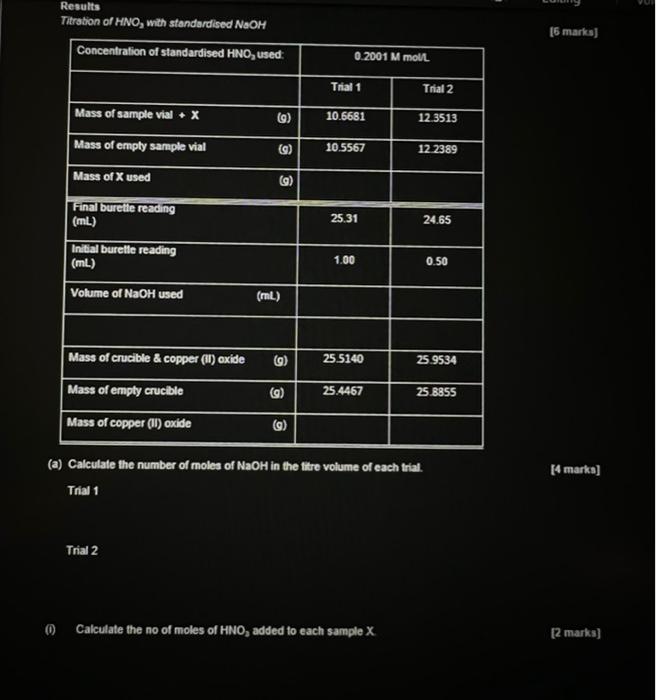
Part B: Acid Base Titrations [Total Part B 32 marks] 2. In Part B of this experiment you are required to determine the ammonia and copper content of an ammine complex cation of copper, Ammine complexes of transition metals are easily prepared in the lab. In this experiment ammonia is reacted with an aqueous solution of copper cations to form the ammine complex of copper. You are provided with a sample X of the freshly prepared ammine complex of copper for analysis. In the first part of this experiment you are required to determine the ammonia content of the ammine complex ion X using the standardised NaOH solution from Part A and a 0.2001 M solution of nitric acid. In the second part of this experiment you are required to determine the copper content of the armine complex ion X using the titrated samples from the determination of the ammonia content of X. Procedure. Determination of Ammonia Content of X 1. Accurately weigh out two samples of approssimately 0.1 g of sample X into two separate 250 ml. Erlenmeyer flasks. 2. Add a 40.00 mL volume of 0.2001 M solution of nitric acid to each flask using a burette, and swirl the solutions until the solids completely dissolve. 3. Titrate the solutions against the standardized NaOH solution from Part A using 3-4 drops of methyl red as an indicator. Gravimetric Determination of Copper Content of X 1. Using the two titrated samples from above, add two pellets of sodium hydroxide (approximately 0.2 g) to each flask and heat the solutions to just below boiling for one hour. 2. Filter the black precipitate of copper (II) oxide which forms through pre-weighed, sintered glass crucibles and wash with approximately 10 mL of distilled water. 3. Place the two sets of precipitates in a drying oven for two hours at 110 C, and allow them to cool in a desiccator before weighing to 0.1 mg. Results Titration of HNO, with standardised NOM [6 marks) Concentration of standardised HNO, used: 0.2001 M moll Trial 1 Trial 2 Mass of sample vial. X () 10.6681 12.3513 Mass of empty sample vial 10.5567 12 2389 (6) 9) Mass of X used (9) Final burelle reading (mL) 25.31 24.65 Initial burelle reading (ML) 1.00 0.50 Volume of NaOH used (ml) Mass of crucible & copper (11) oxide (9) 25 5140 25.9534 Mass of empty crucible (9) 25.4467 25.8855 Mass of copper (11) oxide (a) Calculate the number of moles of NaOH in the titre volume of each trial. (4 marks) Trial 1 Trial 2 Calculate the no of moles of HNO, added to each sample X [2 marks] (11) Calculate the no of moles of ammonia in each sample X for Trials 1 & 2 [4 marks) Trial 1 Trial 2 Calculate the number of moles of Cu in each sample X for Trials 1 & 2. [4 marks] Trial 1 Trial 2 Using the data obtained from the analysis of the ammonia and copper content of X for each trial deduce the formula of the copper ammonia complex cation. (4 marks] Trial 1 Trial 2 Give the final formula of the copper ammonia complex cation you deduced from the two trials. (V) Draw the structure of the copper ammonia complex cation based on the formula you deduced in part (iv) above. [2 marks] (vi) What is the colour change at the end point of the titration between the HNO, solution and the standardized NaOH solution using 3-4 drops of methyl red as an indicator? (2 marks] (vii) is ammonia determined directly in this experiment? If not, how is ammonia analysed and what technique is used in its analysis? [4 marks) Part B: Acid Base Titrations [Total Part B 32 marks] 2. In Part B of this experiment you are required to determine the ammonia and copper content of an ammine complex cation of copper, Ammine complexes of transition metals are easily prepared in the lab. In this experiment ammonia is reacted with an aqueous solution of copper cations to form the ammine complex of copper. You are provided with a sample X of the freshly prepared ammine complex of copper for analysis. In the first part of this experiment you are required to determine the ammonia content of the ammine complex ion X using the standardised NaOH solution from Part A and a 0.2001 M solution of nitric acid. In the second part of this experiment you are required to determine the copper content of the armine complex ion X using the titrated samples from the determination of the ammonia content of X. Procedure. Determination of Ammonia Content of X 1. Accurately weigh out two samples of approssimately 0.1 g of sample X into two separate 250 ml. Erlenmeyer flasks. 2. Add a 40.00 mL volume of 0.2001 M solution of nitric acid to each flask using a burette, and swirl the solutions until the solids completely dissolve. 3. Titrate the solutions against the standardized NaOH solution from Part A using 3-4 drops of methyl red as an indicator. Gravimetric Determination of Copper Content of X 1. Using the two titrated samples from above, add two pellets of sodium hydroxide (approximately 0.2 g) to each flask and heat the solutions to just below boiling for one hour. 2. Filter the black precipitate of copper (II) oxide which forms through pre-weighed, sintered glass crucibles and wash with approximately 10 mL of distilled water. 3. Place the two sets of precipitates in a drying oven for two hours at 110 C, and allow them to cool in a desiccator before weighing to 0.1 mg. Results Titration of HNO, with standardised NOM [6 marks) Concentration of standardised HNO, used: 0.2001 M moll Trial 1 Trial 2 Mass of sample vial. X () 10.6681 12.3513 Mass of empty sample vial 10.5567 12 2389 (6) 9) Mass of X used (9) Final burelle reading (mL) 25.31 24.65 Initial burelle reading (ML) 1.00 0.50 Volume of NaOH used (ml) Mass of crucible & copper (11) oxide (9) 25 5140 25.9534 Mass of empty crucible (9) 25.4467 25.8855 Mass of copper (11) oxide (a) Calculate the number of moles of NaOH in the titre volume of each trial. (4 marks) Trial 1 Trial 2 Calculate the no of moles of HNO, added to each sample X [2 marks] (11) Calculate the no of moles of ammonia in each sample X for Trials 1 & 2 [4 marks) Trial 1 Trial 2 Calculate the number of moles of Cu in each sample X for Trials 1 & 2. [4 marks] Trial 1 Trial 2 Using the data obtained from the analysis of the ammonia and copper content of X for each trial deduce the formula of the copper ammonia complex cation. (4 marks] Trial 1 Trial 2 Give the final formula of the copper ammonia complex cation you deduced from the two trials. (V) Draw the structure of the copper ammonia complex cation based on the formula you deduced in part (iv) above. [2 marks] (vi) What is the colour change at the end point of the titration between the HNO, solution and the standardized NaOH solution using 3-4 drops of methyl red as an indicator? (2 marks] (vii) is ammonia determined directly in this experiment? If not, how is ammonia analysed and what technique is used in its analysis? [4 marks)