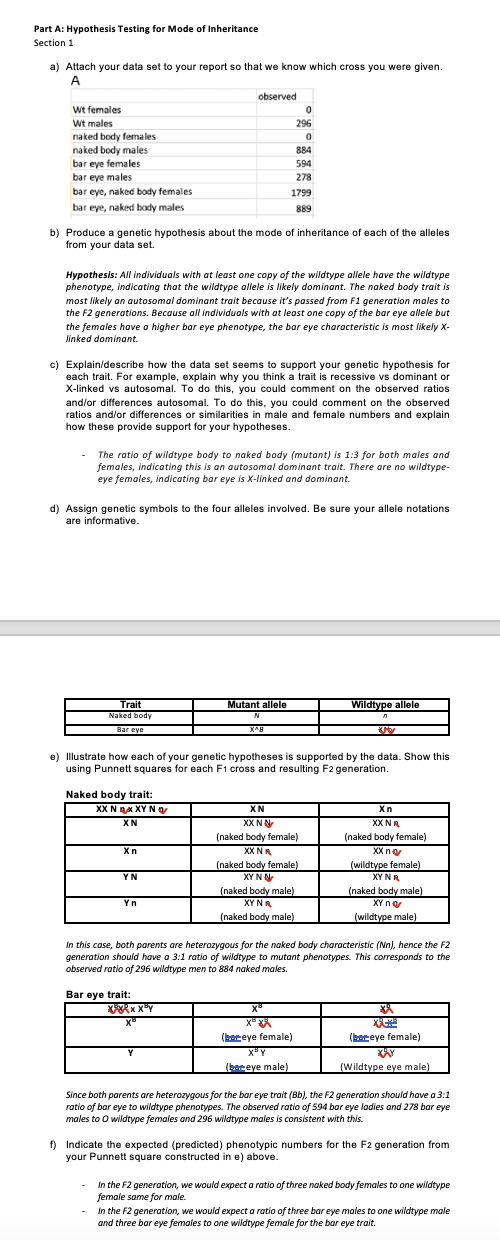
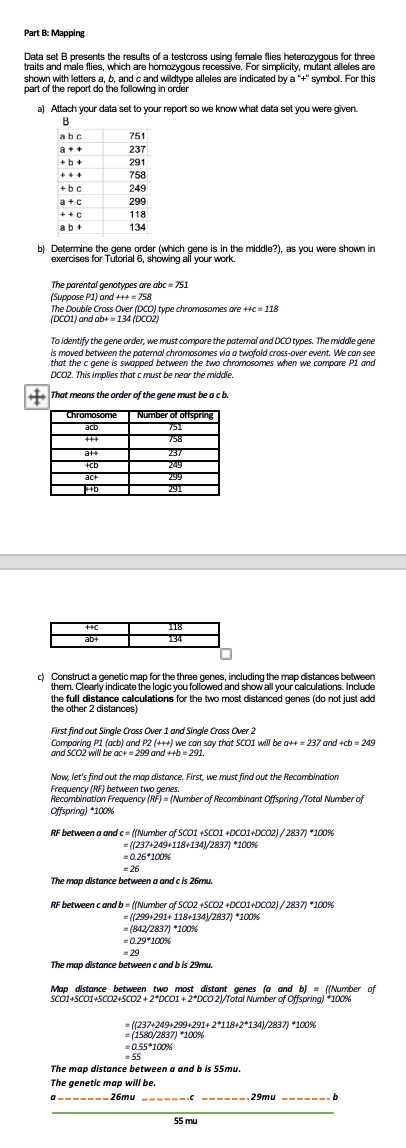
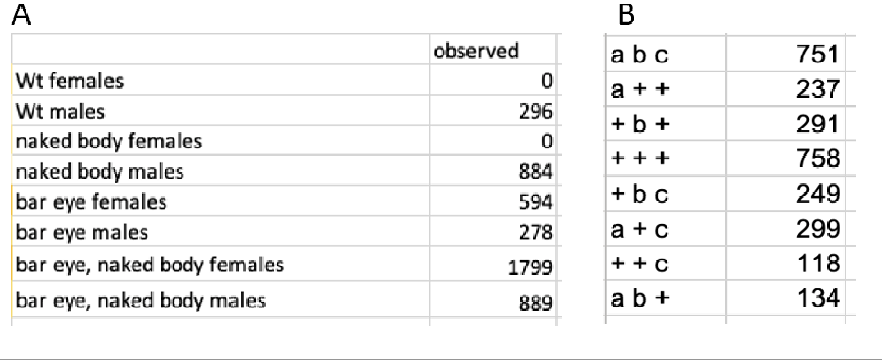
Part A: Hypothesis Testing for Mode of Inheritance Section 1 a) Attach your data set to your report so that we know which cross you were given. A Wt females Wt males naked body females naked body males bar eye females bar eye males bar eye, naked body females bar eye, naked body males observed 296 0 884 594 278 1799 889 b) Produce a genetic hypothesis about the mode of inheritance of each of the alleles from your data set. Hypothesis: All individuals with at least one copy of the wildtype allele have the wildtype phenotype, indicating that the wildtype allele is likely dominant. The naked body trait is most likely an autosomal dominant trait because it's passed from F1 generation males to the F2 generations. Because all individuals with at least one copy of the bar eye allele but the females have a higher bar eye phenotype, the bar eye characteristic is most likely X- linked dominant. c) Explain/describe how the data set seems to support your genetic hypothesis for each trait. For example, explain why you think a trait is recessive vs dominant or X-linked vs autosomal. To do this, you could comment on the observed ratios and/or differences autosomal. To do this, you could comment on the observed ratios and/or differences or similarities in male and female numbers and explain how these provide support for your hypotheses. The ratio of wildtype body to naked body (mutant) is 1:3 for both males and females, indicating this is an autosomal dominant trait. There are no wildtype- eye females, indicating bar eye is X-linked and dominant. d) Assign genetic symbols to the four alleles involved. Be sure your allele notations are informative. Trait Naked body Bar eye Mutant allele Wildtype allele ^ e) Illustrate how each of your genetic hypotheses is supported by the data. Show this using Punnett squares for each F1 cross and resulting F2 generation. Naked body trait: XXNXXY NO XN XN XX N Xn (naked body female) Xn YN XX NR (naked body female) XYNN XX NR (naked body female) XX n (wildtype female) XY NR (naked body male) Yn (naked body male) XY NR (naked body male) XY no (wildtype male) In this case, both parents are heterozygous for the naked body characteristic (Nn), hence the F2 generation should have a 3:1 ratio of wildtype to mutant phenotypes. This corresponds to the observed ratio of 296 wildtype men to 884 naked males. Bar eye trait: x (bereye female) XXCKE (bereye female) XY (boe eye male) XAY (Wildtype eye male) Since both parents are heterozygous for the bar eye trait (Bb), the F2 generation should have a 3:1 ratio of bar eye to wildtype phenotypes. The observed ratio of 594 bar eye ladies and 278 bar eye males to O wildtype females and 296 wildtype males is consistent with this. f) Indicate the expected (predicted) phenotypic numbers for the F2 generation from your Punnett square constructed in e) above. - In the F2 generation, we would expect a ratio of three naked body females to one wildtype female same for male. In the F2 generation, we would expect a ratio of three bar eye males to one wildtype male and three bar eye females to one wildtype female for the bar eye trait. Part B: Mapping Data set B presents the results of a testcross using female flies heterozygous for three traits and male flies, which are homozygous recessive. For simplicity, mutant alleles are shown with letters a, b, and c and wildtype alleles are indicated by a "+" symbol. For this part of the report do the following in order a) Attach your data set to your report so we know what data set you were given. B abc 751 a++ 237 +b+ 291 +++ 758 +bc 249 a+c 299 118 134 ++C ab+ b) Determine the gene order (which gene is in the middle?), as you were shown in exercises for Tutorial 6, showing all your work. The parental genotypes are abc = 751 (Suppose P1) and +++=758 The Double Cross Over (DCO) type chromosomes are ++c=118 (DC01) and ab+=134 (DCO2) To identify the gene order, we must compare the paternal and DCO types. The middle gene is moved between the paternal chromosomes via a twofold cross-over event. We can see that the c gene is swapped between the two chromosomes when we compare P1 and DCO2. This implies that c must be near the middle. +That means the order of the gene must be a c b. Chromosome Number of offspring acb 751 +++ 758 a++ 237 +cb 249 ac+ 299 H+b 291 ++C ab+ 118 134 c) Construct a genetic map for the three genes, including the map distances between them. Clearly indicate the logic you followed and show all your calculations. Include the full distance calculations for the two most distanced genes (do not just add the other 2 distances) First find out Single Cross Over 1 and Single Cross Over 2 Comparing P1 (acb) and P2 (+++) we can say that SCO1 will be a++ =237 and +cb= 249 and SCO2 will be ac+=299 and ++b=291. Now, let's find out the map distance. First, we must find out the Recombination Frequency (RF) between two genes. Recombination Frequency (RF) = (Number of Recombinant Offspring /Total Number of Offspring) *100% RF between a and c = ((Number of SC01 +SC01 +DC01+DC02)/2837) *100% =((237+249+118+134)/2837) *100% =0.26*100% =26 The map distance between a and c is 26mu. RF between c and b = ((Number of SCO2 +SC02 +DC01+DC02)/2837) *100% =((299+291+ 118+134)/2837) *100% =(842/2837) *100% =0.29*100% =29 The map distance between c and bis 29mu. Map distance between two most distant genes (a and b) = ((Number of SC01+SC01+SC02+SC02+2*DC01+2*DCO 2)/Total Number of Offspring) *100% =((237+249+299+291+2*118+2*134)/2837) *100% =(1580/2837) *100% =0.55*100% -55 The map distance between a and b is 55mu. The genetic map will be. a 26mu--- 55 mu 29mu A B observed abc 751 Wt females Wt males naked body females naked body males 0 a + + 237 296 +b+ 291 0 +++ 758 884 bar eye females 594 +bc 249 bar eye males 278 a+c 299 bar eye, naked body females 1799 ++ C 118 bar eye, naked body males 889 ab+ 134
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


