Part C optional but would be extremely helpful
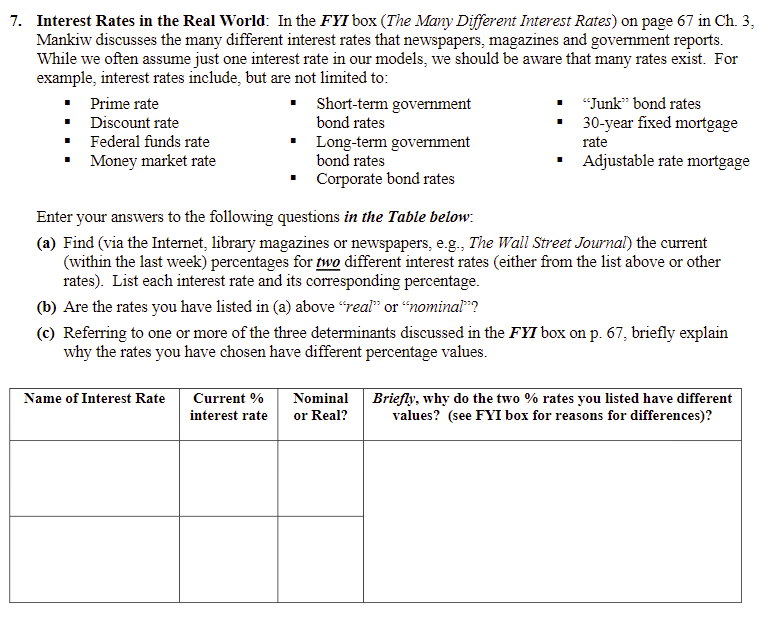
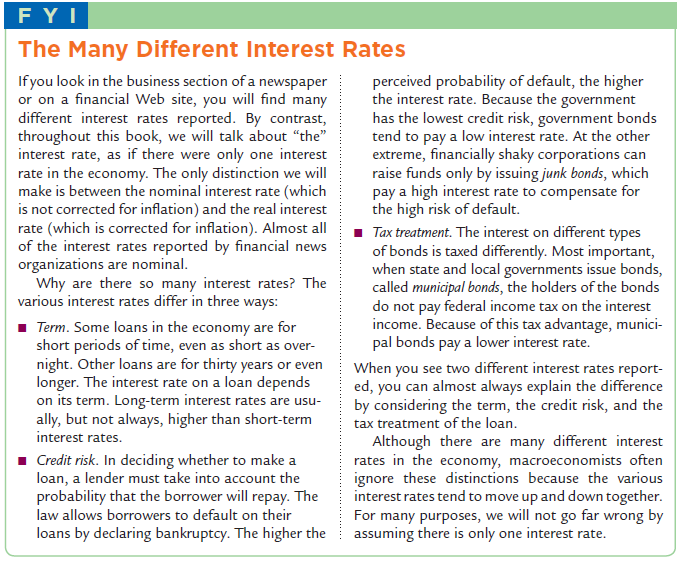
7. Interest Rates in the Real World: In the FYI box (The Many Different Interest Rates) on page 67 in Ch. 3, Mankiw discusses the many different interest rates that newspapers, magazines and government reports. While we often assume just one interest rate in our models, we should be aware that many rates exist. For example, interest rates include, but are not limited to: Prime rate Short-term government . Junk bond rates Discount rate bond rates 30-year fixed mortgage Federal funds rate Long-term government rate Money market rate bond rates Adjustable rate mortgage Corporate bond rates Enter your answers to the following questions in the Table below: (a) Find (via the Internet, library magazines or newspapers, e.g., The Wall Street Journal) the current (within the last week) percentages for two different interest rates (either from the list above or other rates). List each interest rate and its corresponding percentage. (b) Are the rates you have listed in (a) above "real" or nominal? (c) Referring to one or more of the three determinants discussed in the FYI box on p. 67, briefly explain why the rates you have chosen have different percentage values. Name of Interest Rate Current % interest rate Nominal or Real? Briefly, why do the two % rates you listed have different values? (see FYI box for reasons for differences)? I FYI The Many Different Interest Rates If you look in the business section of a newspaper perceived probability of default, the higher or on a financial Web site, you will find many the interest rate. Because the government different interest rates reported. By contrast, has the lowest credit risk, government bonds throughout this book, we will talk about "the" tend to pay a low interest rate. At the other interest rate, as if there were only one interest extreme, financially shaky corporations can rate in the economy. The only distinction we will raise funds only by issuing junk bonds, which make is between the nominal interest rate (which pay a high interest rate to compensate for is not corrected for inflation) and the real interest the high risk of default. rate (which is corrected for inflation). Almost all Tax treatment. The interest on different types of the interest rates reported by financial news of bonds is taxed differently. Most important, organizations are nominal. when state and local governments issue bonds, Why are there so many interest rates? The called municipal bonds, the holders of the bonds various interest rates differ in three ways: do not pay federal income tax on the interest Term. Some loans in the economy are for income. Because of this tax advantage, munici- short periods of time, even as short as over- pal bonds pay a lower interest rate. night. Other loans are for thirty years or even When you see two different interest rates report- longer. The interest rate on a loan depends ed, you can almost always explain the difference on its term. Long-term interest rates are usu- by considering the term, the credit risk, and the ally, but not always, higher than short-term tax treatment of the loan. interest rates. Although there are many different interest Credit risk. In deciding whether to make a rates in the economy, macroeconomists often loan, a lender must take into account the ignore these distinctions because the various probability that the borrower will repay. The interest rates tend to move up and down together. law allows borrowers to default on their For many purposes, we will not go far wrong by loans by declaring bankruptcy. The higher the assuming there is only one interest rate. 7. Interest Rates in the Real World: In the FYI box (The Many Different Interest Rates) on page 67 in Ch. 3, Mankiw discusses the many different interest rates that newspapers, magazines and government reports. While we often assume just one interest rate in our models, we should be aware that many rates exist. For example, interest rates include, but are not limited to: Prime rate Short-term government . Junk bond rates Discount rate bond rates 30-year fixed mortgage Federal funds rate Long-term government rate Money market rate bond rates Adjustable rate mortgage Corporate bond rates Enter your answers to the following questions in the Table below: (a) Find (via the Internet, library magazines or newspapers, e.g., The Wall Street Journal) the current (within the last week) percentages for two different interest rates (either from the list above or other rates). List each interest rate and its corresponding percentage. (b) Are the rates you have listed in (a) above "real" or nominal? (c) Referring to one or more of the three determinants discussed in the FYI box on p. 67, briefly explain why the rates you have chosen have different percentage values. Name of Interest Rate Current % interest rate Nominal or Real? Briefly, why do the two % rates you listed have different values? (see FYI box for reasons for differences)? I FYI The Many Different Interest Rates If you look in the business section of a newspaper perceived probability of default, the higher or on a financial Web site, you will find many the interest rate. Because the government different interest rates reported. By contrast, has the lowest credit risk, government bonds throughout this book, we will talk about "the" tend to pay a low interest rate. At the other interest rate, as if there were only one interest extreme, financially shaky corporations can rate in the economy. The only distinction we will raise funds only by issuing junk bonds, which make is between the nominal interest rate (which pay a high interest rate to compensate for is not corrected for inflation) and the real interest the high risk of default. rate (which is corrected for inflation). Almost all Tax treatment. The interest on different types of the interest rates reported by financial news of bonds is taxed differently. Most important, organizations are nominal. when state and local governments issue bonds, Why are there so many interest rates? The called municipal bonds, the holders of the bonds various interest rates differ in three ways: do not pay federal income tax on the interest Term. Some loans in the economy are for income. Because of this tax advantage, munici- short periods of time, even as short as over- pal bonds pay a lower interest rate. night. Other loans are for thirty years or even When you see two different interest rates report- longer. The interest rate on a loan depends ed, you can almost always explain the difference on its term. Long-term interest rates are usu- by considering the term, the credit risk, and the ally, but not always, higher than short-term tax treatment of the loan. interest rates. Although there are many different interest Credit risk. In deciding whether to make a rates in the economy, macroeconomists often loan, a lender must take into account the ignore these distinctions because the various probability that the borrower will repay. The interest rates tend to move up and down together. law allows borrowers to default on their For many purposes, we will not go far wrong by loans by declaring bankruptcy. The higher the assuming there is only one interest rate








